Contents
The creation of a heating system involves the connection of a boiler and heating appliances (radiators, convectors and a warm water floor). Also, the system must have devices that ensure security. The procedure for connecting this entire economy is called the “boiler piping”.
What is strapping and what is it made of
There are two main parts in the heating system – the boiler and heating radiators or underfloor heating. What binds them and provides security – this is the harness. Depending on the type of installed boiler, different elements are used, therefore, the piping of solid fuel units without automation and automated (more often gas) boilers is usually considered separately. They have different operation algorithms, the main ones are the possibility of heating the TT boiler in the active combustion phase to high temperatures and the presence / absence of automation. This imposes a number of restrictions and additional requirements that must be met when piping a solid fuel boiler.
What should be in the harness
To ensure the safe operation of heating, the boiler piping must contain a number of devices. Must be:
- Pressure gauge. To control the pressure in the system.
- Automatic air vent. To bleed air that has entered the system – so that plugs do not form and the movement of the coolant does not stop.
- Emergency valve. To relieve excessive pressure (connects to the sewerage system, as a certain amount of coolant is bled).
- Expansion tank. Needed to compensate for thermal expansion. In open systems, the tank is placed at the top of the system and is a regular container. In closed heating systems (mandatory with a circulation pump), a membrane tank is installed. The installation location is in the return pipeline, in front of the boiler inlet. It can be inside a wall-mounted gas boiler or installed separately. When using the boiler to prepare domestic hot water, an expansion tank is also required in this circuit.
- Circulation pump. Mandatory for installation in systems with forced circulation. To increase the efficiency of heating, it can also stand in systems with natural circulation (gravitational). It is placed on the supply or return line in front of the boiler to the first branch.
Approximate piping diagram for a floor boiler
Some of these devices are already installed under the casing of the gas wall-mounted boiler. The binding of such a unit is very simple. In order not to complicate the system with a large number of taps, the pressure gauge, air vent and emergency valve are assembled into one group. There is a special case with three outlets. Appropriate devices are screwed onto it.
A safety group is installed on the supply pipeline immediately at the boiler outlet. Set so that it is easy to control the pressure and you can manually release the pressure if necessary.
What pipes to make
Today, metal pipes are rarely used in the heating system. They are increasingly being replaced by polypropylene or metal-plastic. Tying a gas boiler or any other automated (pellet, liquid fuel, electric) is possible immediately with these types of pipes.
When connecting a solid fuel boiler, it is impassable to make at least a meter of the pipe at the supply with a metal pipe and, best of all, with copper. Then you can put the transition to metal-plastic or polypropylene. But this is not a guarantee that polypropylene will not collapse. It is best to make additional protection against overheating (boiling) of the TT boiler.
Which of the polymer pipes is better? Polypropylene or metal-plastic? There is no single answer. Polypropylene piping is good with reliable connections – properly welded pipes are a monolith. (How to connect polypropylene pipes read here). But the maximum allowable temperature of the coolant in the system is not higher than 80-90 ° C (depending on the type of pipe). And then, prolonged exposure to high temperatures leads to the rapid destruction of polypropylene – it becomes brittle. Therefore, the binding of the boiler with polypropylene is done only in low-temperature systems based on automated boilers.
Metal-plastic has a higher operating temperature – up to 95 ° C, which is enough for most systems. They can also be used to tie a solid fuel boiler, but only if one of the protection systems against overheating of the coolant is available (described below). But metal-plastic pipes have two significant drawbacks: narrowing at the junction (fitting design) and the need for regular checks of connections, as they leak over time. So the binding of the boiler with metal-plastic is done subject to the use of water as a coolant. Anti-freeze liquids are more fluid, therefore it is better not to use compression fittings in such systems – they will still flow. Even if you replace the gaskets with chemically resistant ones.
Piping of gas boilers
Modern gas boilers have good automation that controls all the parameters of the equipment: gas pressure, the presence of a flame on the burner, the pressure level and temperature of the coolant in the heating system. There is even automation that can adjust the work to the weather data. In addition, wall-mounted gas boilers in most cases contain such necessary devices as:
- safety group (pressure gauge, air bleed valve, emergency valve);
- expansion tank;
- circulation pump.
In wall-mounted gas boilers, an expansion membrane tank and a safety group are already installed
The parameters of all these devices are indicated in the technical data of gas boilers. When choosing a model, you need to pay attention to them and choose a model not only in terms of power, but also in terms of the volume of the expansion tank and the maximum volume of coolant.
Scheme of piping a wall-mounted gas boiler
In the simplest case, the boiler piping contains only shut-off valves at the boiler inlet – so that repairs can be carried out if necessary. Even on the return pipeline coming from the heating system, they put a mud filter – to remove possible contaminants. That’s the whole harness.
In the photo above there are angled ball valves, but this, as you understand, is not necessary – it is quite possible to put ordinary models, and deploy pipes closer to the wall using corners. Also note that there are taps on both sides of the sump – this is in order to be able to remove it and clean it without draining the system.
In the case of connecting a single-circuit wall-mounted gas boiler, it is still easier – only gas is supplied (gas workers are connected), hot water is supplied to radiators or a water-heated floor and the return from them.
Piping schemes for floor gas boilers
Floor models of gas heating boilers are also equipped with automation, but they do not have a safety group, an expansion tank, or a circulation pump. All these devices have to be installed additionally. Because of this, the strapping scheme looks a little more complicated.
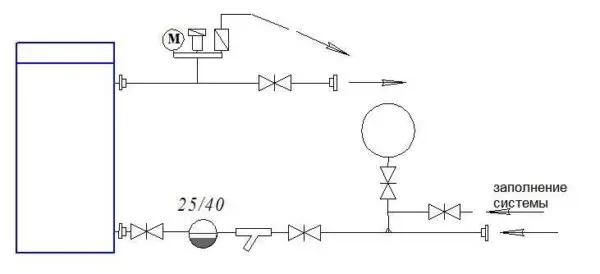
An additional jumper is installed on two schemes of the classic boiler piping. This is the so-called “anti-condensation” loop. It is needed in large systems, if the water temperature in the return pipe is too low, it can cause condensation. To eliminate this phenomenon and arrange this jumper. With its help, hot water from the supply is mixed into the return pipe, raising the temperature above the dew point (usually 40 ° C). There are two main implementations:
- with the installation of a circulation pump with an external temperature sensor in the jumper (and the photo is at the top right);
- using a three-way valve (pictured below left).
In a circuit with a circulator on a jumper (a condensate pump), it is made a pipe with a step of a smaller diameter than the mains. The sensor is attached to the return pipe. When the temperature drops below the set temperature, the pump power circuit is turned on, hot water is added. When the temperature rises above the threshold, the pump turns off. The second pump is the heating system itself; it works all the time while the boiler is running.
In the second scheme with a three-way valve, it opens the hot water mixture when the temperature drops (set on the valve). The pump in this case is on the return pipeline.
Solid fuel boiler piping
Any owner of a TT boiler knows that a lot of heat is released during the active combustion phase. Experience comes with time – when and how exactly to close the damper, for what period of time, etc. But it is worth a little distraction, and the water in the system will overheat and may even boil. To prevent this phenomenon, the boiler piping without automation must contain several devices that prevent the system from boiling. Only in this case can wiring around the house be done with polymer pipes. Otherwise, sooner or later, the superheated coolant will soften the material, the pipes will break through with all the ensuing consequences. Therefore, the piping of a solid fuel boiler, in addition to traditional elements – a safety group, an expansion tank and a circulation pump – contains a substantial number of additional devices and usually requires quite substantial funds.
The cyclic nature of the operation of solid fuel boilers leads not only to the boiling of the system, but also to the fact that the house is either very hot (when the fuel is actively burning), then cold – when everything has burned out. To eliminate these phenomena, there is a solution: install an indirect heating boiler or a heat accumulator. Both are water containers, they just perform different functions and, accordingly, are connected in different ways.
Piping with an indirect heating boiler
An indirect heating boiler heats water for hot water supply and is connected on the one hand to the heating system, and on the other hand to the hot water distribution manifold. Thus, temperature fluctuations are softened, and water is heated for technical needs. Not a bad decision.
How does this scheme work? If the temperature of the water in the water heater is below the set value, the boiler is connected to the heating of the water in the tank. The heating system is turned off for this time and cools down a little. After heating the water to the required temperature, the boiler switches back to work with the heating circuit. When warm water is used up, the temperature in the tank drops again, and the heating is connected again.
It’s not difficult, but with such a scheme, overheating is still possible – the consumption of hot water does not always coincide with the phase of active combustion of the fuel. In this case, overheating is possible.
Scheme with a heat accumulator
The second way is to install a heat accumulator. This is also a container with water, but it is connected only to the heating system. Serves to mitigate temperature fluctuations in the system.
This method is more reliable, but requires the construction of several separate circuits. The boiler heats water in a heat accumulator – it is connected to the TA inputs. This is one closed loop. The second circuit goes to heating – from the outlet of the heat accumulator (in the upper part of the tank), hot water enters the heating system, and the cooled water from the return pipeline enters the lower part of the same tank. If necessary, you can also connect a water heated floor system.
With this construction, there is no sharp increase in temperature, usual for a solid fuel boiler, during active combustion. All because the volume of the tank is added, because there is practically no overheating of water. Then, when the fuel burns out and the house begins to cool down in the conventional system, the heat stored in the heating phase continues to be consumed in the system with TA. In this way, the temperature background is leveled and the time between fireboxes increases.
Such a piping of a solid fuel boiler is more reliable and wiring from TA can be done with polypropylene pipes, but the circuit from the boiler to the tank must be made with metal pipes. In this case, you can use steel, but copper is still better.
Boiler TT piping with overheating valve
The third way to make a solid fuel boiler overheat protection is to install an automatic overheat protection device. This is a special valve with a temperature sensor. The principle of operation is simple: when a certain temperature (usually 95-97 ° C) is exceeded, the valve opens the inlet of cold water from the water supply, and the excess overheated is released into the sewer. This is how, for example, REGULUS DBV 1-02, Regulus BVTS 14480 works.
The valves, although they are manufactured by the same company, have a different structure and installation scheme. So REGULUS DBV is installed at the outlet of the boiler, has a built-in temperature sensor (installation diagram – above). The TT overheat protection valve of the Regulus BVTS 14480 boiler has a remote sensor, it can be mounted both at the inlet and outlet (installation diagram below). Why is this option good? The fact that it can work in systems with natural circulation – it does not need pressure to work.
Their estimated cost – 40-60 € – is much less than the cost of installing a heat accumulator or an indirect heating boiler, but this method does not solve the problem of temperature fluctuations. These valves, by the way, can be used to increase the reliability of the circuit with an installed indirection and thereby precisely eliminate the possibility of the system boiling.
What else is needed in the system
The boiler piping will be incomplete if it does not have a tap to drain and fill the system. And it’s better if they are separate. The specific installation location depends on the structure of the system, but there are certain rules:
- A drain tap is made at the lowest point. This is very important if the heating system needs to be preserved for the winter – it is necessary that as little coolant as possible remains in it. If the system will work constantly in winter, usually a tap (with or without a pipe) is attached to one of the radiators. This will be the place to drain the system.

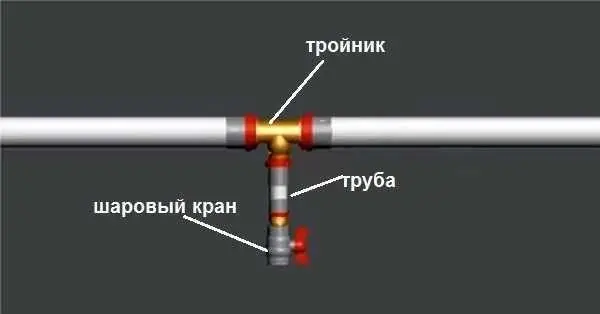
Such a valve for draining the system can be installed in any convenient place (on the return pipeline) - If water is to be used in the heating system, the input from the water supply is usually connected. In the case of a wall-mounted gas boiler, there is a special pipe with a stationary tap for this. Cold water is connected to this inlet, if necessary, the tap is opened for a short time. If a boiler is used without a special pipe, a tap is also installed in the supply pipeline (preferably higher). As an option – on a piece of pipe that goes to the expansion tank.

One of the options for installing a tap to fill the heating system
In some systems, the drain and fill of the system is made from one tap. This is possible if there is a pump that pumps the coolant and there is a pressure gauge that can be used to control the generated pressure. If there is a separate tap for filling the system at a high point, it can also be filled by gravity.