Contents
Chickenpox is an extremely contagious infectious disease. As they say, it spreads with the speed of the wind. A person becomes a carrier of the disease two days before he discovers the first symptoms. It is because of this feature that 90% of the population has time to get chickenpox in childhood. Having not acquired immunity against this disease at the age of 3-12, there is a risk of experiencing it on yourself in adulthood. Despite similar symptoms, the causative agent of chickenpox in the body of adults behaves much more aggressively: a longer period of the course of the disease, more profuse rash, increased itching, temperature up to 40 ° C, painful swallowing, pustular formation, general loss of strength, possible complications.
If you get sick, you will have to establish a quarantine and postpone all personal contacts for at least two weeks. Surely in your environment there are those who have not yet acquired lifelong immunity to chickenpox.
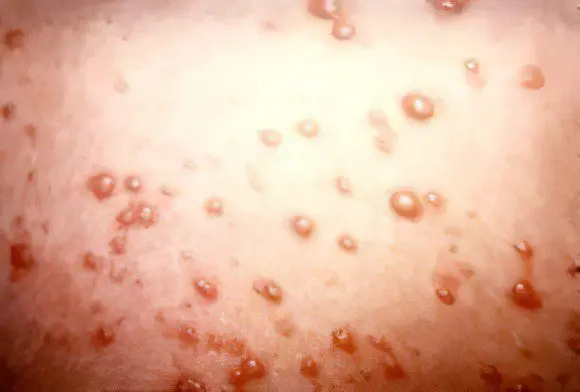
The main irrefutable symptom is rashes that appear all over the body (on the chest and abdomen, arms and legs, face, in the hair on the head, tongue, palate, nose and even in the perineum). The rash will turn into blisters 2-3 mm in diameter, filled with fluid. The bubbles itch unbearably, but you will be tested for endurance, since it is absolutely impossible to scratch them. This threatens with scars and scars in place of blisters, and if this is the area of uXNUMXbuXNUMXbthe eyebrows, beard and mustache, then an ugly bald patch.
What is chickenpox?
Chickenpox is one of the most common acute infectious diseases. It is characterized by rashes on the skin and mucous membranes in the form of small vesicles and fever. Transmitted by airborne droplets. Most often, chickenpox affects children and adolescents. It is believed that it is better to get chickenpox in childhood, since with age this disease proceeds in a complicated form: with encephalitis, primary varicella pneumonia.
Causes of chickenpox
The disease is caused by a virus of the herpes family. The susceptibility of the population to this virus is very high, so 70-90% of people have time to suffer the disease in childhood or adolescence. As a rule, the child picks up the infection in kindergarten or school. The source of the disease is an infected person in the last 10 days of the incubation period of the virus and the first 5-7 days from the onset of the rash.
After suffering chickenpox, lifelong immunity is formed, but re-infection also occurs. The virus can “sleep” for years in the body of a person who has had chickenpox and “wake up” at one moment. The cause may be nervous strain or stress. In such cases, an adult may develop shingles. Having no obvious signs of a rash, nevertheless, such a person is a distributor of the disease.
It is also possible infection with the virus through the placenta – from the mother to the unborn baby.
For pregnant women, it is especially dangerous, as it can cause the development of congenital chickenpox in a child, premature birth, or lead to the death of the fetus.
Complications of chickenpox usually occur in connection with a concomitant secondary infection (abscess, pyoderma, sepsis, phlegmon). Sometimes a week after the rash appears, viral-allergic meningoencephalitis develops. There are also cases of focal myocarditis and nephritis.
Chickenpox symptoms
The incubation period lasts from 1 to 3 weeks. Children are characterized by general malaise, headache, irritability, loss of appetite and tearfulness. In adults during this period, fever, malaise, headache, nausea and vomiting are often diagnosed.
The next stage in the development of the disease is associated with the appearance of a rash on the skin and mucous membranes. The body temperature rises, the level of intoxication of the body increases. In children, the rash appears earlier than in adults. In adults, intoxication is more pronounced, and the fever persists much longer.
The skin is covered with small red spots. After a few hours, they become convex and turn into small bubbles. The rash spreads randomly throughout the body, but is most often localized on the head, neck, face, chest and abdomen. The vesicles contain a clear liquid. After 1-2 days, the bubbles dry up, and crusts form in their place. Sometimes ulcers may appear. After rejection of the crusts, scars may remain. In this case, there is a deterioration in the general condition of the patient. Epidermal lesions become deeper. In adults, vesicles almost always transform into abscesses; the rash lasts longer and spreads more profusely than in children; falling off of crusts occurs later.
Over the course of the disease, more and more spots appear, accompanied by an increase in body temperature. With the appearance of bubbles in children and adults, severe itching begins, especially on the mucous membranes.
The clinical stage of chickenpox lasts from 5 to 8 days. Simultaneously with the cessation of the rash, intoxication also disappears. The vast majority have a favorable outcome.
Shingles as a complication of chickenpox
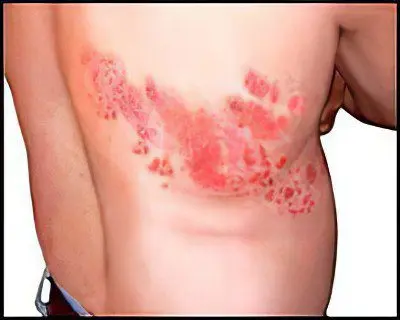
The insidiousness of the varicella-zoster virus is that, once infecting a person, it does not go anywhere, but lives latently in the body for years and, as a result of stress, can remind itself of itself in adulthood with shingles.
The source of infection in most cases is a patient with herpes zoster. However, the virus can also become active after contact with a patient with chickenpox.
Shingles susceptibility has been seen in people in the age group of 50 years and older. More than half of the elderly have time to transfer the disease. This is due to the fact that with age, immunity weakens, chronic diseases appear, the body becomes susceptible to viruses.
As a rule, with shingles, rashes appear on one side of the body (front or back) along the affected nerve. Sometimes rashes are located on the head and face. The disease is diagnosed with red plaques on the skin, itching, burning and tingling of the skin.
Pain, like a rash, is localized on one side of the body. In addition, the patient complains of weakness, weakness, high temperature.
The next stage of the disease is the formation of blisters filled with fluid. They burst, and ulcers appear in their place. Recovery takes two to five weeks while the sores heal and crust over. The disease reminds of itself for a long time with painful sensations along the course of the affected nerve.
Herpes zoster is dangerous with complications: rheumatism, arthritis, pneumonia, myocarditis, neuralgia. Anti-herpetic drugs are taken to prevent them.
Other forms of chickenpox
Along with the typical forms of chickenpox, there are also erased forms that can occur without clinical manifestations. Such forms of the disease are considered severe. These include:
bullous form – a concomitant severe disease that develops only in adult patients. It is characterized by the formation of large flabby blisters on the skin, turning into sluggishly healing ulcers.
Hemorrhagic form – observed in patients with hemorrhagic diathesis. Typical for her is the appearance of vesicles with bloody contents, the development of hematuria, nosebleeds. Patients have hemorrhages on the skin.
Gangrenous form – occurs in debilitated patients, proceeds against the background of a rapid increase in vesicles in size and the transformation of their contents into a hemorrhagic form. After the sores dry up, black crusts form, which have an inflammatory rim.
Chickenpox can lead to severe complications associated with exposure to the virus and the body’s response to it, such as chickenpox laryngitis, tracheitis, encephalitis, meningitis. Deep lesions of the epidermis of the skin with the formation of noticeable scars are also possible. With the spread of chickenpox flora, such complications of the disease as nephritis, hepatitis, myocarditis, arthritis can be observed. Secondary attachment of bacterial flora and purulent inflammation are also possible.
Chickenpox in pregnant women
Chickenpox in pregnant women deserves a separate discussion. In addition to the risk for the expectant mother, there is a danger for the fetus. As a result of chickenpox, the course of pregnancy can be disrupted and even spontaneously interrupted. That is why the treatment of chickenpox for pregnant women should be carried out under the strict supervision of a doctor. Do not worry too much, because anomalies in such a newborn are diagnosed in only one case out of a hundred. With chickenpox without complications, premature birth and spontaneous abortions in women were not observed.
However, deviations are sometimes possible, since the virus can enter the fetus from the mother through the placenta. Cases of congenital malformations, pathologies of the visual apparatus, mental and physical retardation, paralysis are described.
It has been noticed that the disease of chickenpox in a future mother in the early stages (up to 3,5 months) is practically not dangerous for the fetus. With the development of chickenpox for up to 5 months, the risk for the unborn baby increases slightly, and from 5 to 9 months it is almost reduced to zero. The last days of gestation are an exception. They are the main danger. If a pregnant woman fell ill a few days before giving birth, then in 15% of cases the virus affects the internal organs of the baby. To prevent such a situation, serum with antibodies is administered as soon as possible to the mother and the newborn. The baby is isolated from the mother until the danger of infection passes.
Treatment of chickenpox

Chickenpox is treated at home and only in severe cases of the disease – in the hospital. The decision on hospitalization is made by the attending physician.
As a rule, no special therapy is required. Until the rash stops, the patient should be isolated. Bed rest for up to 8 days is recommended for a child and adult with chickenpox. It is desirable to change bed linen as often as possible, and underwear – every day. Clothing made from soft natural fabrics is suitable.
The patient needs to drink more fluids and follow a diet of a milk-vegetable nature (mashed fruits and vegetables, milk porridge). Juices are best diluted with water in a ratio of 1:1. Sour, spicy and salty dishes should be excluded from the patient’s diet.
At home, red spots and blisters are treated with green paint or a 1-2% solution of potassium permanganate. If rashes appear in the oral cavity, mouth rinses should be carried out with antimicrobial agents (for example, furacilin solution).
Throughout the entire period of the disease, the patient is worried about constant itching (methods of treating itching). However, scratching can introduce infection into the wound. If this happens, the spots on the skin take longer to heal and may even remain as scars. It is best to cut your nails short, and the baby should wear cotton mittens on the handles. In addition, itching increases with the appearance of sweat, so doctors do not advise wrapping the patient in warm blankets. It is worth noting that the warm air in the room also exacerbates itching. It is best to give the patient a damp cold cloth – let him apply it to those places that you want to scratch.
Medicines containing ibuprofen or paracetamol are used to reduce fever. With chickenpox, aspirin is contraindicated, which increases the susceptibility to the development of Reye’s syndrome.
To reduce the severity of the disease, antiviral drugs are sometimes used, which are prescribed by a doctor. It can be antibiotics or immunoglobulin.
Chickenpox vaccine for adults
The disease transferred in childhood usually gives stable lifelong immunity. But for people who did not get sick in childhood, and for those who are at risk for developing severe forms of the disease, there is the possibility of vaccination. On the territory of Russia, the vaccines Varilrix and Okavax are officially registered.
The chickenpox vaccine forms a stable and long-lasting immunity in the human body. Suitable for both routine and emergency vaccinations. If the vaccine is administered within the first 72 hours after the first contact with the patient, then protection against infection is almost 100% guaranteed.
No side effects or serious complications have been reported with vaccination, so these drugs can be used in people with a weakened immune system or with severe chronic diseases.









