Contents
Bloody discharge in cows can occur at different times. After calving, a cow does not always stop bleeding immediately. At other times, bleeding may be an indicator of disease or other problems.
Why is the cow bleeding?
A cow can bleed for a variety of reasons. In the pasture, the animal may swallow a hard object that will scratch the intestines when it comes out. Along with the feces, blood will be released.
The mucous membrane in the nose of a cow is very sensitive to shock, infection, and mechanical damage. There can be many reasons. Before treatment, you need to accurately determine the cause of nosebleeds:
- getting objects into the nostrils;
- use of medical instruments;
- the appearance of tumors;
- contagious infections;
- non-communicable diseases;
- metabolic changes;
- lung and stomach diseases;
- reproduction of parasites.
Blood from the vagina. It does not always accompany diseases and is often a completely physiological phenomenon.
Some bloody secretions are dangerous, while others are quite harmless in different groups of cows.
Blood discharge from a pregnant cow
Early detection of pregnancy is important for livestock production. Reducing the service period reduces the costs of dairy farms. At the moment, there are several types of determining pregnancy in an animal – ultrasound diagnostics, rectal and hormonal methods. In Our Country, it is the rectal method that has become widespread.
Its advantages are the definition of pregnancy and functional disorders in infertility. Cons – laboriousness, the need for the presence of an experienced veterinarian, the pregnancy period is from 2 to 3 months.
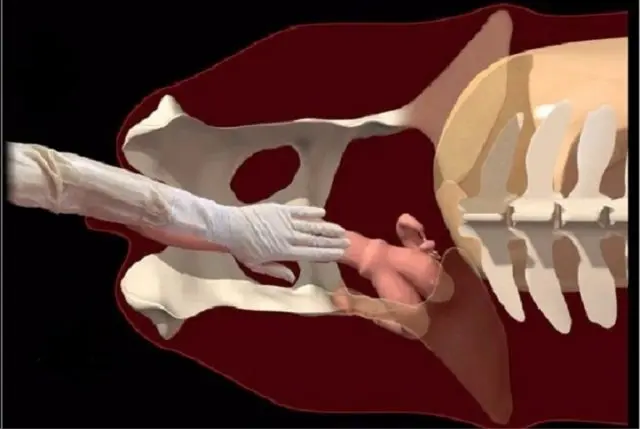
Bleeding in a cow during pregnancy may be the result of a failed insemination. Possible manifestations of vaginitis (endometritis). Secrets in these diseases of the uterus can be purulent and without exudate. The onset of the disease is characterized by clear sputum streaked with blood.
Blood from the vagina before calving may indicate the onset of an abortion in the early and middle stages. Most often it occurs 2-3 weeks after insemination. This may be the result of placental abruption and fetal death. Sometimes, even after bleeding, pregnancy persists until calving, but the development of the fetus occurs with complications. In the later stages of calving, a miscarriage is possible.
Often the blood comes after insemination. It’s not scary. If the bleeding lasts no more than one day, this may indicate a slight damage to the vessels caused by the procedure. There are several reasons for this:
- improper diet;
- chronic untreated inflammation after previous calving.
In case of prolonged bleeding, it is worth calling a veterinarian. Ovulation can cause some short-term bleeding. With an increase in the uterus, small vessels are torn already in the first day. This phenomenon indicates readiness for mating.
Prenatal outflow of mucus with blood indicates damage to blood vessels during the movement of the calf through the birth canal. This pathology is treated after calving. After checking the uterus, washing with furatsilin or potassium permanganate is carried out. To fight bacteria, vaginal or rectal suppositories with an antibiotic are prescribed.
If a pregnant cow bleeds, and vaginal secretions are brown before the birth of a calf, this indicates severe internal bleeding due to extensive damage to the birth canal. Homogeneous discharge indicates vaginal bleeding. The appearance of blood clots means the presence of uterine bleeding – it is life-threatening for the cow. In this case, the fetus and placenta after calving are pulled out manually, and the cow is injected with saline with glucose.
The incorrect position of the fetus with the hooves up can also lead to uterine bleeding with brown discharge.
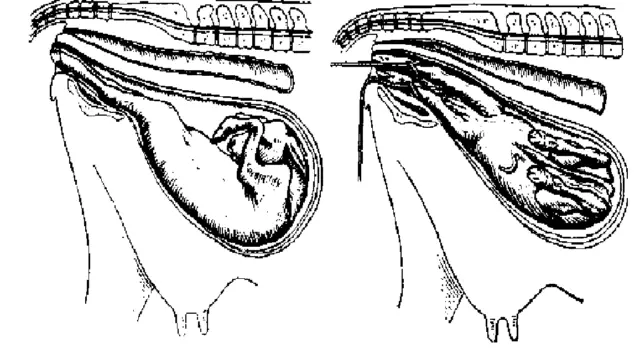
The hotel requires obstetrics and turning the calf by hand. If this is not possible, surgical assistance should be sought.
Bloody discharge from a cow after calving
Basically, blood from the vagina is associated with calving. The incidence of endometritis becomes the basis of inflammation of the walls of the uterus. The vagina secretes mucus from day 4 with blood streaks. After some time, the amount of secreted mucus increases. There is more blood in it. The secrets themselves change color to a red-brown hue. The animal’s temperature rises with a decrease in appetite and loss of strength.
Diagnosis of the disease highlights the swelling of the uterus with blood fluid at the bottom. Acute endometritis can turn into a chronic disease without timely treatment.
The second most important reason is the absence of the placenta after calving. May be complete or incomplete. This causes severe inflammation in the animal. It is necessary to help the cow and pull out the placenta manually no later than in a day. The delayed placenta may begin to rot and decompose. In this case, the animal may die.
The next reason may be the release of lochia containing mucus, blood and particles of the uterus. At the very beginning, they come out in the form of blood clots, then the amount of mucus increases. The absence of lochia within 4-5 days after calving indicates endometritis.
Purulent lochia with an unpleasant putrid odor is a sign of purulent-catarrhal endometritis. The cow suffers from increasing secretions, the amount of milk decreases. The disease is treated by administering the hormone oxytocin and the drug Rifapol.
Discharge of blood with dirty yellow patches is a sign of fibrous endometritis. The appearance of flakes in the discharge serves as an indicator of the urgency of treatment. A neglected disease threatens to infect the blood.
Heavy calving can lead to necrotizing metritis.

Necrosis goes to the muscles. Ulcers appear. Crumbs are formed along with the blood. The cow is weak. If you miss the treatment of the disease, then paralysis develops.
Running cases turn into metritis – a deadly condition. In the absence of urgent treatment, the cow dies after a few days.
What to do if a cow is bleeding
When blood appears, it is necessary to determine the source and danger to the animal. The cow has a multiple placenta, which reduces the risk of miscarriage. With small bleeding, blood accumulates between the placentas, and then resolves.
Help with uterine bleeding should be provided immediately after childbirth. During the removal of the placenta, the problem is stopped immediately, or after the end of this procedure.
To reduce blood loss from the uterus, drugs are administered that cause its contraction. With significant bleeding, drugs are administered intravenously to support the work of the heart.
Prevention of blood loss from the uterus is a careful attitude to the birth canal of the animal and a decrease in the trauma of surgical interventions.
Pregnant cows need to be prepared for calving. To do this, regularly examine them, give good nutrition. Periodic examinations to prevent vaginitis and endometritis will help reduce the number of complications after calving. Timely piercing of the animal with vitamin complexes will help reduce the risk of uterine inflammation. They will increase the body’s resistance to infections by increasing immunity.
Conclusion
If a cow has blood after calving, this does not mean that the animal is sick. A decrease in the intensity of bleeding indicates the normal functioning of the body or the frivolity of the disease. With an increase in spotting or an increase in the level of red fibers in the mucus, you should pay attention to the onset of inflammation. The cow must be treated immediately.









