Contents
In line with its mission, the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony makes every effort to provide reliable medical content supported by the latest scientific knowledge. The additional flag “Checked Content” indicates that the article has been reviewed by or written directly by a physician. This two-step verification: a medical journalist and a doctor allows us to provide the highest quality content in line with current medical knowledge.
Our commitment in this area has been appreciated, among others, by by the Association of Journalists for Health, which awarded the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony with the honorary title of the Great Educator.
Botulinum toxin infection is a typical food poisoning in the course of which (botulinum toxin) is produced by specific botulinum toxins (Clostridium botulinum), in addition to the human body, in a contaminated food product.
A few words about botulism sticks
Botulinum toxins (Clostridium botulinum) are gram-positive bacteria belonging to the Clostridiaceae family, the Clostridia class. The cells found in these bacteria have a cylindrical shape and are located singly, double or in short chains. Characteristic for microorganisms is the production of spores characterized by high heat resistance. The primary source of botulism is canned food. The spore forms contained in them transform into vegetative forms, multiplying under anaerobic conditions, and then undergo autolysis, saturating the food product with venom. The source of poisoning can be any kind of canned food (meat, fish, vegetable, fruit).
After ingestion, the venom is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. It is the strongest known bacterial poison, it damages the nervous system, canceling the conduction of stimuli in the neuromuscular synapse.
Botulinum toxin produced by botulinum toxins can be divided into eight serotypes: A, B, C1, C2, D, E, F and G. So far, infection with toxin A, B, E, less often F and G have been observed in humans. types A and B are found, for example, in spinach, beans and tomatoes. In recent years it has been proven that botulinum toxin can also be secreted by certain strains of Clostridium butyricum and Clostridium baratii.
The brooding period of botulism depends on the amount of ingested toxin. It may be several hours or several days.
Types of botulism infection
Infection with botulism (botulism) can be divided into several different forms.
1. Botulism jatrogenny – arises as a result of ingesting botulinum toxin (type A) in the form of injection. A characteristic symptom of this poisoning is general weakness of the patient, accompanied by dry mouth, ptosis, diplopia and dysphagia.
2. Food botulism – it is associated with the consumption of food infected with botulinum toxin, which, after getting into the digestive system, is transformed and reaches the bloodstream from the small intestine. Then, through the blood, it is transported to the muscle-nerve plates.
3. Child botulism – is the most common condition in infants. It is produced as a result of the consumption of honey, which contains botulinum toxin spores. Therefore, children under the age of one should not be given honey. The spores usually germinate in the baby’s large intestine, leading to colonization of the gut. In adults, the toxin usually does not colonize the intestines, because they have a normal bacterial flora (unlike infants, where it is not fully stabilized, which promotes the multiplication of pathogens).
4. Inhalation botulism – his first case was described in 1962 in Germany. It concerned three workers who became infected as a result of contact with an aerosol containing botulinum toxin type A, during necropsy of animals previously exposed to this toxin in the air. The symptoms of inhalation toxin were similar to those of food botulism.
5. Botulism przyranny – it is formed as a result of multiplication of botulinum toxin spores in deep wounds with tissue necrosis. The additional infection of the wound with aerobic bacteria creates an anaerobic environment in which the spores secrete toxins. Some of the wound toxin is absorbed by the blood and causes symptoms similar to food botulism. In addition, a high temperature appears, and the botulism period is 2-3 weeks.
6. Adult botulism of intestinal origin – its formation is conditioned by pathological changes occurring earlier in the digestive system, e.g. a change in the composition of the bacterial flora as a result of taking an antibiotic.
Symptoms of botulism infection
The initial symptoms of botulism include:
- weakness,
- tiredness,
- dizziness,
- dry mouth.
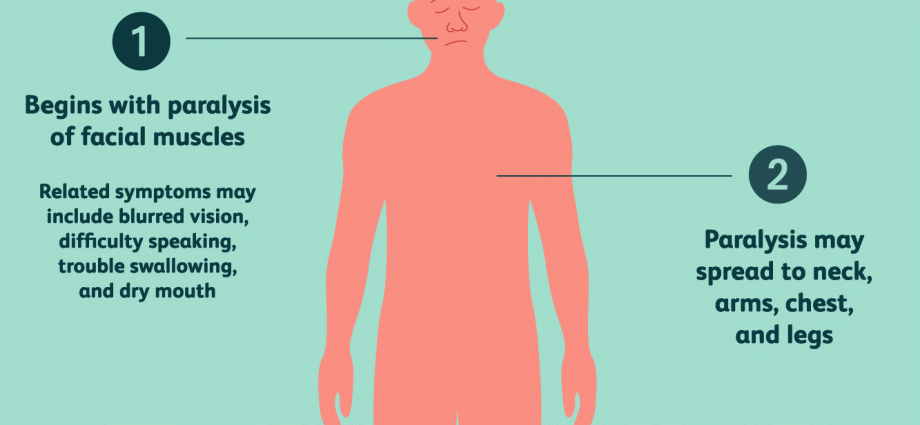
Hours later, neurological symptoms join in, such as: double vision, mydriasis, convergent strabismus, ptosis, photophobia. In addition, mucus secretion is inhibited, swallowing is difficult and speech is low. Paralysis of intestinal peristalsis causes abdominal distension and persistent constipation, and urination is disturbed. As the infection develops, there is increasing muscle weakness, especially in the neck and respiratory muscles. The death of a sick person may occur due to paralysis of the respiratory center, and sometimes as a result of unexpected cardiac arrest.
Botulinum toxin infection – diagnosis
The oldest method of recognizing botulinum neurotoxin is a biological test carried out on mice, which is characterized by high sensitivity. This test allows you to determine the type of botulinum toxin. A patient with suspected botulism is given an antitoxin, but before this happens, a blood sample is also taken. Then the patient’s serum is treated with an antitoxin, which neutralizes the botulinum exotoxin. The preparation prepared in this way is injected into mice. If the mice survive, it means there was botulinum exotoxin in the serum. Biological examination allows to detect even microscopic amounts of botulinum toxin.
Gastrointestinal infection with botulinum toxin can also be diagnosed in the stool and gastric contents. On the other hand, in the case of inhalation botulism, the toxin can be detected in a swab from the nasal mucosa within XNUMX hours (an ELISA test is used for this purpose).
Treatment of botulism infection
Hospital treatment often fails. However, it should be implemented as soon as possible after eating contaminated food in order to remove the toxin. For this purpose, it is recommended to induce vomiting, gastric lavage and deep enemas (of course in a hospital setting). Antitoxic serum (directed against type A, B and E toxins) should be administered to the patient as soon as possible to inactivate the venom still in the blood.
In patients who survive, recovery is very slow, especially in the case of visual impairment and muscle weakness.
Botulinum toxin infection prevention
Avoid eating stale canned food after its use-by date, even in metal cans. A signal of deterioration is the swelling of the bottom, and when it is opened, a characteristic hissing sound may be heard.