Contents
The bluish mushroom frightens inexperienced mushroom pickers, who consider it poisonous. But experienced lovers of quiet hunting are always happy to meet this mushroom in the forest. In value, it is only slightly inferior to its “relatives”.
Description of the blue mushroom
Belongs to the Syroezhkov family of the Mlechnikov family. The Latin name is Lactarius repraesentaneus. Other names for the blue mushroom:
- golden yellow lilac;
- purple;
- yellow bluish;
- lilac;
- canine;
- spruce mushroom;
- milky representative.
The epithet “dog” breast was awarded, most likely, for the “increased shaggyness” of young fruiting bodies.
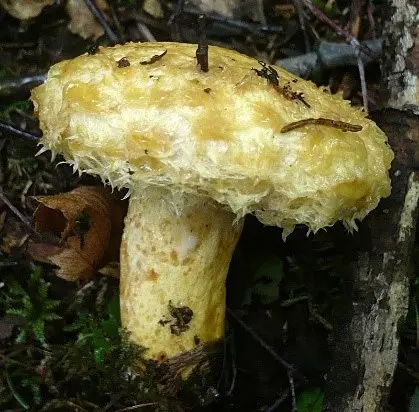

The flesh of the dog mushroom is yellowish in color, dense, slightly bitter in taste. The smell is “usual” mushroom. At the break, white milky juice is abundantly released, which quickly turns blue upon contact with air.
The color varies from light yellow to orange-yellow. At an older age, it can be with a brown tint.
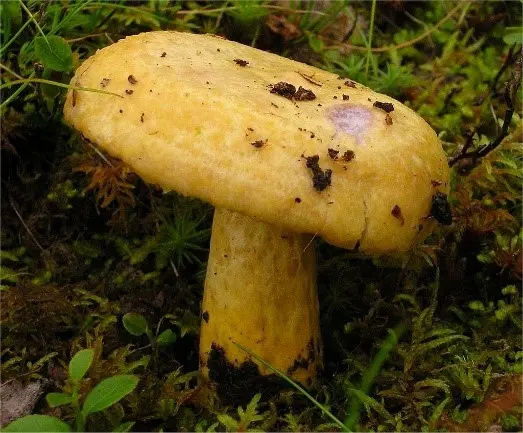

Cap Description
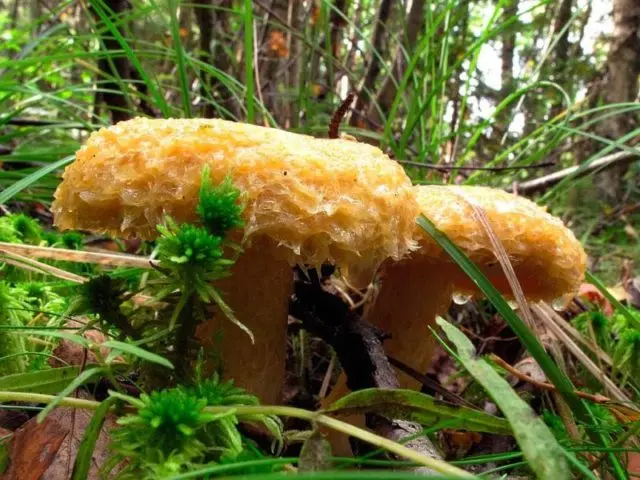
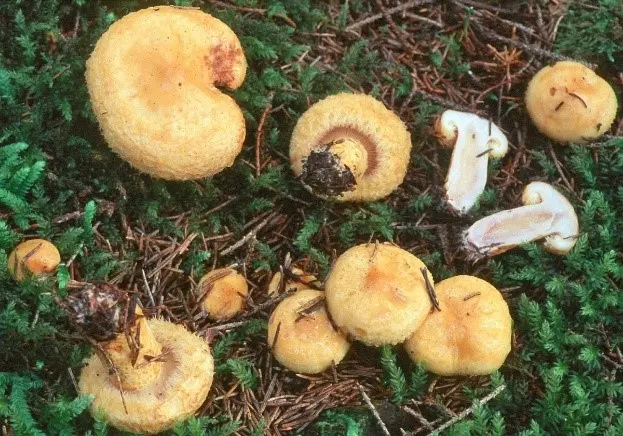
The cap diameter is from 6 to 14 cm. It is convex at a young age, then straightens and becomes funnel-shaped in a mature mushroom. The edges are wrapped inside, pubescent. In youth, the hat is “shaggy” over the entire surface. Later, well-developed “wool” remains only at the edges. Yellow color. The skin is dry. In wet weather, sticky and slimy. There may be barely noticeable concentric rings on the surface of the cap.

Hymenophore – thin narrow plates of light yellow color with a slight purple tint. The lower ends of the plates “go” on the leg. They turn blue at the site of injury.
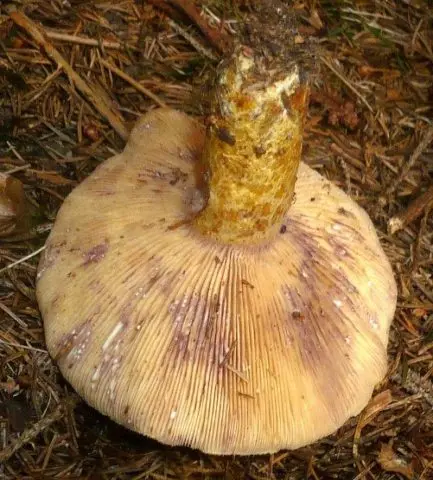

Description of the leg
Length 5-12 cm. Diameter 1-3 cm is the same along the entire length. A variant is possible when the stem expands downwards. The thickness of the stem is equal along the entire length or may increase slightly downward. Located in the center of the hat.
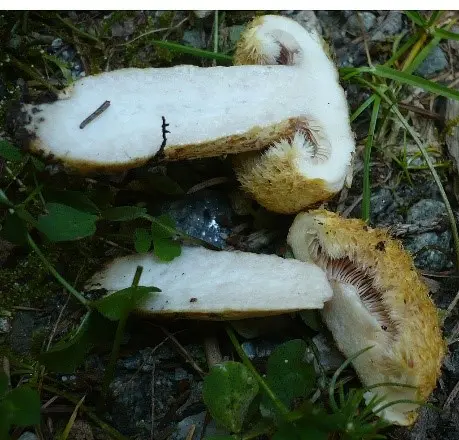

In young mushrooms, the flesh of the stem is firm, but fragile. With age, the leg becomes hollow, and its flesh is loose. The surface is sticky, with depressions. Color pale yellow to orange yellow. With age, the stem becomes lighter than the cap.

Where and how does the blue mushroom grow
In English, the representative milkman is also called:
- northern bearded;
- milk cap;
- northern milk cap.
English names to some extent indicate the distribution area of the blue milk mushroom. The southern border of the range of the representative milkweed runs along the latitude of the Vologda Oblast. The fungus is widespread in Eurasia, up to the Arctic zone: it is found in Greenland and Taimyr. It is common in North America.
It grows in deciduous and mixed forests, as it is a symbiont of birch, willow and spruce. Prefers calcium-poor soil. Found in groups or singly in damp places.
Fruiting season in September.

Is the mushroom edible or not?
The blue mushroom almost fully justifies the name of the family to which it belongs: Russula. No, you can’t eat it right in the forest. The milky juice is too bitter. But after soaking, raw mushrooms are simply salted without heat treatment. Many mushroom pickers even believe that these mushrooms cannot be boiled, since after heat treatment all taste is lost. But it all depends on personal preference. Nothing prevents the use of milk mushrooms in boiled and fried form.
No deaths have been registered. Only abdominal pain was noted. At the same time, substances that cause “poisoning” have not been found so far. With a high degree of probability, the reason is the improper preparation of the dog breast: it was not soaked beforehand. Irritation in the stomach, apparently, causes unremoved milky juice.

How blue milk mushrooms are prepared
The main thing in the preparation of dog mushrooms is long soaking. Depending on preferences, this procedure can last from 3 to 7 days. Water must be changed at least once a day. The advantage of blue mushrooms is that they do not begin to ferment even with such a long stay in the water. After removing the milky juice, mushrooms can be used based on personal preference.
Salted or pickled blue milk mushrooms for making snacks. Everyone has their own secrets here, but you can usually find a couple of recipes.
Pickling
One of the simple recipes:
- 2 kg of mushrooms;
- 3 Art. l salts;
- allspice in peas;
- Bay leaf.
Spices are added to taste, but taking into account the fact that milk mushrooms are bitter on their own. Bay leaf also gives bitterness and it is not necessary to be zealous with it.
Bay leaves are pre-crushed. Soaked mushrooms are laid out in layers in a container for pickling and sprinkled with salt and spices. The load is placed on top and the container is placed in a cool place. After a week, the finished product can be decomposed into jars and stored in the refrigerator.
Pickling
For pickling, peeled, washed milk mushrooms should be boiled for 15 minutes in boiling water. The foam that forms on the surface is removed.
For pickling 2 kg of mushrooms you will need:
- 2 tbsp. l. salt and sugar;
- 45 ml of table vinegar;
- 8 things. bay leaves;
- allspice peas to taste;
- several cloves of garlic;
- currant leaves;
- 2 L of water.
Add all ingredients except vinegar to a pot of water and boil for 10 minutes. Put the boiled mushrooms in a 3-liter jar, pour boiling solution and add vinegar. Remove to refrigerator. The product will be ready in a month.
Freezing
Before freezing, milk mushrooms are boiled to remove bitterness. Cook for an average of 15 minutes. If the mushrooms are large, they boil longer. The water is drained and the semi-finished products are allowed to cool. After that, you can put the mushrooms in the freezer.
To freeze a ready-to-eat product, mushrooms are fried with spices and salt. In the future, the resulting semi-finished product is used in any mushroom dish.

Twins and their differences
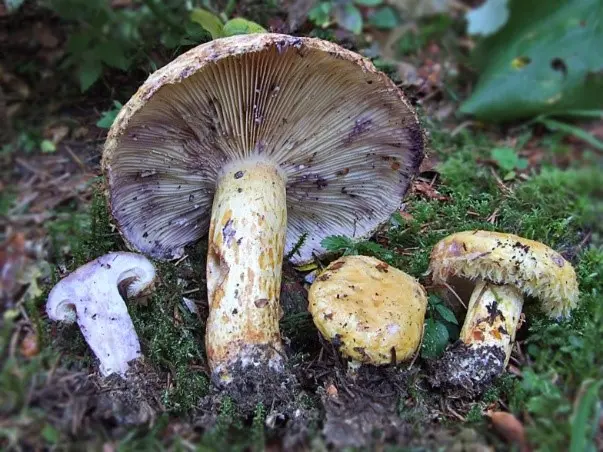
Opinions about the presence of twins in the blue milk mushroom differ. According to some sources, it is too original and cannot be confused. According to others, there is at least 1 double. In the photo, blue and yellow milk mushrooms are really very similar. But when collecting in the forest, it is difficult to confuse them, since the latter turns yellow at the break, and does not turn blue.
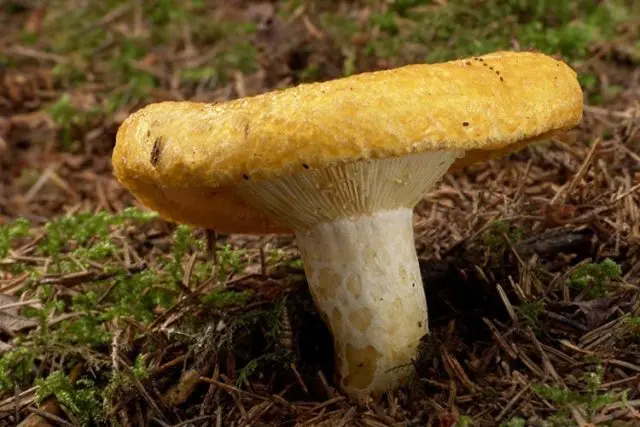

Желтый грузд (Lactarius scrobiculatus)
Synonyms:
- scraper;
- yellow loader;
- yellow wave.
Color variations from light brown to yellow. There may be barely noticeable concentric circles on the hat.
The yellow load is very large. With a stem height the same as that of the blue one, the yellow hat can grow up to 25 cm. At a young age, it is convex, later straightens and becomes funnel-shaped in a mature scraper. The skin may be smooth or woolly. In the second version, the yellow breast really becomes like a blue one. In rainy weather, the cap is slimy, in dry weather it is sticky. Milky juice appears at the break, which becomes gray-yellow in air.
Grows on limestone soils. In this it differs from the blue one, which prefers calcium-poor soil. It is found next to birch and spruce, with which the yellow pod forms mycorrhiza. Found in small groups. Distributed in the north of Eurasia. In Eastern European countries and Our Country, yellow wave is considered valuable and belongs to the first category. In terms of value, the scraper is almost on a par with the white mushroom. Some mushroom pickers even prefer yellow to white.
Collection season July-October.

Yellow, in turn, is credited with resemblance to a white mushroom. It would be logical to assume that blue and white are very similar. But no. It’s all about color variation. Yellow can be almost the same color as white, but blue is not.
Conclusion
The bluing milk mushroom is loved by experienced mushroom pickers of the northern regions. The only bad thing is that it is rare and it is difficult to collect enough for winter harvesting. But you can make a mushroom platter.









