Contents
- What it is?
- Causes
- Symptoms of candidal stomatitis
- Types of candidal stomatitis and stages of development of the disease
- Which specialist should be contacted?
- Diagnosis of the disease
- How is candidal stomatitis treated?
- Features of manifestation and treatment in infants
- Consequences if not treated
- Prevention
Candidiasis stomatitis is a fungal disease that is accompanied by an inflammatory process in the oral cavity. It can be caused by microorganisms such as: Candida albicans, Candida glabrata, Candida krusei, Candida tropicalis, Candida parapsilosis.
Candidiasis stomatitis is often diagnosed, as the impetus for the disease is a decrease in immunity. Even the slightest failure can cause disease. Candidiasis stomatitis is rarely complicated, but treatment should not be delayed.
What it is?
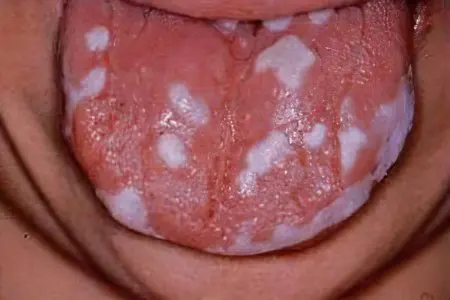
Candidal stomatitis is called fungal stomatitis or thrush. The main manifestation of the disease is a white coating on the tongue and on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity on the inside of the cheeks. It is easily peeled off with a medical spatula.
Fungi of the genus Candida are always present in the human oral cavity, but normally they do not lead to disease. Therefore, many people are not even aware of such a neighborhood. Certain microbes that also live in the human oral cavity prevent the reproduction of the fungus. If the balance of microflora is disturbed and there are more harmful bacteria than beneficial ones, Candida begins to actively grow and increase its number. Thus, candidal stomatitis develops.
The disease can be diagnosed in people of all ages and genders. It has been observed that Candida glabrata affects the elderly more often, and Candida parapsilosis prefers to multiply in the oral cavity of infants. People with serious illnesses (HIV, cancer, diabetes) are more likely to have candidal stomatitis caused by Candida rugosa or Candida sake.
In the international classification of diseases of the 10th revision, candidal stomatitis is assigned code B37.0.
Causes
The reasons why mushrooms of the genus Candida begin to increase in numbers in the oral cavity and lead to the development of fungal stomatitis:
Weak immune system. If the body’s defenses are not weakened, then the likelihood of developing the disease is minimal. When immunity fails, fungi grow rapidly, causing characteristic symptoms.
Poor oral hygiene. People who wear dentures and braces need to take special care of their teeth. For such persons, special rules have been developed that must be impeccably observed.
Xerostomia (dry mouth). This problem occurs in people who use breath fresheners too often or brush their teeth with a toothpaste containing sodium lauryl sulfate. Another cause of dry mucous membranes in the mouth is Sjögren’s syndrome.
Hormonal imbalance. Hormones affect the microflora of the oral cavity. If there is a failure in their natural balance, a person may develop candidiasis. This reason is especially relevant for pregnant and lactating women who are prone to fluctuations in hormones.
Treatment with antibiotics or steroid hormones. People who use these medicines for topical oral treatment are more likely to develop thrush. They destroy not only harmful, but also beneficial flora. Therefore, when taking antibiotics, you need to receive drugs that are aimed at maintaining the natural biocenosis in the oral cavity.
Early childhood. In a child who has just been born, the microflora in the oral cavity is not sufficiently formed, since his body has just begun to exist in the external environment. Therefore, it is not surprising that candidal stomatitis often develops in infants. Also, infection can occur during the passage of the child through the birth canal, if the woman suffered from thrush during the period of childbirth.
Elderly age. The older the person, the weaker his immune system.
Diabetes. Patients with such a diagnosis often encounter candidal stomatitis, since there are all prerequisites for the development of the disease.
HIV. This disease reduces the human immune system, so fungi will multiply in conditions that are comfortable for them.
Risk factors for the development of candidal stomatitis:
Allergy to food;
Deficiency of B vitamins, vitamin A, C, E;
Diseases of the oral cavity (gingivitis, stomatitis, caries, etc.);
The presence of bad habits;
Hereditary predisposition.
Symptoms of candidal stomatitis
Candidiasis stomatitis has different manifestations in children and adults. Symptoms depend not only on age, but also on the state of health of the patient. The brighter the clinical manifestations of the disease, the worse the state of the patient’s immune system.
Symptoms of candidal stomatitis in children:
The appearance of plaques in the mouth, which are covered with a curdled coating. They form on the tongue, on the inner surface of the cheeks. The plaque is easily removed, and bleeding ulcers are found under it.
The child is naughty, refuses to eat, his weight will decrease.
The fungus can spread to the organs of the digestive system and cause pain.
Symptoms of candidal stomatitis in adults:
Pain and burning in the mouth.
Hyperemia of the mucous membranes.
White coating on the tongue, on the gums. A bleeding surface is visible underneath.
Deterioration of taste perception, the appearance of a taste of metal in the mouth.
Dry mouth.
Pain while swallowing food.
Types of candidal stomatitis and stages of development of the disease
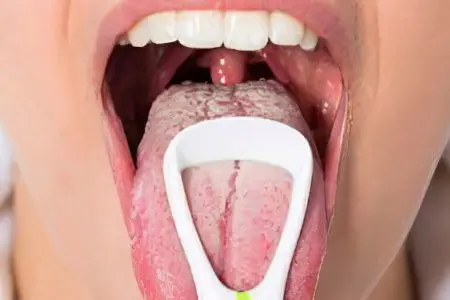
Depending on the clinical picture and morphological changes in the oral cavity, the following forms of candidal stomatitis are distinguished:
atrophic form. This form of the disease is most often diagnosed in adults who have been treated with hormonal or antibacterial drugs for a long time.
pseudomembranous form. This type of stomatitis develops mainly in children, as it is caused by infectious diseases and bronchitis.
erosive form. Such stomatitis is not often diagnosed. The disease can affect people with diabetes, with autoimmune polyendocrinopathy. In addition to a large number of plaques covered with plaque, multiple eroded areas are formed in the mouth.
hyperplastic form. The disease affects people with severe pathologies in the body, for example, with blood cancer or tuberculosis, as well as patients who have been taking antibacterial drugs for a long time. The symptoms of this form of the disease are more pronounced than the symptoms of pseudomembranous candidal stomatitis. In addition to plaque in the oral cavity, a person complains of burning and pain. The tongue becomes inflamed, the mucous membranes become very red and swollen due to the rush of blood to them.
Depending on the nature of the course of candidal stomatitis, there are:
Acute candidal stomatitis. Only the tongue is involved in the pathological process. It becomes dry and red, it is difficult for the patient to move it. The disease is preceded by such signs as: a general deterioration in well-being, increased weakness, fever. Hyperthermic reaction is not always observed.
Chronic candidal stomatitis. The chronic form of the disease develops due to the fact that an acute infection was not cured. A person complains of pain and burning in the mouth, it is difficult for him to eat food, as this causes discomfort. When examining the mucous membranes, you can see that they are thin and excessively dry. Even the color of the mucosa changes, it acquires an unnaturally bright color, plaques form on its surface, covered with a curdled coating.
Pseudomembranous and atrophic candidal stomatitis are varieties of the acute form of the disease.
Candidiasis stomatitis develops in several stages:
The first stage. Small areas of redness appear in the mouth. It is difficult to understand that they indicate candidal stomatitis, since many diseases begin in this way.
The second stage. In the place where there were previously ulcerative defects, a plaque appears, resembling cottage cheese in appearance.
The third stage. If you try to remove the plaque, then bleeding mucous membranes will be visible under it. At this time, the oral cavity is especially vulnerable to pathogenic flora, as the risk of infection of open wounds increases.
Fourth stage. Possible increase in body temperature. If the disease has a severe course, then it is complicated by infection of the respiratory tract.
Which specialist should be contacted?
If the disease develops in a child, then you need to visit a pediatrician. When such a need arises, the doctor sends the baby to an immunologist. If there are carious teeth in the mouth, a consultation with a pediatric dentist is required.
If candidal stomatitis develops in an adult, then you need to visit the dentist’s office. To find out the cause of the disease, you need to go to an appointment with an immunologist and a therapist.
Diagnosis of the disease
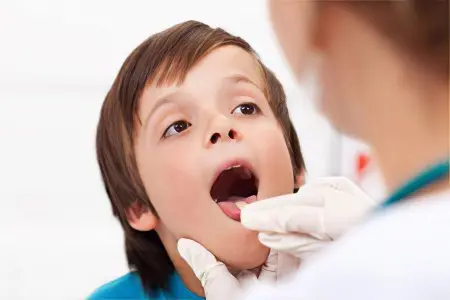
As a rule, the diagnosis does not cause any difficulties for a specialist. The doctor will examine the oral cavity, evaluate the nature of the plaque.
If in doubt, diagnostic measures such as:
Examination of a smear from a candidal plaque under multiple magnification. The fungus is clearly visible under a microscope. Additional tests can also be carried out to determine the sensitivity of pathogenic flora to drugs.
Donating blood for clinical analysis. If an increase in the level of leukocytes is detected, then this indicates an inflammatory reaction.
Serological studies. Testing is carried out to detect diseases such as HIV, tuberculosis, etc. The analysis allows you to detect antibodies to the relevant infections.
How is candidal stomatitis treated?
Treatment of candidal stomatitis depends on which form of the disease develops in a person, as well as how intense its manifestations are. There is no single treatment regimen, since the infection occurs in different people in different ways.
However, the doctor has very specific tasks:
Suppress the activity of the fungal flora. For this, antifungal agents are used.
Increase the body’s resistance.
Relieve pain and inflammation, stop the effects of allergies, if any.
Relieve the patient of comorbidities.
Normalize the microflora of the oral cavity.
In addition to these activities, the patient will need to follow a diet. It is shown to people of all ages. The diet is designed in such a way that it helps to increase immunity and helps in the fight against infections.
The basic principles of dietary nutrition for candidal stomatitis:
Reducing the amount of simple carbohydrates in the menu.
Refusal of fast food, semi-finished products, alcoholic beverages, conservation.
Avoid foods that contain yeast. This applies not only to baking, but also to beer.
Daily inclusion in the menu of fermented milk drinks.
Eating fresh vegetables and fruits.
Features of manifestation and treatment in infants

In infants, candidal stomatitis is often diagnosed and is acute. In premature babies, the likelihood of developing the disease increases by 2 times. Candidiasis develops rapidly. In a few hours, areas of redness in the oral cavity may become covered with a white coating. It affects the cheeks, palate, tongue, gums, larynx. The inflamed areas crack, blood oozes from them.
Sometimes children have a fever. The kid refuses to eat, cannot sleep. In such a situation, hospitalization is required. Through ulcerative defects, an infection can enter the body, which threatens to become infected.
Breast treatment. Infants must be examined by a doctor. Most often, stomatitis has an uncomplicated course in them, so hospitalization is not required. The mother of the child should also receive therapy, as often it is she who becomes the spreader of the infection.
Treatment continues for 30 days, until the symptoms of the disease are completely stopped. During this time, the mother should carefully care for her nipples to prevent re-infection.
Consequences if not treated

If the disease was diagnosed at a later date and there was no treatment, then the likelihood of developing severe complications increases. First, a person stops eating, begins to lose weight. Then immunity decreases. There is a risk of spreading the disease to the larynx, esophagus and further, to the intestines.
Complications of candidal stomatitis can be as follows:
Endocarditis, accompanied by inflammation of the lining of the heart.
Meningitis, which affects the brain. A person either dies or becomes disabled.
Nephritis, in which the kidneys suffer.
Dermatitis, that is, damage to the skin.
If the treatment was not chosen correctly, then the disease becomes chronic and often worsens. Relapses happen with every decrease in immunity.
Prevention

To prevent the development of candidal stomatitis, the following recommendations must be observed:
Carefully care for the oral cavity, treat all diseases in time and visit the dentist regularly.
Wash hands with soap before eating.
In the chronic form of the disease, antifungal drugs should be taken to prevent the development of the disease. However, this should be done only after visiting a doctor.
If a person is being treated with antibacterial drugs or steroid hormones, rinse your mouth after taking them.
Pregnant women need to get rid of vaginal candidiasis. This must be done before childbirth.
The mucous membrane should not be overdried.
It is necessary to consume as many vegetables and fruits as possible, but the consumption of sweets should be limited, since fungi feed on sugars.
To increase immunity, you need to take vitamin complexes.









