Contents
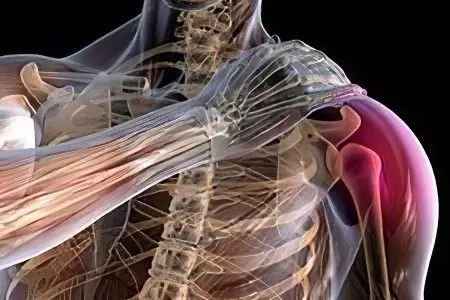
Atrophy of the muscles of the hand, hands, forearms develops mainly as a secondary disease against the background of a violation of innervation (nutrition, blood circulation) in a certain area of uXNUMXbuXNUMXbmuscle tissue and less often, as a primary one (usually with myopathy), when the motor function is not impaired.
Causes of atrophy of the muscles of the arm, shoulder and hand
For the development of muscle atrophy, the predisposing causes are: professional factor (constant overstrain during heavy physical labor), arthrosis of the wrist joint, endocrine pathology – obesity, diabetes mellitus and thyroid disease, acromegaly; cicatricial processes after trauma, metabolic and systemic diseases (lupus erythematosus), tumors of various origins, congenital pathologies of the development of the lower limb.
Symptoms of atrophy of the muscles of the arm, shoulder and hand
Muscle atrophy is a serious disease, as a result of which damage occurs mainly to muscle fibers. The main typical sign is the symmetry of the lesion (except for myasthenia gravis) and the slow development of the disease (with the exception of myositis), atrophy of the affected muscles and weakening of tendon reflexes with preserved sensitivity.
Most peripheral nerves have a mixed structure, and when damaged, the work of sensory, motor and autonomic fibers is disrupted. It happens that one of the fibers is affected the most.
If motor fibers are involved in the process, then paresis of the muscles that are innervated by this nerve occurs. The patient complains of muscle weakness, low muscle tone. Atrophy does not develop immediately, but 2-3 months after the lesion. In the absence of proper treatment, after a year and a half, the muscle will completely atrophy.
If sensitive fibers are involved in the process, the clinic is manifested by parasthesia – patients feel a tingling sensation, goosebumps. Neurological symptoms are expressed in the form of hyperesthesia (increased sensitivity), or hypesthesia (reduced sensitivity). A feeling of numbness in the affected limb appears with extensive damage to the nerve fibers.
In most cases, there is a decrease in pain sensitivity while maintaining tactile sensitivity. In the later stages of the development of the disease, deep hypesthesia occurs up to a complete lack of sensitivity. Redness or blanching of the skin, the appearance of a marble pattern indicates vascular disorders that occur when the vegetative fibers are directly affected.
As a rule, increased or decreased sweating of the affected limb joins. The burning pain of a hyperplastic nature is disturbing, radiating to the entire limb involved in the process. The trophism (cellular nutrition) of tissues is disturbed due to deep vegetative disorders.
Atrophy of the muscles of the hand begins, as a rule, with the most remote or distal sections of the upper limbs. The hand takes on the appearance of a “monkey hand” due to damage to the interosseous muscles and fingers. There is a complete loss of tendon reflexes, but sensitivity is preserved in the affected limb. As the disease progresses, the muscles of the neck and trunk are included in the process.
Diagnosis of atrophy of the muscles of the arm, shoulder and hand
The diagnosis does not currently cause any particular difficulties in connection with the introduction of the method of electromyography and biopsy of the affected muscles into the clinical examination. The patient is prescribed mandatory biochemical and general blood tests, urinalysis; in the blood serum, the activity of muscle enzymes is determined (mainly by the CPK method). In the urine, the indicators of creatine and creatinine are calculated. According to the indications, the patient is sent for CT or MRI of the cervicothoracic spine and brain, examination for endocrinological pathology.
Treatment of atrophy of the muscles of the arm, shoulder and hand
When choosing a method of treatment, the following factors are taken into account: the form of the disease, the severity and prevalence of the process, the age of the patient. Along with drug treatment, great importance is attached to proper nutrition, physiotherapy, courses of therapeutic massage and gymnastics, and electrotherapy. In some cases, it is appropriate to prescribe psychotherapy sessions to the patient.
Currently, there is no drug that can completely cure muscle atrophy, but the right choice of treatment method and a timely diagnosis can slow down the pathological process, restore muscle regeneration and return lost abilities to the patient. The main thing is to strictly adhere to the recommendations of the doctor.
[Video] How to treat muscle atrophy:









