
The salivary glands are located under the mucous membrane of the oral cavity. The function of any salivary gland is to produce saliva. The secret is secreted through the ducts into the oral cavity, which facilitates the process of digestion. The enzyme amylase present in saliva promotes the breakdown of starch and conversion to maltose.
There are two groups of salivary glands:
large – in the ears (parotid), under the jaw (submandibular) and under the tongue (sublingual glands). They are paired, three on each side of the head and neck. Parotid – the largest salivary gland, located in front and below the auricle. The submandibular glands occupy the upper part of the neck.
small glands – located on the lips, in the oral cavity and in the pharynx. There are about 600 of them, they mainly secrete mucus, which performs a protective and moisturizing function.
Congestion in the salivary glands, or in other words, blocking the normal flow of saliva provokes edema, which is unstable, occurs during meals, and is accompanied by painful sensations. Treatment of saliva stasis may not be necessary, often this pathology goes away on its own, but in some cases, surgical intervention is indispensable.
Blockage of the salivary glands can form in the large salivary glands and their ducts, in the submandibular glands, in the parotid. In the parotid glands, it is much less common, since their ducts are wider. The sublingual glands are rarely blocked. Obstructive signs are manifested as a result of the appearance of mucous plugs in the ducts that excrete saliva. In some cases, namely with stenosis (narrowing of the canal opening), it occurs as a secondary symptom of a chronic injury.
All factors that contribute to a decrease in saliva production or a change in its consistency (thickening) lead to the process of stone formation. So one of the reasons for the appearance of stones in the salivary glands are minerals contained in saliva. Basically, calcium is found in their composition. Also among the causes are dehydration, malnutrition.
It is not uncommon to take certain medications of an antihistamine and psychotropic nature and drugs intended to normalize blood pressure and urinary function. Damage to the salivary glands is also one of the reasons that increases the risk of blockage. While the process is only developing, there are no symptoms that cause concern to the patient.
But, as soon as this leads to blockage of the duct, the outflow of saliva is disturbed, and pain appears, swelling of the gland is observed. The pain is spasmodic in nature, with the progression of the process, the condition can worsen significantly and infection joins. X-ray is considered an effective method for diagnosing blockage of the glands; it is performed in several projections, including inside the oral cavity. Sialography or X-ray examination using a contrast agent is often performed.
Treatment of blocked salivary glands
The treatment is to stimulate salivation by sucking on a lemon or sour fruit. If the blockage occurs due to the formation of a stone, the dentist manually pushes the seal out of the duct. Larger stones require surgical intervention. Today, doctors use sialoscopy, a new method of stone removal developed in Europe.
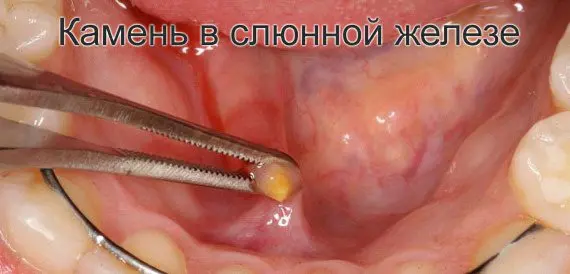
Irreversible processes in advanced cases are dangerous by surgical removal of the entire gland. The attached infection is eliminated with antibiotics.
Most salivary blockages go away on their own over time, but conservative treatment, such as gland massage, can help get rid of such a pathology in the first place. It is possible to improve the function of the glands through the use of medicinal substances that stimulate the production of saliva, they are prescribed by a doctor.
Most often, blockage affects the submandibular gland, rarely the parotid glands, and almost never the sublingual glands.
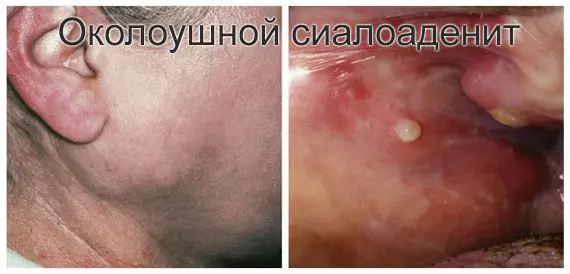
The pain is so severe that an NSAID may be needed. In people prone to blockage of the salivary glands, relapses are frequent. So far, there is no evidence-based method for preventing blockage of the salivary ducts. But according to the observations of doctors, this occurs in those who live in areas with hard tap water, in those suffering from urolithiasis and from the formation of stones in the gallbladder.
There are no special rules for the prevention of blockage, it all depends on the individual characteristics of each person. Be sure to avoid the influence of various traumatic factors. And it is important to remember the rules of oral hygiene. They need to be taught to children from an early age.










шүлсний булчирхайг гэрээр яаж эмчлэх вэ