Contents

Blood typing may be required before an upcoming operation, during pregnancy, when donating blood, and in other situations. If we consider the term “blood type” from a medical point of view, then we will talk about determining the indicator in the AB0 erythrocyte system, which Landsteiner discovered in 1901.
Scientist Karl Landsteiner received the Nobel Prize for his great discovery. However, his scientific research did not end there. Throughout the rest of his life, he was looking for other antigens that are on the surface of red blood cells. In 1940, another great discovery was made, which “gave” the world the Rhesus system. Prior to this event in 1927, MNs and Pp proteins were found in the erythrocyte system. All these discoveries can be considered breakthrough, since they allowed the transfusion of blood from one person to another without fear that it could kill him. Since those times, the process of blood transfusion has become safer every year and continues to improve today.
Blood type – what is it?

The blood type implies an individual antigenic set of proteins that a person receives from birth. It determines the peculiarity of a particular individual – a person, an animal, and even microorganisms. Thus, these antigens (isoantigens, alloantigens) make it possible to isolate a particular individual within a particular species. Blood antigens do not have common features with antigens that appear in the body against the background of the development of cancerous tumors, as well as with proteins that cause infectious diseases that enter the body from the external environment.
Karl Landsteiner began to study the properties of these antigens during his lifetime. He mixed the red blood cells of some people with the serum of other people. In the course of such experiments, the scientist found that sometimes red blood cells begin to stick together with each other (this process is called agglutination), and sometimes their color remains uniform.
Karl Landsteiner managed to identify 3 blood groups – A, B and C. The fourth blood group – AB was discovered by another scientist Jan Jansky. In America and England, the first standard sera, which contained specific antibodies that determine blood groups, were obtained as early as 1915. In Russia, the blood type began to be determined in 1919. At first, the calculation was carried out according to the AB0 system, and in 1921 digital designations were introduced into practice. In the future, they began to use the nomenclature of letters and numbers. In this case, antibodies were denoted by the Greek letters α and β, and antigens by the Latin letters A and B.
Antigens on human erythrocytes
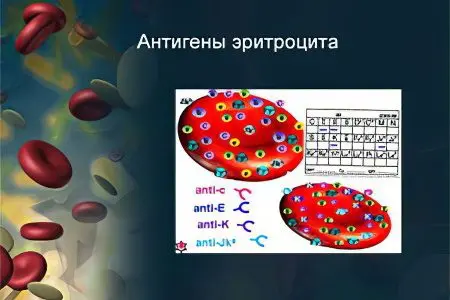
Modern science dealing with immunohematology has identified about 250 antigens that are on the surface of red blood cells.
The basic system of antigens contained on erythrocytes includes:
AB0, which includes varieties of antigens A, B, H.
MNSs (M, N, S, s, U).
Rhesus, which is determined by the Rh value with variations D, C, E, d, c, e.
Lutheran, which is referred to as Lutheran with variations of Luaand Lub.
Kell, which is designated as K, k (Kell).
Lewis, which is referred to as Lewis, with variations of Lea, Theb. This system of antigens was actively used in forensic medicine in past years, until that moment in time genetic fingerprinting was not disclosed.
Duffy with Duffy designation and Fy variationsa, Myb.
Kidd with Kidd designation and Jk variationsa, Jkb.
Diego with Diego designation and Di variationsa, Sunb.
Li with the designation I, i.
Xg with Xg varianta.
These sets of antigens are used when it is necessary to select blood for transfusion, as well as in obstetrics. Many systems, with the exception of AB0 and Rh, can be quite difficult and very expensive to detect. Therefore, the term “blood group” most often implies the basic system of AB0 antigens located on the surface of red blood cells with blood groups 1, 2, 3, 4.
Blood group and Rh factor
Possible options for blood type and Rh factor
O- (first negative or 1-) | A- (second negative or 2-) | B- (third negative or 3-) | AB- (fourth negative or 4-) |
O+ (first positive or 1+) | A+ (second positive or 2+) | B+ (third positive or 3+) | AB+ (fourth positive or 4+) |
After the 50s of the 20th century, scientists began to gradually discover other antigens, including:
Platelet antigens, which for the most part copy erythrocyte antigens, but they are not so pronounced. Therefore, determining the blood group on platelets is a difficult task.
Nuclear cell antigens. First of all, we are talking about lymphocytes. This discovery made it possible to move forward in transplantation of internal organs and other tissues. Also, the discovery of antigens of nuclear cells has expanded the possibilities of determining various genetic diseases.
Plasma protein antigens, of which more than 10 have been isolated so far.
All these discoveries made it possible to determine the blood type with high accuracy, and also allow you to fight a number of diseases. Therefore, the process of blood transfusion today is a safe procedure, and organ and tissue transplantation operations are gaining momentum and becoming more accessible.
Four blood types, possible set of antigens and antibodies
A person’s blood type depends on the A and B antigens (agglutinogens). These antigens are composed of proteins and polysaccharides. They are tightly bound to the erythrocyte stroma, but do not depend on hemoglobin.
Antigens A and B can be found in platelets and leukocytes, as well as in various tissues and body fluids. They are present in amniotic fluid, in saliva and in human tears. However, their concentration there is extremely low.
So, on the erythrocyte stroma, these antigens are present, which form a pair. Possible combinations: AB, BB, AA, A0, B0. If they are not found, then the pair is called 00.
In the blood plasma, there are globulin fractions – agglutinins α and β. They are compatible with antigen A with ?, B with ?. Such combinations are called natural antibodies.
In a person with the first blood type, in which there are no antigens, both antibodies will be present – both ? and ?. A person with the fourth blood group has no antibodies. If they enter such blood, then α will stick to the B antigen, and β will stick to the A antigen.
Therefore, a person, depending on his blood type, will have different antigens, these sets are presented in the table.
Blood type | Possible antigens and antibodies |
First | 00 antigens, α and β antibodies |
The second | Antigens AA or A0, antibodies only β |
The third | BB or B0 antigens, antibodies only α |
The fourth | Antigens only A and B, no antibodies |
This is the basic blood type classification system, but there are people on Earth whose blood does not fit into any of the proposed sets. Such blood is called Bombay, since it was first discovered in a resident of Bombay back in 1952. In the blood of such people, antigens A and B are absent. However, in addition to antibodies α and β, they secrete anti-H antibodies. It is they who do not allow antigens A and B to gain a foothold on erythrocytes, but instead they have substance H on erythrocytes. People with Bombay blood and some other varieties of blood groups live all over the world. Such a rare blood type is a kind of disadvantage, because if it is necessary to transfuse a donor, you will have to wait a very long time.
Blood group of the child and parents: how to calculate?
The AB0 blood group is inherited by a person from his mother and father. Moreover, one antigen passes from one parent, and the other from the other. Therefore, half of the phenotype can be the mother and half the father. The combination of these two traits can be created in such a way that the child’s blood type does not match the blood type of either parent.
Sometimes men who learn about the mismatch of the blood type of his child with his blood type and the mother’s blood type begin to suspect a woman of treason. However, such suspicions are born due to absolute ignorance of the laws of genetics. To avoid unnecessary suspicion and even parting with your spouse, you need to contact a specialist or independently find information that will allow you to put everything in its place.
There are several possible options for what blood type a child will have, depending on the blood type of his parents. All of them are presented in the table.
Option | Parents’ blood type | The child’s blood group |
1 | If mom’s blood type is first 00 and dad’s blood type is first 00 | The child has only the first blood type 0. The genes that produce antigens of the first group are recessive, they can only exist in the homozygous state (provided that another dominant gene is absent) |
2 | If the mother has the second blood type A and the father has the second blood type A, then several options are possible. There is a possibility of a combination of two identical traits and dominant AA, and one or both parents may have a second blood group, but in combination with A0 (recessive variant in combination with a dominant warrant). In this case, the child’s blood type can be not only the second, but also the first. | Possible options: |
One parent is AA (Blood Type II) and the other parent is AA (Blood Type II) | Child AA (second blood group) | |
One parent is AA (second blood type), the second parent is A0 (second blood type) | Child AA (second blood group) | |
One parent is A0 (second blood type) and the other parent is A0 (second blood type) | The child is either AA (second blood type), or A0 (second blood type), or 00 (first blood type). The third and fourth blood groups in a child cannot be. | |
3 | Parents have a third blood group with a set of genes AA + AA or AA + A0 | The child will either have a third blood type or a first blood type. At the same time, he cannot have a second blood group or a fourth blood group. |
4 | One parent has the first blood type, and the other parent has the second blood type. There may be two options. | Possible options: |
One parent has A0 (second blood type), the second parent has 00 (first blood type) | A child has A0 (second blood group) and 00 (first blood group), he cannot have the third and fourth blood groups. | |
| One parent has AA (blood type II), the other parent has 00 (blood type I) | The child has A0 (second blood group) |
5 | If one of the parents has the first blood type, and the other parent has the third blood type, then the development of events can occur according to the option described above, but with the second group replaced by the third. | A child has a third blood group or a first blood group, but he cannot have a second and fourth blood type. |
6 | Parents have blood type A (second group) and B (third group). There may be several options for the development of events. In this case, the fourth blood group and the child can be in the case when both antigens are equal in the phenotype and equally manifest themselves in the new blood (A + B = AB). | Child’s blood group options: |
AA (second group) + BB (third group) | AB (fourth group) | |
A0 (second group) + B0 (third group) | AB (fourth) or 00 (first) or A0 (second) or B0 (third) | |
A0 (second group) + BB (third group) | AB (fourth) or B0 (third) | |
B0 (third group) + AA (second group) | AB (fourth) or A0 (second) | |
7 | If one parent has a second blood type, and the other parent has a fourth blood type. | Possible options. The child cannot have the first blood type. |
AA (second group) + AB (fourth group) | AA (second) or AB (third) | |
A0 (second blood type) and AB (fourth blood type) | AA (second), A0 (second), B0 (third), AB (fourth). | |
8 | If one parent has a third blood type, and the other parent has a fourth blood type. |
Possible options |
BB (third group) + AB (fourth) | BB (third) or AB (fourth) | |
B0 (third) + AB (fourth) | A0 (second) or BB (third) or B0 (third) or AB (fourth) | |
9 | If one parent has the first blood type, and the other parent has the fourth blood type, then the child will have either the second blood type or the third blood type, but he will not have the first and fourth blood types. |
Possible options |
A + 0 | A0 (second group) | |
B + 0 | B0 (third blood type) |
Based on the table, your child can have any blood type. With confidence about the blood type of the child, you can talk if the mother and father had the first blood group. Based on this rule, a child with the second and third blood groups cannot appear. According to another rule, if one parent has the fourth blood type, and the other has the first blood type. In this case, the child will either have a second or third, the phenotype of the blood group of the parents will be lost.
Table: the blood type of the child based on the blood types of the parents:

Blood group compatibility
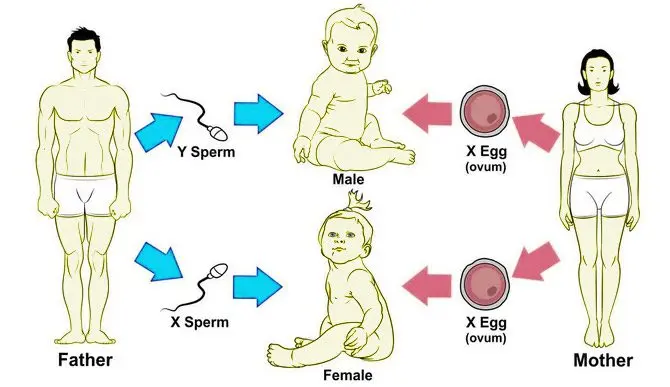
In ancient times, parents who wanted to conceive a boy placed reins under their pillows. Now some parents are trying to “calculate” the sex of the child, dividing the age of the man by 4, and the age of the mother by 3. Whose remainder is greater, this gender will be the child. Medicine considers all these methods of determining the sex of a baby to be unfounded from a scientific point of view, but it does not prohibit practicing them.
The blood type does not allow determining the sex of the child, but it makes it possible to establish the group compatibility of the parents. In some cases, anti-A and anti-B antibodies can form in the mother’s body, which can disrupt the normal course of pregnancy or interfere with breastfeeding.
It is worth noting that the Rh factor rarely causes abortion, but, nevertheless, certain risks exist. Also, if the blood type of the mother and father are incompatible, the child may be born with hemolytic disease. It leads to serious health complications, ranging from the development of deafness to death.
Pregnancy and blood type
After a woman is registered for pregnancy, she must be sent to the laboratory in order to determine the Rh factor and blood type.
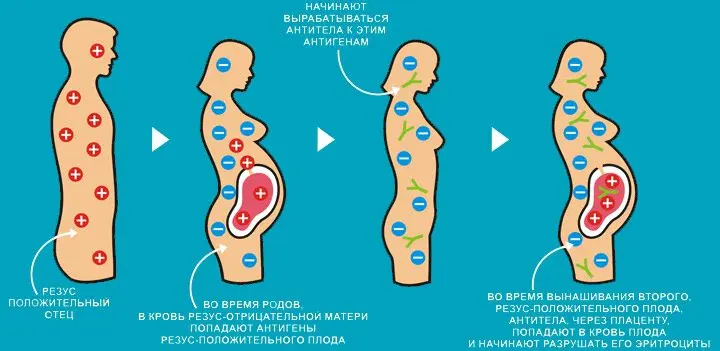
If the pregnant woman is Rh negative and the man is also Rh negative, then you should not worry about blood incompatibility.
Provided that the Rh factor of a woman is negative, but she is pregnant for the first time, and before that there were no miscarriages and abortions, then she also may not worry. The Rh system does not have natural antibodies. The body will only recognize the “foreign” (fetus), but will not give a negative reaction to it. Immunization will occur during childbirth. So that the body does not have time to remember the presence of foreign antigens, an anti-Rhesus serum will be introduced to the woman on the first day after the birth of the child, which will save all subsequent pregnancies.
However, if immunization is strongly expressed, then even despite serious and prolonged treatment, the pregnancy will end in miscarriages. The body of women with a negative blood group once “remembers” a foreign protein and later, after it appears inside the body, begins to direct all the power of its immune system to it. Therefore, a fetus with a positive Rh factor will always be rejected.
In addition to the Rh factor, other blood systems, such as the Kell and the HLA system, can influence the compatibility of the mother’s body and the fetus’s body. Each of them can present an “unpleasant surprise.” A woman entering into an intimate relationship with a man, even before the onset of pregnancy, gives a reaction to his antigens. Her body begins to produce antibodies against him. This process in medicine is called a sensitization reaction. The degree of its severity depends on how many immunoglobulins and antigen-antibody complexes are formed in the woman’s body. The more of them, the lower the chance of conception. Such incompatibility requires long and laborious treatment, which often ends in failure.
A negative reaction of the woman’s body to the fetus is also possible if the mother and child do not have the same blood type. This is observed when the placenta is damaged, when the mother’s red blood cells enter the baby’s blood.
Video: pregnancy, blood type and Rh conflict:









