Contents
A boiled water burn is a type of thermal damage to the skin and mucous membranes caused by the traumatic effect of boiling or hot liquids and their vapor. It occurs most often in everyday life, being the main cause of temporary disability among all types of burn injuries. The mechanism for obtaining them can be represented by placing the limb in a boiling liquid or spilling it on the surface of the skin.
Most often, burns with boiling water proceed favorably and do not cause serious consequences. It all depends on the volume and depth of the skin lesions. They, in turn, depend on a number of factors:
The temperature of the hot liquid and its composition. Pure water has less damaging effect than syrup or brine;
The volume of boiling water and the area of contact with the skin;
Speeds and pressures under which contact occurred;
Time of exposure to boiling liquid with a burnt surface;
Features of the structure and resistance of the affected areas to high temperatures.
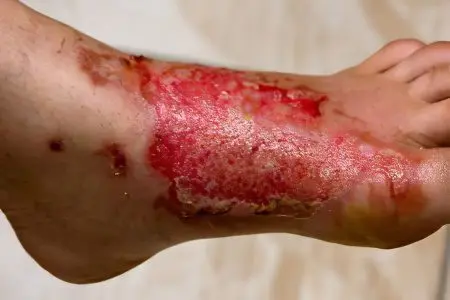
There is a clear pattern – the hotter the liquid and the time of its contact with the skin, the more severe the consequences. This fact determines the scope of activities that must be carried out without fail in such situations.
Most often, the upper limbs (hands and forearms) are burned with boiling water, less often the feet, thighs, lower legs, abdomen and chest. Small areas, fortunately, prevail over large ones. With regard to the degree of burn, superficial damage occurs in 85% of cases. Among other features of this type of burn injuries, the best prognosis for recovery can be noted. The exception is burns in children, especially young children. Due to the small surface area of the skin, a significant part of it is affected.
With regard to the degrees of damage during burns with boiling water, there are no features. The classification, which uses 4 degrees (1-2-3-4), is quite understandable and quite convenient. The first is characterized by the appearance of reddened areas. For the second – bubbles with a transparent liquid. The third is characterized by the appearance of either wound surfaces with moderate bleeding, or blisters with sanious fluid. The fourth degree is the defeat of the entire thickness of the skin and deep-lying tissues (it almost never occurs with burns with boiling water). The most common are injuries of 1 and 2 degrees. The area of the burn is determined by the rule of the palm (palm = 1% of the skin), or nines (each segment of the body = 9 or 18%).
Depth of defeat
Before proceeding with the treatment of a burn, it is necessary to determine its degree and the area of the affected area. First and second degree burns can be treated at home, while third and fourth degree burns require medical attention.
1 degree – there is a lesion of the surface layers of the epithelium, swelling and redness, pain, burning sensation appear. Such burns usually heal on their own in a few days without additional intervention.
2 degree – the depth of the lesion is greater, it captures not only the surface layers of the skin, but also part of the tissues that lie deeper. The pain sensations are stronger and more prolonged, second-degree burns are characterized by the formation of thin-walled blisters filled with liquid. After two weeks, they heal on their own without scarring, medical assistance may be needed only in case of infection.
3 degree – damage to superficial and deep-lying skin tissues. Third-degree burns are further classified into grades A and B. A-grade is characterized by the formation of thick-walled blisters and scabs. Tissue regeneration occurs due to the surviving epithelial cells, secretory glands and hair follicles. Grade B is characterized by severe injuries with tissue necrosis and purulent inflammation, a wet wound is formed, after which a scar remains after healing.
4 degree – when the skin is damaged in areas where the layer of subcutaneous fat is thin, black scabs and charring are formed.
If the healing of the burn of the first and second degree does not occur within two weeks, the inflammatory process intensifies, and signs of infection appear, it is necessary to consult a specialist. Treatment of burns of the 3rd and 4th degree of severity is carried out only in a hospital setting.
How to correctly determine the area of skin lesions?
Wallace’s method or the rule of nines – each part of the body corresponds to 9 or 18% of its area. The area of one arm is taken as 9%, one leg for 18%, head, back and front surface of the body – 18%, inguinal region – 1%.
Glumov’s method or the palm rule – the area of u1buXNUMXbone palm is taken as XNUMX% of the total area and the affected area of uXNUMXbuXNUMXbthe body is measured with the palms.
First aid for burns with boiling water
First aid measures must be truly urgent. The timeliness of their provision will determine the severity of the process and its consequences. Do not panic, no matter who this trouble happens to. Only a clear sequence of actions can help in the fight against the prevention of serious complications.
Other activities include:

Elimination of direct or indirect contact of the boiling liquid with the skin surface. To do this, the heat source must be removed from the burnt surface. In the same way, all items that were on the skin at the time of the burn (clothes, rings, bracelets, etc.) are removed;
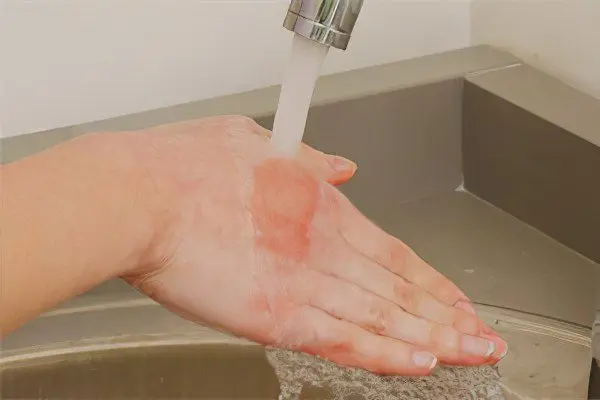
Creation of hypothermic conditions for the burn surface. This is necessary in order to cool the overheated tissues, which maintain a high temperature for a long time after the burn, aggravating the severity of the primary lesion. For these purposes, it is necessary to place the affected segment in cold water (like a cold bath, or running water). The duration of hypothermia should last at least half an hour. After this time, the limb can be removed. If a burning sensation appears, the procedure is repeated. Cooling can also be achieved with the help of ice or cold objects.
Imposing on the burnt surface of the limiting dressings. They can be presented either dry, or wet-drying, or ointment on a water-soluble basis. At the pre-hospital stage, you should not waste time looking for various special tools. You need to use what is at hand or in the first aid kit. It would be correct to include antiseptic solutions (furatsilin, dioxidin) and local anesthetics (lidocaine, novocaine) in the dressing, which will have an analgesic and antibacterial effect, which will prevent infection of the burn surface.
For large or deep burns, accompanied by severe pain, pain medication is indicated.
What to do with a burn with boiling water?

What can not be done with a burn with boiling water:
Apply therapeutic ointments to the skin immediately after the burn – first, the affected area must be cooled;
If a bubble has formed during the burn, it should never be pierced – this increases the risk of infection and may slow down healing;
It is impossible to use alcohol-containing products (iodine, brilliant green, tinctures of medicinal plants), toothpaste, vinegar and urine for the treatment of burns, as these substances cause skin irritation and aggravate its condition. Sea buckthorn oil enhances tissue regeneration and promotes wound healing without scarring, but it is not recommended to use it for the first time after a burn. Oils close the pores, creating a film on the skin, preventing it from breathing.
If the affected area is covered with clothing, then it should be removed immediately. Tissue adhered to the wound surface should be carefully cut off at the edges.
To wash the wound immediately after the burn, clean water is used, and not slightly alkaline or acidic liquids (a solution of soda or citric acid, kefir). Acid causes skin irritation and makes it difficult to heal, increases pain, and dairy products also increase the risk of infection.
What to do with a burn with boiling water in the first place:
Immediately stop exposure to the factor that caused the burn. If boiling water gets on areas of skin covered with clothing, it must be removed immediately before it sticks to the wound.
The thermal effect on the skin and nearby tissues does not stop immediately after its source is removed, so the affected area must be cooled for fifteen minutes under running cold water or an ice compress should be applied to it.
For first-degree burns, the best remedy for relieving pain and accelerated wound healing is sprays containing dexpanthenol, which have a healing and anti-inflammatory effect – panthenol or its analogues Pantoderm and Bepanthen. It is applied to the surface of the burn directly from the bottle, without touching the skin, and left until absorbed.
For the treatment of burns of the second degree and more severe, after washing the wound, a bandage is applied. A bandage is not used on the face, a thick layer of petroleum jelly is applied to the affected area.
A victim with deep tissue burn injuries must be warmed, drink tea, and drink plenty of water or alkaline drinks (herbal or green tea, lemon water). With severe pain, it is necessary to inject an anesthetic and continue treatment on an outpatient basis.
What to do if you get a burn with boiling water at home?
For first-degree burns, the bandage can be applied independently. Bepanten or an antiseptic ointment is applied to the wound, after which it is covered with a dressing, which can be used as a cotton cloth. Gauze and bandages are not recommended as dressings, as they stick to the wound and injure it when the dressing is changed. Change the bandage every 3-4 days. If the wound has healed by the time the bandage is changed, then it is not necessary to bandage it again.
For burns of the second degree of severity, the doctor applies the bandage, carrying out the primary treatment of the affected area. The bandage is changed after two days on its own, following the instructions of the doctor.
Procedure for the procedure of closed treatment:
Anesthetize the patient;
The skin around the wound is treated with an antiseptic;
Adhering tissue and impurities, dead epithelium are removed from the surface of the burn;
Large burn blisters are cut from the sides, liquid is released from them, leaving the upper part intact to protect the wound from mechanical damage;
Apply a bandage treated with a bactericidal agent (streptomycin, levosulfametacaine).
Treatment of severe burns with boiling water
Third and fourth degree burns are treated only in a hospital. Immediately upon admission, the patient is given anti-shock therapy, injections of painkillers are given.
For the treatment of burn lesions in the face and perineum, where the skin is especially thin and sensitive, only the open method is used (without the use of a bandage). Antiseptic ointments and petroleum jelly are used, which are applied to the affected areas three times a day.
Surgical treatment of severe burns (grades 3 and 4B) is aimed at excision of necrotic tissues and correction of the defect, after which plastic surgery is performed. The main tasks in the treatment of burns are to remove toxic substances, prevent suppuration and inflammation in the wound area, accelerate healing and removal of dead areas.









