Contents
The human body can adapt to almost any environmental conditions. We can feel comfortable both under the hot southern sun and in the conditions of the Siberian winter. Including adaptation mechanisms, our body chooses the optimal variant of existence, capable of supporting all important life processes.
But the body’s resources are not unlimited. If the environmental conditions are too aggressive, the adaptation mechanism fails, and the work of all organs and systems deteriorates. In particular, this happens when the body is overcooled.
What is hypothermia
Hypothermia is a condition in which the body temperature drops so much that the body is unable to maintain the desired level of metabolism and function normally. During hypothermia, the temperature of the internal organs of a person drops below +35 ° C. In medical practice, this condition is called hypothermia.1. If at this moment the person is not helped, then the body temperature will continue to decrease further.
Hypothermia has three degrees of severity, which depend on body temperature indicators: first (mild), second (medium), third (severe).
An important point – the table shows the rectal temperature (it is measured in the rectum).
| Degree of hypothermia | Temperature |
| 1 degree (mild) | from 35 to 32,2 C ° |
| 2nd degree (medium) | from 32,2 to 29 C ° |
| Grade 3 (severe) | below 29 C ° |
Each degree of hypothermia is characterized by its own symptoms, by which it is possible to determine the severity of a person’s condition and take the necessary measures.
Symptoms of hypothermia
- First (light) degree of hypothermia
With a mild degree of hypothermia, a person’s skin turns pale, takes on the appearance of “goosebumps”. Chills appear and muscle tone increases1. The muscles of the neck and shoulder girdle are the first to tense: the person seems to be trying to pull his head into his shoulders. Later, the muscles begin to shake violently, and it is impossible to stop it. Trembling is a defensive reaction of the body, a way to generate some heat mechanically. There are also speech disorders, it becomes difficult to talk. With a mild degree of hypothermia, frostbite of 1-2 degrees is possible.
- Second (medium) degree of hypothermia
With the transition of hypothermia to the second degree, the shivering disappears, blood circulation slows down, the number of heartbeats decreases to 30-50 per minute. The heart rhythm is disturbed and blood pressure drops to 80-90 / 40-50. Due to the deterioration of peripheral blood flow, frostbite of 1-4 degrees often develops.1.
Consciousness is clouded, a person can fall asleep. In this case, as a rule, dreams are positive. Most often, a person dreams that he is in a warm room. However, sleep in the second stage of hypothermia is very dangerous, because the body practically stops producing energy, and a person can die.
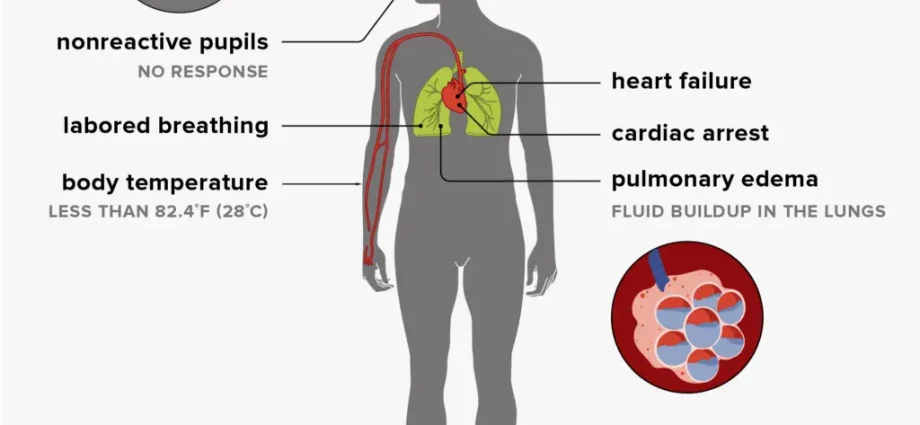
- Third (severe) degree of hypothermia
If the temperature continues to decrease, the third degree of hypothermia of the body will come. It is characterized by muscle tension (rigidity), an even greater slowing of the heartbeat (up to 30-36 beats). Oxygen starvation of the body increases, blood pressure drops. The skin becomes bluish, the person loses consciousness or falls into a coma1.
When the rectal temperature drops to 23 degrees, all vital processes are rapidly inhibited, the heart stops, and clinical death occurs. The chances of saving the victim at this stage are very small.
If you notice the first signs of hypothermia in yourself or another person, you must immediately take measures to prevent further deterioration of the condition.
First aid for hypothermia
Having noticed the first signs of hypothermia, take the victim to heat, remove frozen or wet things from him, wrap him in a warm blanket or dress him in dry clothes. Give the person a warm drink and make sure they move as little as possible.1.
Remember the main thing – you need to warm a person gradually: first the body, then the arms and legs. If you do general heating or warm only the limbs at first, shock and cardiac arrest can be provoked. It is necessary to attach something warm to the back of the head, chest, inguinal and axillary areas. If possible, you can immerse the victim in a bath of warm water (about 28 ° C)2.
When providing first aid for hypothermia, you need to remember a few rules:
- You can not rub the limbs with snow or something else;
- You can not move a person to a room that is too warm;
- Do not allow the victim to walk and move;
- You can not intensively heat a person (under running hot water or in a hot bath);
- Do not use alcohol, coffee and open fire for warming.
If the casualty has lost consciousness, proceed to emergency care and immediately call a doctor or take him to the hospital.
Causes of hypothermia
The most common cause of hypothermia is prolonged exposure to cold water (such as falling through ice).
Hypothermia can also provoke a long stay in wet or light clothes at sub-zero or close to zero temperatures. This is especially dangerous if a person has been without movement or headgear for a long time. The situation is exacerbated by strong winds and high humidity. A mild degree of hypothermia can cause even the use of large amounts of ice-cold drinks.
Most often, open areas of the body are exposed to hypothermia (the so-called “local hypothermia”): face, hands and feet. Prolonged hypothermia can lead to frostbite.
Most often, hypothermia affects the elderly and debilitated people, people under the influence of alcohol, infants and young children. It is more difficult for people to endure low temperatures after malnutrition, overwork, and prolonged exposure to stressful situations.
Methods of treatment for hypothermia of the body
As a rule, even a slight hypothermia does not pass without a trace, since in itself it is a strong stress for the body. The consequences of mild hypothermia can be eliminated on your own, in more serious cases, you will need the help of a doctor2.
Home conditions
The consequences of mild hypothermia include general malaise and a cold with a runny nose, sneezing and sore throat. As a rule, these manifestations pass independently.
To recover faster, give your body a good rest, take a warm bath, drink more warm liquids. But it is better to refuse coffee and alcohol, as well as walking in cold weather.
A mild cold can be cured quickly with plenty of fluids and symptomatic remedies. If the illness persists and you begin to feel worse, be sure to consult a doctor.
Under the supervision of a doctor
The average degree of hypothermia of the body can lead to serious consequences such as tonsillitis, bronchitis, pneumonia and other diseases. Some chronic diseases may also worsen: diabetes mellitus, bronchial asthma, pathologies of the heart, kidneys, bladder, and others. Of course, in this situation, qualified medical care is indispensable.
A severe degree of hypothermia is accompanied by insufficiency of organs (liver, kidneys) or entire body systems (cardiovascular, respiratory). As a rule, this degree of hypothermia is accompanied by severe frostbite. This will require qualified medical care in a hospital setting, and possibly surgical intervention.2.
Consequences of hypothermia
All the consequences caused by hypothermia of the body can be both local and systemic. Let’s talk about the most common ones in more detail.
Cold from hypothermia
It is a mistake to think that hypothermia in itself causes a cold. All respiratory diseases provoke viruses and bacteria. If your immune system is weakened, or you suffer from chronic diseases, hypothermia further reduces the body’s defenses and makes it vulnerable to infections.
Therefore, at the first sign of a cold, you need to take action quickly. For example, drink as much warm liquid as possible – water, tea, fruit drink. You can gargle with a weak salt solution. At high temperature, you can do cooling compresses, take over-the-counter antipyretics. All other medications must be prescribed by a doctor. Timely action will help you avoid more serious complications.
temperature from hypothermia
Hypothermia does not cause an increase in temperature, but rather lowers it. But if the temperature began to rise, then we are talking about complications. For example, with a banal acute respiratory disease, a temperature of 37 to 38,5 ° C helps the body fight a viral or bacterial infection, so it should not be knocked down. If the temperature of 38,5 lasts more than 3-5 days or continues to rise, you should consult a doctor.
Cough from hypothermia
With hypothermia, the nose and pharynx are primarily affected, which are a protective barrier to infection. Cough usually indicates an inflammatory process in the nasopharynx. It can occur both with inflammation of the pharynx itself, and from irritation with its secretions of the nasal mucosa. But coughing can also be a symptom of more serious complications, such as bronchitis, pleurisy, and pneumonia. The doctor will help you determine the true cause of the cough and prescribe treatment.
All other consequences
Hypothermia can exacerbate existing chronic diseases, such as diabetes, asthma, arthritis. Hypothermia of the body can cause serious diseases of the bronchi and lungs (tracheitis, bronchitis, pneumonia), inflammatory processes in the kidneys and bladder. The cardiovascular system can respond to hypothermia by circulatory disorders – hence heart attacks, strokes, peripheral vascular lesions.
Very serious consequences of hypothermia include frostbite, which in severe cases leads to amputation.
Prevention and timely detection of symptoms of hypothermia at an early stage will help you avoid these consequences. If any of these symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Prevention of hypothermia at home
Prevention of hypothermia is a simple matter. It is enough to follow a number of rules of conduct:
- Try not to leave the house unnecessarily in the cold;
- When you go out, dress for the weather. In cold weather, it is better to wear loose and layered clothing, it retains heat better. Pay special attention to shoes. Let it be warm and not squeeze the foot;
- In severe frost, apply a protective cream to exposed areas of the body;
- Before going out into the cold, eat food and do not drink alcohol;
- Do not smoke in extreme cold. Nicotine constricts peripheral vessels and contributes to hypothermia of the extremities;
- If possible, avoid wearing metal jewelry (rings, bracelets, earrings) in cold weather. In places of contact with them, the skin cools down much faster;
- Do not go outside immediately after a shower and with a wet head. Wet skin increases heat dissipation;
- Feeling the first signs of hypothermia, go into a warm room and warm up;
- When returning home after a walk in cold weather, check exposed parts of the body (hands, face, nose and earlobes) for frostbite and take a warm shower.
Pay special attention to the prevention of hypothermia in children and the elderly. In children, thermoregulation is not yet fully formed, and in old age it can be impaired due to chronic diseases.
Popular questions and answers
Is it possible to get sick after a cold shower or ice cream and answers other popular questions general practitioner Mikhail Lystsov.
What to do with hypothermia so as not to get sick?
Can you get sick from ice cream?
Can you get sick from a cold shower?
Is it possible to get sick from a fan at home in the heat?
Sources:
- Охлаждение организма. Сидоренко В. И., Ширинский П. П. Большая медицинская энциклопедия в 30 т. М., 1982. — Т. 18. https://xn--90aw5c.xn--c1avg/index.php/%D0%9E%D0%A5%D0%9B%D0%90%D0%96%D0%94%D0%95%D0%9D%D0%98%D0%95_%D0%9E%D0%A0%D0%93%D0%90%D0%9D%D0%98%D0%97%D0%9C%D0%90
- The method of intensive therapy of general hypothermia. Tsarev A.V. Dnipro, 2017. https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/sposob-intensivnoy-terapii-obschego-pereohlazhdeniya/viewer