Contents
Bursitis of the elbow joint – this is an inflammatory process that has arisen in the tissues surrounding the olecranon. In order to understand what we are talking about, you should know that around any joint, including the elbow, there are synovial bags filled with a small amount of fluid, which in Latin are called bursa. In their normal state, they perform the same role as lubricants in the engine, that is, they prevent the joints from rubbing against each other when moving. Therefore, they are not injured as a result of natural human activities.
If we consider specifically the elbow joint, then it is surrounded by three bursas:
Interosseous
Ulnar subcutaneous
Interosseous ulna
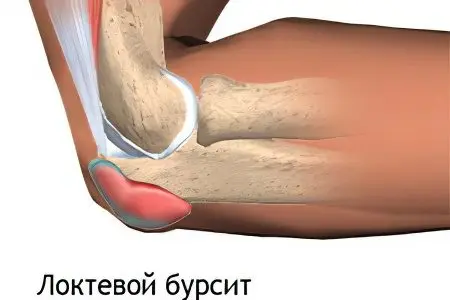
Each of them contains a certain amount of fluid, which normally performs its function, so a person does not experience pain when moving his hands. But sometimes, for a number of reasons, inflammation occurs in the cavity of one or several synovial bags at once, the fluid begins to arrive, its composition changes, and the elbow becomes painful. This condition is called elbow bursitis.
Doctors classify bursitis according to several parameters:
Depending on the place of localization (by the name of the synovial bags).
By the nature of the course of inflammation – acute, subacute or chronic type.
Depending on the composition of the fluid (exudate) accumulating in the synovial sac – purulent, serous, fibrous, hemorrhagic.
If bursitis is caused by any microorganism, then it may be called nonspecific (microorganisms from the group of strepto- and staphylococci) or specific (for example, caused by gonococci, spirochete pallidum, tuberculosis or syphilitic bacterium).
Inflammation of this slit-like formation on the elbow is a fairly common phenomenon and is in second place after inflammation of the shoulder joint.
Causes of elbow bursitis
Bursitis of the elbow joint can occur for a number of reasons, among which it is customary to single out the following:
In the first place, as a factor leading to the development of bursitis, is arthritis of any nature – psoriatic, rheumatoid or gouty. That is, against the background of acute inflammation in the cartilage itself or in the synovial bag, fluid begins to accumulate, which leads to the formation of bursitis.
Bursitis can be the result of a microtrauma, but this is somewhat less common. The elbow is injured due to constantly repetitive monotonous movements, therefore this disease is unofficially called the “professional” illness of all those people whose activities are associated with the support of the elbow on a hard surface. These can be students, engravers, chess players, draftsmen, etc. In such people, the subcutaneous ulnar bursa most often becomes inflamed, and, for example, in tennis players, the interosseous ulna. Such a difference is associated with the peculiarities of the distribution of the load on the elbow, and hence the place of occurrence of microtraumas.
Sometimes bursitis occurs some time after a mechanical injury to the elbow. In the event that a person hits or falls on this part of the body.
Bursitis can also occur as a result of ingestion of an infection. Especially often this happens when the skin tissue immediately next to the bursa has been damaged, and a certain microorganism or bacterium has got inside. Panaritium can also serve as an infectious cause of bursitis, when bones and soft tissues of the fingers are exposed to acute inflammation. Also, the infection can get into the synovial sac not from the outside, but “from the inside”, that is, it can be carried through the blood (hematogenous pathway) and through the lymph (lymphogenic pathway).
Extremely rarely, however, there is an idiopathic inflammation of the synovial bag, that is, one whose etiological causes remain unclear.
Some chronic diseases, such as diabetes mellitus, are also among the risk factors leading to inflammation in the elbow joint. The cause of suppuration can also be a general weakening of the immune system, metabolic disorders, as well as taking steroid drugs.
Symptoms of elbow bursitis
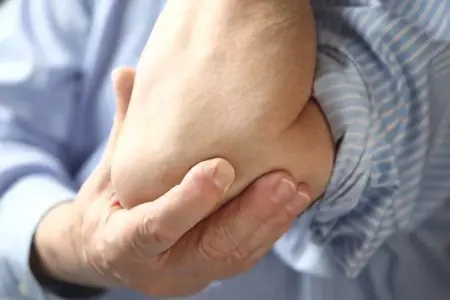
As the main symptoms of bursitis of the elbow joint, it is customary to distinguish the following:
The appearance of swelling in the corresponding area. Sometimes it can occur for no apparent reason, be completely painless and not interfere with the free movement of the hand.
If the swelling is left unattended, then over time it will become much more noticeable, significantly increase in volume and there will be a feeling of discomfort and pain.
Often there is reddening of the skin around the elbow and its sharp filling.
A person’s body temperature may rise, up to the onset of febrile conditions. With a similar course of bursitis, severe pain occurs in the elbow region and the general condition deteriorates sharply.
There are accompanying symptoms of intoxication, which are characterized by headaches, general weakness, sweating, apathy and loss of appetite.
Since the increase in the joint bag in size, the mobility of the arm becomes somewhat limited, when you try to bend the arm, pain occurs.
If you continue to ignore such a condition and leave elbow bursitis without appropriate therapy, then it will turn into a purulent form, and fistulas protruding outward and subcutaneous phlegmon will appear at the site of inflammation.
Enlargement of lymph nodes.
Depending on the form of bursitis, accompanying symptoms will also differ:
Acute serous inflammation of the synovial bursa is characterized by swelling, slight pain and an increase in skin temperature in the area of swelling. The general condition is disturbed not too pronounced.
If serous bursitis is not treated, then it may either disappear on its own or become chronic. With it, pains, even not during the period of exacerbation, will continue to disturb the person, especially during physical exertion, the movement of the elbow is somewhat limited, on palpation, doctors detect a fluctuating formation, which can be both elastic and loose. If bursitis proceeds in a chronic form for quite a long time, then several seals can be found. Chronic bursitis often recurs.
If the bursitis is purulent, then the painful sensations do not cease to disturb the patient, they are twitching or bursting. The elbow itself becomes bright red, hot to the touch. The general condition of the person is disturbed.
If any of these symptoms occur, you should not try to diagnose yourself, much less start treatment. After all, the signs of bursitis are quite similar to those of arthritis, gout or polyarthritis. In each case, a variety of treatment is required, with the use of various drugs. Therefore, if there is a suspicion of the presence of bursitis, it is worth bandaging the elbow with an immobilizing bandage, providing it with peace and going to the orthopedic department to the appropriate specialist.
Purulent bursitis of the elbow joint
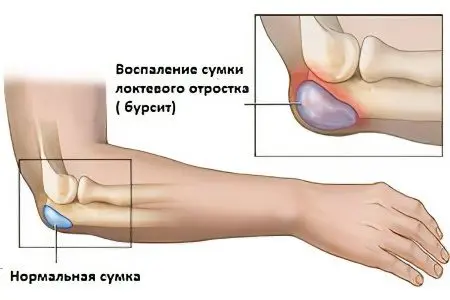
Purulent bursitis is characterized by the formation of purulent contents in the joint bag of the elbow. It is caused by bacterial infections of this cavity.
Most often, purulent bursitis of the elbow is caused by streptococci and staphylococci, which penetrate the bag as a result of mechanical trauma to the skin in the corresponding area. It can even be a small scratch or abrasion, but if it damages the synovial bag, then in almost 100% of cases it leads to the formation of bursitis, which, in the absence of specialized therapy, becomes purulent over time. The presence of pustular formations on the skin near the elbow joint or directly on it will lead to an early infection and suppuration.
But sometimes microtraumas caused by professional activities can lead to the formation of purulent inflammation.
Symptoms of purulent bursitis characteristic of any inflammatory process, the swelling is located at the top of the elbow and, depending on the severity of the disease, can have different sizes. The pain is intense, the skin is red and hot to the touch, the human body is weakened, the body temperature rises to high values.
If a purulent nature of the disease is suspected, the patient’s blood is taken for a general analysis and to establish the level of sugar, it is also necessary to collect urine. If necessary, doctors can prescribe an ultrasound scan and take a puncture to determine the nature of the contents, but as a rule, such manipulations are rarely required.
Purulent bursitis should be distinguished from similar arthritis. With the last hand movement, it is almost impossible to make, the pain is felt directly inside the joint itself.
For treatment, surgical intervention is necessary in order for the pus to come out. After that, the excised surface is treated with antiseptics and a sterile bandage is applied. Often, healing is slow and a second operation is required.
This may cause the following complications:
Phlegmon muscular and subcutaneous.
Purulent arthritis, when the entire joint is involved in the process.
Inflammation of the lymph nodes or skin ducts (lymphadenitis and lymphangitis).
Prevention includes the exclusion of traumatic situations and the timely treatment of the onset of the inflammatory process.
How to treat elbow bursitis?

If the bursitis is not complicated and is the result of a mild bruise, then it can go away on its own, with the restriction of the mobility of the sore spot and the application of a cold compress, followed by the use of dimexide as a resolving agent.
In all other cases, qualified medical assistance is required. To begin with, the doctor prescribes non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, for example, ibuprofen in combination with nimesulide and diclofenac. If a bacterium has become the cause of the development of inflammation, then antibiotics are necessary. In the absence of effect and with a significant accumulation of fluid, it is necessary to perform a puncture. With its help, fluid is aspirated, which almost instantly helps to relieve pain symptoms and significantly reduces pressure on nearby tissues. During puncture, depending on the indications, either antibiotics or steroid drugs are administered orally to relieve inflammation.
Surgery for bursitis of the elbow joint
Surgical intervention is carried out only in extreme cases, when all the tried methods are ineffective. Most often, surgery is needed for recurrent bursitis, or purulent-hemorrhagic inflammation, as well as for persistent serous.
Bursectomy is a rather traumatic intervention, which further disables the arm for a long time, depriving a person of his ability to work. That is why surgeons in their practice increasingly began to use the following, no less effective treatment regimen: the operation site is cut off, then a puncture is performed with a rather thick needle, which allows the liquid to be aspirated. Then, with the help of special manipulations, a catheter is inserted into the bursa, which has a compressed pear at one end. After that, it gradually straightens out and completely removes the entire contents of the cavity of the bag. Thus, its global excision is not required, and healing occurs in a much shorter time.
Sometimes bursitis requires treatment even at the stage of remission. The method of therapy is determined by the doctor; quite often and very successfully, ultrasonic heating and electrophoresis are used. These procedures allow you to relieve spasms and tension from sore muscles. Cryotherapy is used to relieve swelling. After the main symptoms are eliminated, massage and paraffin applications can be prescribed.









