Contents

Burbot is a representative of the genus of the same name, the class of ray-finned fish and the cod family. This family appeared on our planet many millions of years ago. Features of burbot is that it is considered the only freshwater fish of this family. In addition, this is the only fish in our reservoirs, which shows its main activity in the winter. It is an object of both sports and amateur fishing. In addition, it is of commercial interest.
Burbot fish: description
Almost all domestic experts agree that the burbot genus belongs to the Lotidae Bonaparte family, but scientists have not come to an unequivocal conclusion regarding the multitypic nature. Some scientists distinguish only a couple of subspecies. For example:
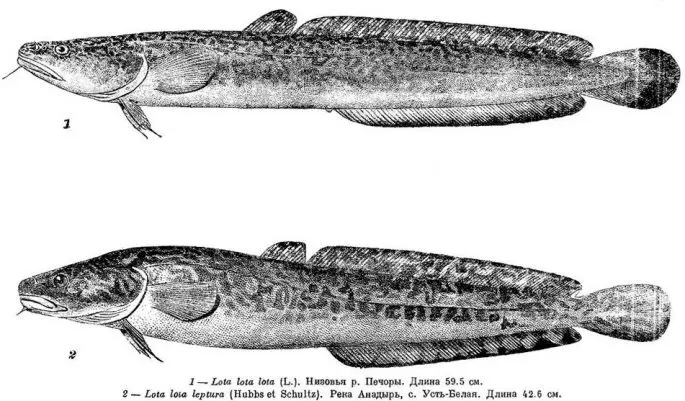
- Common burbot (Lota lota lota), which is considered a classic representative of the reservoirs of Europe and Asia, including the Lena River.
- Burbot fine-tailed (Lota lota leptura), which inhabits the waters of Siberia, from the channel of the Kara River to the waters of the Bering Strait, as well as including the Arctic coast of Alaska and up to the Mackenzie River.
In North America, the subspecies “Lota lota maculosa” lives, which is considered controversial. The appearance of burbots, as well as their way of life, indicates that the fish has not undergone any major changes since the Ice Age.
Appearance

Burbots have a long but low body, rounded in the front and somewhat laterally compressed in the back. The head is slightly flattened and relatively long, and the eyes are quite small. The mouth, on the contrary, is large, and the lower jaw is somewhat shorter than the upper. In the mouth you can see small, bristle-shaped teeth. There is one antennae on the chin, the length of which is approximately one fifth of the head. But on the upper jaw grows one pair of whiskers.
The color of burbots depends on the habitat conditions that correspond to the characteristics of the soil, the illumination and transparency of the water, including the age of the fish. Therefore, their colors can be very diverse. It is believed that the classic coloring of burbots consists of dark brown or blackish-gray hues, which brighten with the age of the fish.
On the body of burbots, you can always see light spots of large size, especially on unpaired fins and from the sides. At the same time, the shape and size of the spots can be varied, but on the fins and on the belly their color is always light.
Burbots are characterized by the presence of two dorsal fins. As a rule, the first of them is short, and the second is longer than the first and significantly. The anal fin also differs in a certain length. Together with the dorsal fin, they come close to the caudal fin, but do not form one whole with it. The pectoral fins are round in shape. The pelvic fins are located in the throat area, in close proximity to the pectorals. The ventral fin forms a second ray that resembles a characteristic long filament of sensory cells. The caudal fin has a characteristic rounded shape.
Interesting to know! Burbots of the Ob basin have the best indicators of weight gain, as well as Vilyui burbot. The largest burbot, reaching a mass of about 18 kilograms, is found in the Lena River.
The body of burbots is covered with rather small cycloid scales, which are located almost over the entire surface of the body, including in the head area, up to the gill cover and nostrils. The lateral line runs almost to the tail and beyond, but may be interrupted. It can grow to a size of 1,2 meters, while the growth rate largely depends on the availability of food in the reservoir.
Behavior and lifestyle
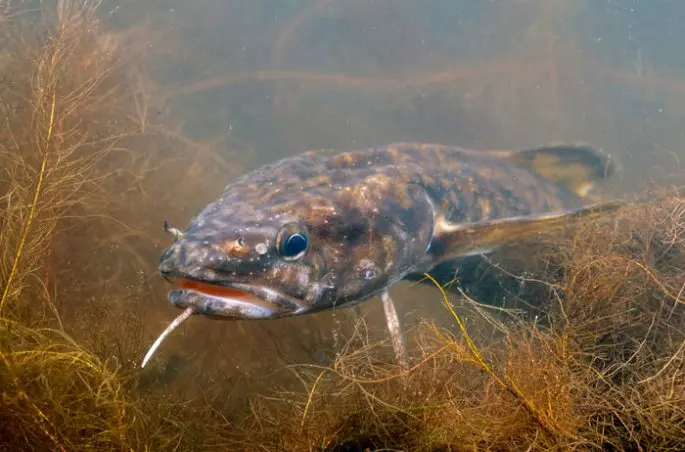

The uniqueness of this fish lies in the fact that burbot shows its greatest activity in cold water, while its spawning takes place in conditions when December and January frosts are on the street. Therefore, we can safely say that the peak of burbot activity occurs in the winter. This predator prefers to lead a benthic lifestyle and goes hunting only at night.
Burbot and its varieties feel comfortable in conditions when the water temperature does not exceed +11,5 degrees. When the water in the reservoir warms up to a higher temperature, the burbot becomes inactive or falls into a state of suspended animation.
Although burbot does not belong to schooling species of fish, a flock of burbots consisting of several dozen individuals can easily be found. As a rule, this is characteristic of smaller individuals, and trophy specimens keep apart. With the onset of heat, burbots begin to seek shelter for themselves, hiding in holes or among a heap of stones.
Interesting fact! Adult burbots are able not to eat for a long period.
This fish chooses places for its camps where cold springs beat. In addition, this fish does not tolerate light, so it feels uncomfortable even on moonlit nights. With the onset of heat, burbots stop eating completely and go hunting when periods of cooling come, and then only at night.
Paradise Unlost: Burbot Fish of Winter
How long does burbot live
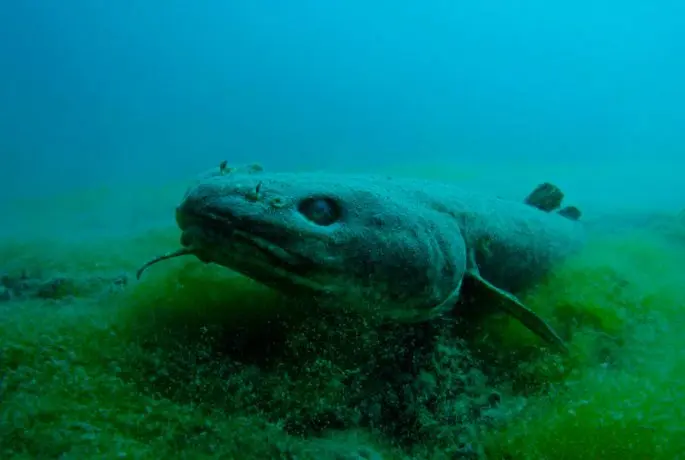

Burbot does not belong to long-lived fish, since even under the most favorable conditions it can live no more than 25 years.
Range, habitats
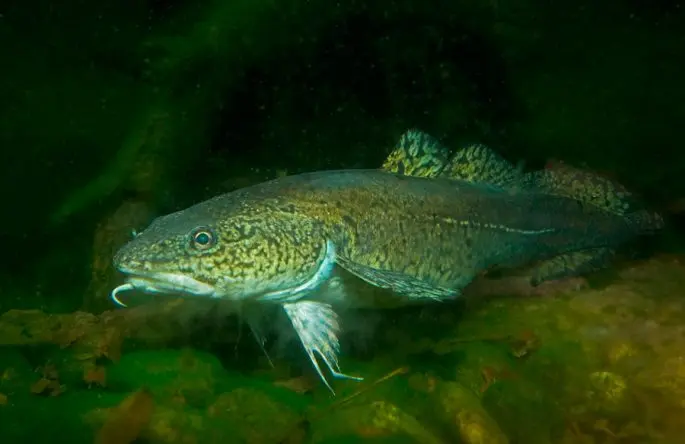

Burbots are distinguished by the fact that they mainly live in rivers flowing into the Arctic Ocean. Although, if we take the British Isles, the remains of burbots are found everywhere here, but in natural conditions, especially today, burbots cannot be found here. A similar situation exists for other countries, such as Belgium and Germany, although in the latter of them burbots are still found in the waters of the Elbe, Danube, Oder and Rhine. In countries such as the UK and Germany, intensive work is underway to recreate the burbot population.
A common occurrence for the water bodies of Sweden, Norway, Estonia, Lithuania, Latvia and Finland, when burbots are often found in nature here, although their populations are minimal in Finland. This is due to many factors, and the main one is environmental pollution. In addition, processes of water acidification and the dominance of alien species are noted, which displace native species.
The main reserves of burbot in Slovenia are dispersed in the waters of the Drava River and in Lake Cerknica. The Czech Republic can boast that burbots live in the Ohře and Morava rivers. As for Russia, burbots are distributed almost everywhere on its territory, both in the waters of the temperate and the Arctic zones. As a rule, these are the basins of the White, Baltic, Barents, Caspian and Black Seas, including the basins of many Siberian rivers.
The habitat of burbots is limited to the coast of the Arctic Ocean, while burbots are found on the Yamal Peninsula, on Taimyr, on the New Siberian Islands, as well as in the basins of the Ob and Irtysh, as well as Lake Baikal. In addition, representatives of this family can be found on the Amur and within the Zhenltoy sea, on the Shantar Islands and on Sakhalin.
The diet of burbots

The diet of burbots consists of objects of animal origin, which burbot finds within the bottom. Young individuals that have not reached 2 years of age feed on various insects, small crustaceans and worms, including eggs of various fish species. After 2 years of age, their diet already includes frogs, their larvae and fish eggs. Older individuals prefer to feed mainly on fish, and the size of the fish can be up to 30% of their own weight.
At the same time, adult burbots eat differently, depending on the season. If we take the spring and summer periods, then the basis of their diet is crayfish and worms, regardless of the size of the predator. When the heat sets in, burbots may generally refuse to eat. During this period, they prefer to be at a depth, near the bottom sources of cold water. With the onset of autumn, burbots become active and leave their shelters. They only go hunting at night.
In search of food, burbots visit shallow water. With a decrease in water temperature, the appetites of these predators increase. The peak of their activity falls on the winter period, when other types of fish, on the contrary, begin to lead a sluggish lifestyle, therefore they often fall into the mouth of this predator. As a rule, these are fish such as char, ruff, gudgeon, but there are more cautious fish, such as crucian carp, for example, which often manages to escape from the pursuit of a predator.
The burbot bites in a special way, as it grabs its prey by any part of the body and immediately tries to swallow it. At the same time, the predator does not make sudden movements. Burbot rarely uses his eyesight, as he prefers to spend most of his life at depth, but he has a highly developed sense of smell and hearing.
Interesting Facts! Burbots can also eat carrion. Often they have to swallow enough spiny fish, such as stickleback or ruff. It should also be noted that ruff is considered a favorite dish of a predator, therefore it is a classic victim of burbots during their night hunting.
Burbots at a great distance can determine their potential prey. In winter, burbots have a moment when they do not eat for one week. As a rule, after this, burbots go to spawn.
Breeding process
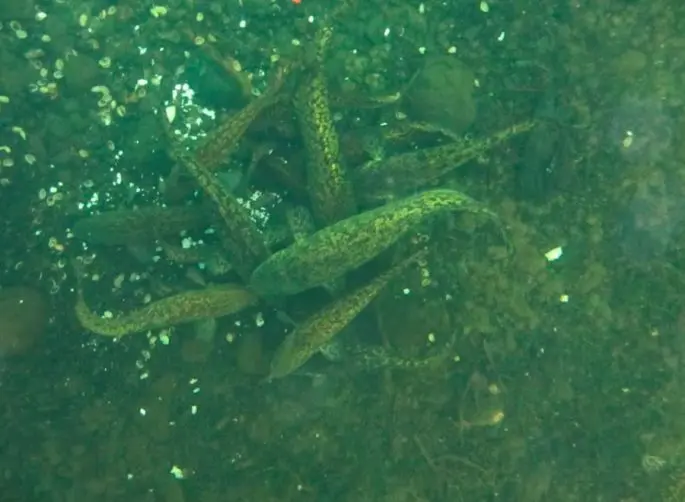

Having lived for 2 or 3 years, burbots are ready to continue their race. By this point, there are always many more males than females. Each female is accompanied by at least 2 males, while mature eggs are present even in the youngest individuals. In reservoirs, both large and small species of burbots can live, which differ in their almost black body color. Lake burbot species grow and develop somewhat faster than river species. River species are sent to spawn with a body length of at least 30 cm, while gaining a weight of at least 1,5 kg. The fry that emerged from the eggs grow and develop quite quickly and by the middle of summer grow up to 10 cm in length.
Adult individuals are the first to spawn in groups of several dozen pieces. Following them, individuals of medium size spawn. The last to spawn are the youngest individuals, as well as those that spawn for the first time. At the same time, juveniles stray into numerous flocks. Burbots go to spawn, rising upstream exclusively at night. For spawning, the fish chooses areas of the reservoir with a solid bottom, located in shallow water.
It is important to know! Up to one year of life, young burbots prefer to hide among the stones. The next year of life, with the advent of summer, they go to the depths. The habits of a real predator begin to appear upon reaching puberty.
Burbots, among the cod family, are particularly prolific. Each adult female is able to lay up to half a million eggs, which are yellowish in color and very small in size. Their maximum size is about 1 mm. Despite the fact that burbots lay a lot of eggs, their survival rate is very low, so predator populations do not differ in large numbers.
Natural enemies of burbots
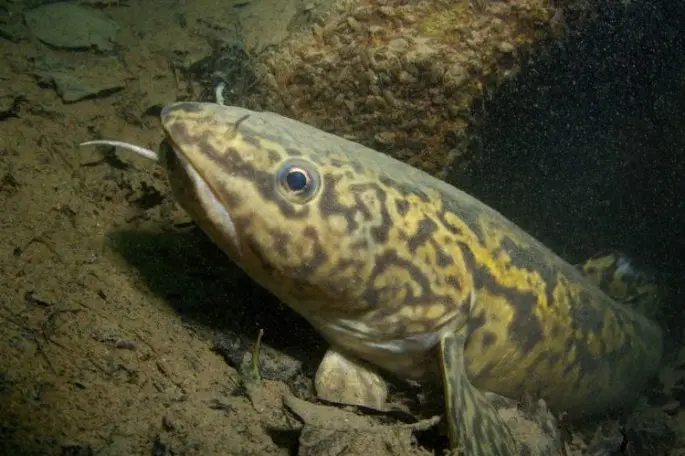

If you take an adult burbot, then he has very few natural enemies. But at the stage of development of eggs and juveniles, many surprises await burbots, so only a few survive to puberty. In addition to the fact that many species of fish do not mind tasting burbot caviar even in winter, after they are born, other predators hunt for juveniles, such as perch, ruff, goby, silver bream, etc. In the summer, when even adult burbot becomes less active, it can easily become food for catfish, which is much larger.
Population and status of burbots
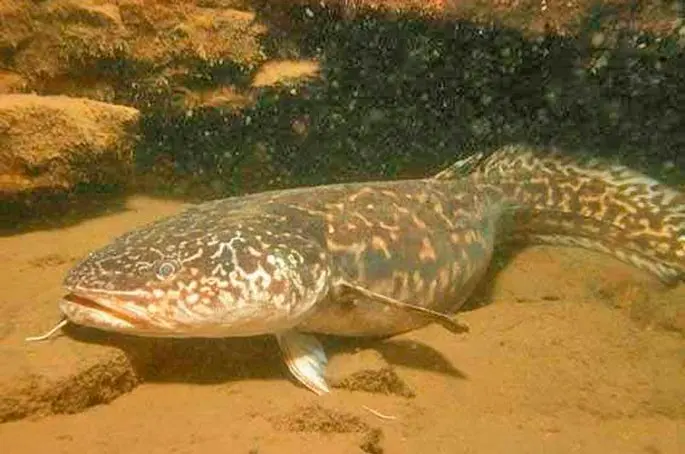

Today, in many countries, burbots are on the verge of extinction, and in some countries they have disappeared altogether and find only remnants of them. The general population of burbots is also decreasing. In some countries, serious measures are being taken to restore burbot as a species. Although this is not so easy to do. The thing is that water resources are polluted at a high rate, therefore, extremely complex measures are required, which requires huge costs. A more or less stable population of burbots is observed in the rivers and lakes of Switzerland.
It is important to know! Burbot populations around the world are affected by a number of factors, often associated with uncontrolled harvesting of this fish. The environmental factor should also not be discounted. Poachers cause great damage to the number of fish, the fight against which should reach a new level.
As a rule, modern factors that negatively affect the number of burbots in the water bodies of Europe and Asia are of a general nature. Today, this is a rather serious problem that requires immediate intervention at the level of the governments of some European and Asian countries. If we take Slovenia, then in this country the catching of burbot is prohibited at all, and in Bulgaria this predator was given the status of a “rare species”.
In other words, in those countries in which care is taken that burbot does not disappear as a species, its numbers remain within optimal limits. It should not be forgotten that measures to preserve the population of the species today require huge costs and not every country can afford it.
Commercial value of burbot
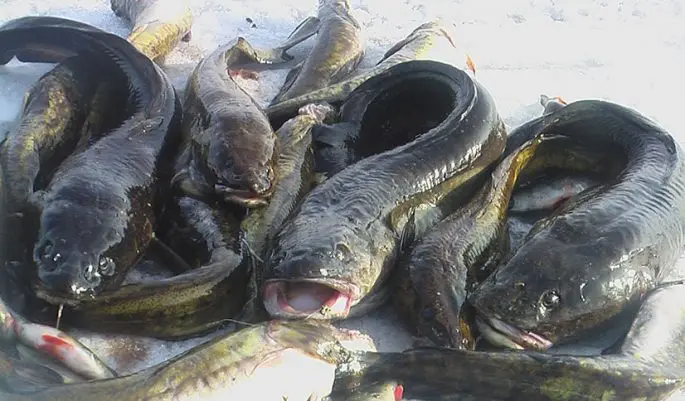

Burbot is considered to be quite valuable commercial fish, since its meat is quite tasty, sweetish in taste and tender. The meat of this predator is characteristic in that after freezing or even a short storage, it can quickly lose its taste. It is especially worth noting the burbot liver, which is notable for its rather large size and is characterized by an incredible taste and the presence of a whole range of useful components. Burbot meat, like the meat of other representatives of the underwater world, has a low fat content, therefore it is suitable for preparing various dietary dishes. This is especially true for those who have extra pounds and urgently need to lose them. Dishes from burbot, and especially boiled ones, are useful for any category of citizens. The only problem is the personal intolerance of the body, although there are very few such people. Eating fish dishes every day, a person regularly replenishes his body with the necessary vitamins and minerals. Thanks to this, the functions of many organs, including the central nervous system, are normalized in a person. Moreover, fish dishes prevent aging of the body, rejuvenating the skin. As a rule, diseases appear against the background of a lack of certain trace elements, therefore, by eating fish dishes, it is possible to prevent the appearance of many ailments in a person.
In conclusion
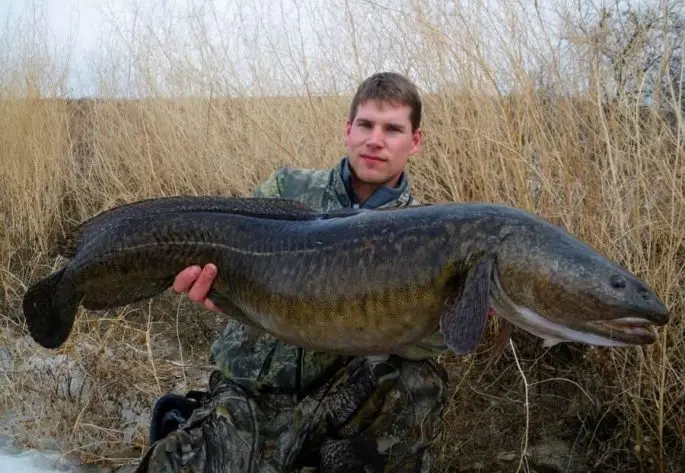

In our time, it is difficult to find a species of fish that would not be on the level of extinction. If we take, for example, salmon, then today many of the representatives of this family are on the verge of extinction and their fishing is generally prohibited or allowed, but only under license. This approach indicates that control over the catch of fish is being introduced. If this is not done, then soon a person will only see in the pictures what this or that type of fish looked like. The same can be said about burbots, one of the most amazing representatives of the cod family living in fresh water.
As already mentioned, the factors affecting the abundance of burbot in our waters are of a general nature, which means that we will all have to take the same measures to restore the population of many species of fish, including burbot.
ONE ON ICE. Night fishing. BURBOT. Departure first 2018









