Contents
Bursitis of the big toe – this is a consequence of a specific hallux valgus, in which there is a gradual curvature of the big toe outward. It can be argued that this pathology is determined from a genetic point of view, although this is far from the only factor in its formation.
So, the risk group includes those who, by the nature of their activities, have to stay on their feet for a long time. This is especially true for ballerinas, who spend almost all of their time in rehearsals and use their toes while dancing.
Symptoms of bursitis of the big toe
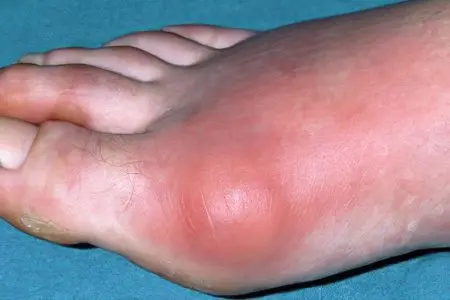
Due to the growth of bursitis of the big toe and periodic irritation, the cells of the articular capsule of the first metatarsophalangeal joint become inflamed. A fluid called exudate begins to accumulate in the joint cavity. Over time, the exudate may well be subject to suppuration.
All this happens when accompanied by symptoms such as:
painful sensations;
anemia;
loss of confidence while walking and other gait disturbances. The insidiousness of this pathology lies in the fact that initially painful sensations and gait disturbances are not very noticeable, and the patient does not attach much importance to them.
However, it is quite easy to carry out an independent diagnosis of the presented ailment, for this you just need to squat down and take a few steps in the starting position. Pain in the area of the big toe indicates bursitis.
Later symptoms are as follows:
not only a change in shape, but also a curvature of the thumb;
painful sensations of a wave-like nature. They appear only at those moments when the bursa (that is, the joint bag or sac around the joint that is filled with fluid) begins to become inflamed;
there are problems in the process of wearing shoes (the old shoes are uncomfortable and even small);
calluses form directly on the bump, which can bring pain in later stages.
All this is evidence that bursitis of the big toe is at the very last stage of its formation.
Symptoms of the final stage of bursitis are as follows:
the appearance of bursitis of a purulent type as a result of inflammation of the bag;
incessant pain, not only while walking, but also in a static position.
From a physiological point of view, the symptoms of the presented disease are as follows:
there is a deviation of the big toe to the outer part, as a result of this, the forefoot changes its shape, and, therefore, there is a violation of depreciation;
as the disease develops, the cartilage begins to hurt, a specific arthrosis of the joints of the metatarsophalangeal region is formed and a permanent type of bursitis is formed;
the pommel of the primary metatarsal bone begins to grow (“bones” on the first toes in the foot area);
flatness of the foot is manifested, which is characterized by a transverse flow;
painful sensations are formed in the area of uXNUMXbuXNUMXbthe sole of the feet next to the top of the primary metatarsal bone;
deformations of the arch of the foot of the transverse type are formed;
pressure is transferred to the tops of the middle metatarsal tissues, that is, they are significantly overloaded;
in the plantar region of the foot, not only corns begin to form, but also calluses, which greatly complicate the process of walking due to sudden and sharp pain.
Causes of bursitis of the big toe
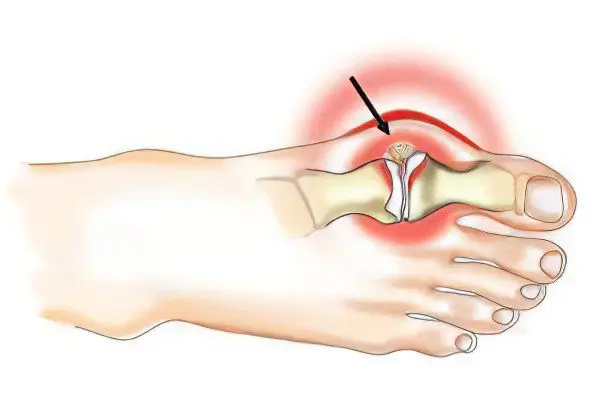
Bursitis of the big toe is formed due to the fact that in the bag of the synovial type there is an accumulation of excess fluid, which is sometimes purulent.
This may be due to reasons such as:
bruises in the area of this part of the foot;
lack or excess of calcium;
small injuries that do not heal for a long period of time;
poor-quality or uncomfortable shoes (narrow, made of hard material);
flat feet (acquired or congenital, which is in a neglected state and has never been treated);
foot deformity acquired at birth;
allergic reactions (they occur quite rarely, mainly when you change your place of residence, for example, from Europe to Africa);
diseases of an autoimmune nature (regardless of the type, they can affect the bunion of the big toe only if timely prevention is not carried out);
destabilization of all processes associated with metabolism;
intoxication processes;
infection.
The first five points should be considered the main and most common causes, all subsequent ones are quite rare or are quite specific. Inflammatory processes that cause bursitis of the big toe may well spread from tissues located in the neighborhood if a powerful inflammatory process is observed in that area.
Another reason is diseases that eventually lead to the destruction of joint tissues:
arthritis;
psoriasis;
rheumatism.
If we consider this problem from a physiological point of view, then two such violations of biomechanical processes lead to the formation of the presented pathology, such as:
combination in violation of the ability to move;
excessively high degree of mobility of the primary bone of the metatarsal type.
In the case when both deviations described above are in history at the same time, the joint of the big toe is exposed to excessive pressure precisely at the stage when the limb is ready to push off the ground. Wherein:
the muscles and tendons of the thumb must be stretched to counteract the tension, and also to create a restriction on the motor skills and degree of joint mobility;
being in such a stretched position causes the big toe to flex outward so that the tip of the toe points towards the farthest toe;
all parts of the thumb press on the first metatarsal bone, and it also begins its outward displacement.
As a result, the proximal phalanx and metatarsal bone form a formation that resembles an arc. Thus, bunion is a slowly progressive disease that occurs in several stages. That is why it is very important to carry out adequate and timely treatment. Because any disease is much easier to treat at an early stage than at a later stage.
Treatment of bursitis of the big toe
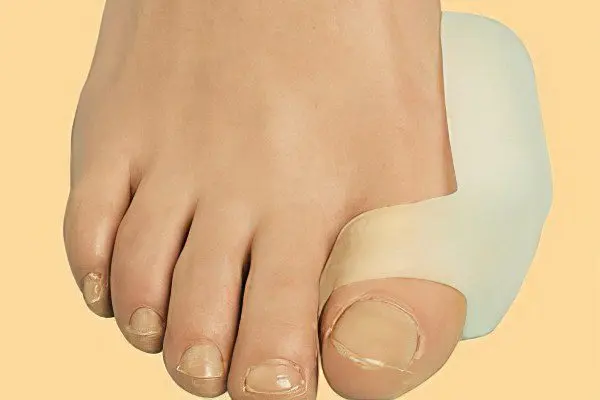
The treatment of bursitis of the big toe must begin with hygienic measures. Properly selected shoes will greatly reduce the load on the big toe. As part of this, it is advisable for female representatives to abandon the “boats” and all high-heeled shoes. With deformities of the big toe, it is desirable to wear specific shoes with orthopedic insoles and soft pads located in the area of the big toe.
Bursitis itself should be treated with anti-inflammatory ointments and gels, such as Voltaren Emulgel. When exudate accumulates in the joint cavity, specialists puncture it, that is, a puncture. After that, the exudate is sucked off, and Kenalog or some other steroid-type hormone is injected into the joint voids. The goal remains the same – to neutralize inflammation. If there are infectious complications of bursitis of the big toe and pus begins to accumulate, it is necessary to take antibiotics.
During the recovery period, it is necessary to carry out physiological procedures, such as electrophoresis, paraffin treatment, ozoknerite. Although in the presented case, such treatment is assigned an exclusively auxiliary role. At the same time, when bursitis of the big toe is only a complication of another disease, this disease is treated in a whole complex of procedures.
The most common recovery scenario is as follows:
a special plaster is applied to the patient, which fixes the necessary joint;
necessary medications are prescribed, most often we are talking about anti-inflammatory drugs;
there is a need for rest in a home or hospital setting. At the same time, any physical labor and loads associated with sports are prohibited. Exercise therapy is acceptable, where exercises will be carried out in coordination with a specialist;
in the most advanced cases, it is desirable to carry out a course of antibiotics, which will take place separately or together with hormonal drugs, which is determined depending on the stage and severity of the disease;
after a few days, UV irradiation, UHF therapy are prescribed, and alcohol compresses are also prescribed.
In more complex cases, when bursitis of the big toe is started to purulent, surgical intervention may be necessary. In this case, the pus is removed by surgery.
Indications for surgical intervention for bursitis may be:
low efficiency in the implementation of conservative treatment;
change in the nature of painful sensations to a stronger one;
change in the valgus angle in size;
exacerbation of violations in time.
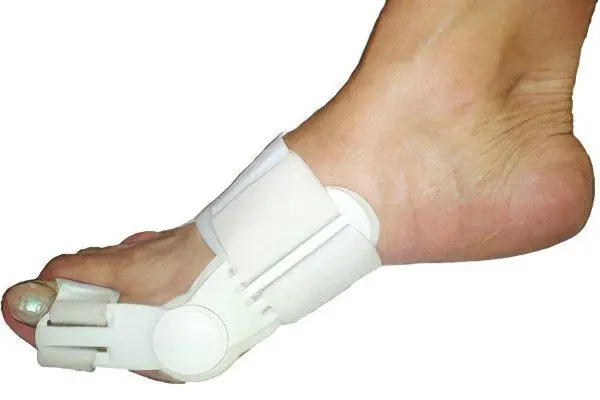
The simplest and least traumatic method should be considered bursectomy. As part of this operation, the bone outgrowth is removed and, if necessary, the hypertrophied area of the metatarsal bone. To do this, an incision must be made in the area of the growth. Through it, with the help of a surgical electric knife, excess bone tissue is removed.
In the same case, when bursitis of the big toe is running, plastic surgery of this area is performed using osteotomy. As part of the operation, a certain number of deep incisions are made, both on the big toe and on the back of the foot. After that, according to a certain technique, the bone tissues of the finger and the primary metatarsal bone are moved. Those bones that have been displaced are fixed using metal structures. The goal of this treatment is to eliminate or at least reduce the valgus angle.
Over the next six to eight weeks, careful care of the foot area is necessary – wearing comfortable and not narrow shoes, cleansing not just the wound itself, but also the area around it. It is also desirable to avoid moisture and hypothermia.
In some cases, doctors prescribe a course of calcium treatment. This cause of the formation of bursitis of the big toe is quite rare and it is easy to cope with it if you start using drugs with a high calcium content in time. In the case when this substance is in excess in the body, we are talking about removing it or compensating it with other elements.
When the disease is caused by calcium deficiency, it progresses very quickly, but if there is a lot of it, then, on the contrary, it takes a long time. This is due to the chemical processes that occur in the human body. Therefore, substitution therapy, as well as the study of not only the hormonal background, but also general blood and urine tests should be taken every six months.
After the treatment is carried out, throughout the rest of his life, the patient will need to wear special shoes, do simple exercises every day and monitor the level of calcium.
Do not neglect the norms of prevention of the presented disease. They boil down to avoiding the causes that initially contributed to the development of the disease, and also, in general, avoid wearing uncomfortable shoes, treat wounds in time, remember about foot hygiene, and avoid excessive physical exertion.









