What is alopecia?
Alopecia (baldness) – a disease that is characterized by loss of hair on the head and a violation of the growth of new hair. Currently, the following types of disease are described in the medical literature:
Alopecia areata (in other words, alopecia areata)
Alopecia areata
Alopecia occurring after a traumatic situation
Diffuse alopecia
Alopecia, which is based on hereditary factors
Androgenetic alopecia
seborrheic alopecia
Alopecia accompanied by scarring (scarring alopecia)
Causes of Alopecia
The etiology of some forms of diseases is currently not fully known, so alopecia is considered a multifactorial disease.
The cause of focal alopecia can be stressful situations, prolonged intoxication, autoimmune processes. Alopecia can also develop against the background of unfavorable heredity or as a result of a traumatic situation, due to pulling out hair during a fight, game, etc. Alopecia can be caused by pulling (traction) of hair when styling it in a hairstyle. The occurrence of cosmetic alopecia with frequent use of forceps for straightening or twisting hair, the use of hot styling is described.
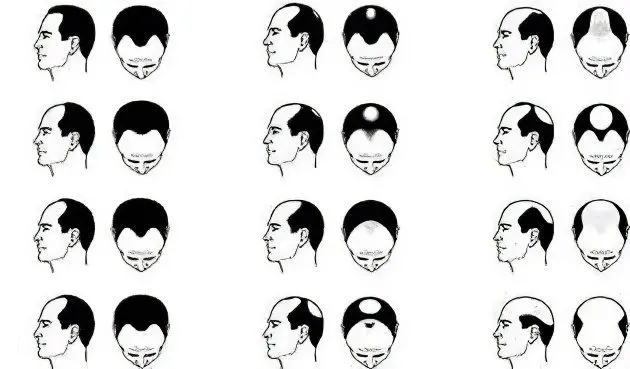
Alopecia can also be caused by hormonal imbalances. A shift in the balance between androgens and estrogens towards a decrease in the amount of estrogens in the blood can cause the development of the so-called androgenetic alopecia, which, manifesting itself in a mild form in men, is not a cause for concern and is not considered a pathological process. In women, such a violation of the ratio of hormones can be the cause of an increase in the production of androgens by the adrenal glands or ovaries.
Diffuse alopecia can be a consequence of prolonged intoxication, chronic poisoning, and long-term severe infectious diseases. Such a pathology often accompanies the course of pregnancy.
Alopecia can be passed down from generation to generation, in this case they speak of hereditary alopecia. Most often, the type of inheritance is autosomal recessive, but in some cases there is also an autosomal dominant type of transmission of genetic information.
If the cause of alopecia is the destruction of hair follicles due to the appearance of scar tissue on the skin, then such a pathology should be attributed to cicatricial alopecia. Various skin injuries (burns, exposure to radiation), the manifestation of certain infectious diseases – such as syphilis, tuberculosis, leishmaniasis or tumor growth – can cause cicatricial alopecia.
Symptoms of alopecia

The main clinical manifestation of alopecia is hair loss. The pathological process can manifest itself in the form of small foci of baldness and in the form of complete baldness. Symptoms of alopecia are directly dependent on the form of the disease.
Alopecia areata is accompanied by focal hair loss, and the foci of alopecia are round or oval in shape. This type of pathology is characterized by an increase in the area of the lesion over time. Hair that is on the border with the focus becomes thinner and dystrophic. Alopecia is often accompanied by vitiligo and onychodystrophy.
After a few weeks or months, new hair may appear in place of the fallen hair, but after a while the grown hair also falls out, after which the foci of the pathological process grow, occupying an even larger area. Alopecia acquires a total character and is accompanied by loss of eyelashes and eyebrows.
Baldness can also begin with a smooth surface of the skin (so-called ophiasis). In this case, the course of the disease is malignant and, as a rule, is accompanied by pathology of the endocrine system, as a result of hypofunction of the thyroid gland or adrenal insufficiency.
Traumatic alopecia also has separate lesions. Areas with a complete absence of hair border on areas of skin covered with whole or damaged (broken) hair; when examining the patient, traces of damage to the skin are also noticeable.
Symptoms of hereditary alopecia are mainly found in children. In this case, the pathology is accompanied by atrophy of the hair follicles in all areas of the skin. The disease may be accompanied by other anomalies and malformations. A characteristic feature of hereditary alopecia is the presence of the disease in several family members.
Androgenetic alopecia has a progressive course. Hair loss in most cases begins with the frontal zone, over time, baldness spreads to the crown of the head.
How is the treatment carried out?
Here is a list of the most popular treatments:
The best shampoo for hair restoration and growth
Medical treatment of alopecia (full list of drugs)
Minoxidil for hair loss
Finasteride for hair loss
Hair transplant: answers to basic questions
Treatment is carried out with the help of vitamin and multivitamin preparations. Fitin, biotin, immunocorrective agents – such as decaris or taktivin are also used. Treatment of alopecia areata can be supplemented with angioprotectors and drugs that positively affect tissue microcirculation (trental). In the most severe cases, treatment of alopecia with the use of hormonal drugs is recommended, while taking into account the risk of recurrence of the disease against the background of the development of steroid atrophy of the skin. Therapy with corticosteroids can be carried out in the form of taking drugs orally or in the form of chipping foci covered by the pathological process. Seborrheic and premature alopecia can resolve when the patient is given antiandrogen therapy.
In the treatment of all types of diseases, procedures using Darsonval currents, chloroethyl, cryomassage, ultraviolet radiation can be useful. In the treatment of severe lesions, UV rays can be combined with the appointment of a patient with drugs that enhance the body’s photosensitivity, you can also refuse to use ultraviolet radiation and switch to photochemotherapy.
Externally, in the treatment of alopecia, rubbing in alcohol tinctures (red pepper, Naftalan oil extract), creams containing corticosteroids, or the complex drug “Regain” can be useful.
In the treatment of alopecia, great attention should be paid to proper shampooing. It is recommended to use boiled water, neutral (fatty) soap. It is better to rinse your head with infusions and decoctions of medicinal herbs (nettle, burdock, chamomile, succession, celandine, etc.). With seborrheic alopecia, hair should be washed once a week. With seborrheic and premature alopecia, it is recommended to exclude from the diet products that have an irritating effect – such as alcohol, smoked meats, coffee, marinades, etc. Also, patients should refrain from sweets and starchy foods, reducing the amount of fats and carbohydrates entering the body.
In all forms of the disease, fresh vegetables and fruits, foods high in gelatin, and seaweed will be useful.
In the treatment of alopecia, attention is paid to disorders of the endocrine and nervous systems. Recommended therapy for chronic diseases of the digestive tract, liver, kidneys, elimination of foci of chronic infection, treatment of helminthiasis.
Author of the article: Herman Olga Leonidovna, trichologist, specially for the site ayzdorov.ru









