Contents
Blockage of the esophagus in a cow is a serious disease that is quite common in cattle. In the event of such a problem with the health of the animal, urgent medical measures are required. The outcome of the disease will depend on the quality and speed of the assistance provided.
What is an esophageal blockage
A blockage of the esophagus is a partial or complete blockage of the lumen of the esophagus. Pathology occurs due to the ingress of a foreign body, large food into the digestive organs. Complete blockage is possible due to the rapid consumption of large feed, and partial blockage due to accidental ingestion of foreign objects, often oblong in shape. Blockage of the esophagus can be primary or secondary, arising from muscle paralysis, spasms, paresis, and edema.
Causes of blockage of the esophagus in cattle
The causes of this disease are varied. Most often, it occurs when feeding poorly crushed tubers and root crops, pumpkin, oilcake, corn cobs. It happens that the disease occurs after foreign objects enter the cow’s esophagus. This happens in hungry animals, which greedily grab food without chewing it properly, swallow it quickly. If a cow does not receive a complete mineral supplement, it is common for her to chew and swallow foreign objects.

Much less often, a narrowing of the esophagus can be the cause of blockage of the esophagus. It occurs after various injuries of the mucous membrane and muscle tissue of the esophagus, enlargement of the lymph nodes, which can become inflamed with leukemia, tuberculosis. Paralysis of the esophagus, which occurs with certain infections, such as rabies, inflammation of the brain, bruises, can also cause blockage.
Symptoms of blockage of the esophagus in a cow
Symptoms with complete blockage of the esophagus appear very abruptly. In this case, the animal experiences severe discomfort:
- there is anxiety, fear;
- loss of interest in food
- the cow makes swallowing movements, trying to move the food further;
- chewing gum disappears;
- belching stops;
- the cow shakes its head sharply;
- profuse frothy salivation appears.
Complete blockage of the esophagus leads to gastric arrest, accumulation of gases in the rumen, and constipation. The general condition worsens significantly, other symptoms join. It is difficult for the animal to breathe, coughing, shortness of breath appear, mucous membranes turn pale. The cow is trying to beat her belly with her hoof. If the blockage of the esophagus is partial, then the cow can drink and eat liquid food. On palpation, there is some induration in the region of the jugular groove.
With partial, minor obstruction of the esophagus, the symptoms may not make themselves felt for some time, although the behavior of the cow should alert the owner. The most pronounced symptoms begin to appear when the stomach of the animal stops. At this moment, gases accumulate in the scar, the diaphragm is compressed. If you are late with help, the cow may die from asphyxia earlier than in a day. If tympania is suspected, an emergency puncture of the scar with a special instrument with a trocar should be made.
What is dangerous blockage of the esophagus in a cow
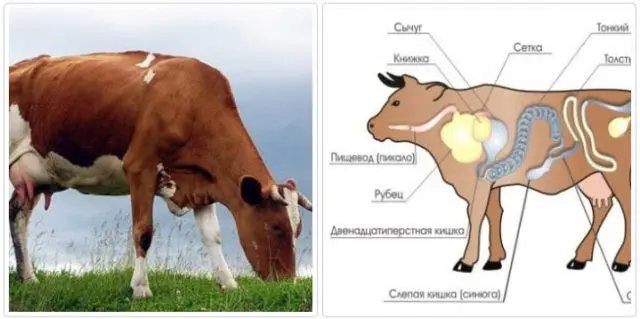
The scar is the pancreas of the digestive tract in cattle, with a capacity of up to 300 liters. This is one of the most important organs in the cow’s digestive system, is involved in many processes of the gastrointestinal tract, produces vitamins and enzymes for the animal’s body.
When tympania occurs (swelling of the scar), this organ stretches, increases in volume. And since it is in close proximity to the thoracic region, the lungs and heart are compressed, blood circulation and metabolic processes in the body are disturbed.
Thus, complete occlusion of the esophagus and not provided or illiterate assistance can lead to cardiac arrest and subsequent death of the animal.
With partial, but long-term blockage of the esophagus, inflammatory processes, tissue necrosis, and rupture of the scar membrane appear.
In especially severe cases, aspiration pneumonia develops – inflammation of the lungs and bronchi, which occurs due to the ingress of foreign objects into the respiratory tract.
Diagnostics for blockage of the esophagus
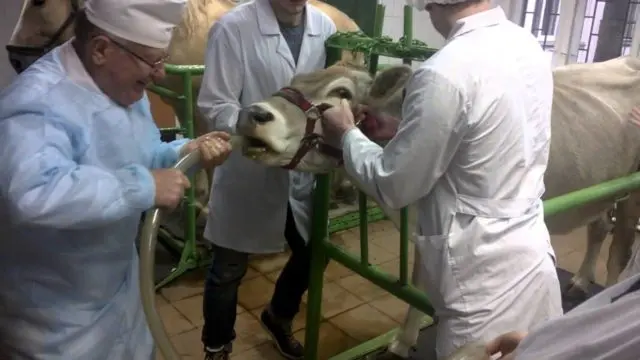
To make a correct diagnosis, the cow is first examined and palpated. Further, if necessary, sounding, x-ray, esophagoscopy can be used. All of these studies are carried out only by a veterinarian.
When examining cattle, the specialist carefully observes the jugular depression, which is somewhat enlarged, whether there is swelling, rupture.
Palpation is performed with the left hand, and the right veterinarian probes the cow’s neck along the jugular groove. With this method of examination, the presence of foreign bodies can be detected.
Before probing, a probe is selected depending on the weight of the cow. The method helps to determine the cause of the ailment and determine the treatment regimen. In addition, probing helps in some cases to significantly reduce gases in the intestinal section.
X-ray is rather an auxiliary research method for the subsequent diagnosis. It is performed with additional diagnostic methods.
Esophagoscopy is the most effective method for studying the digestive tract of a cow. Using it, the veterinarian can view the entire gastrointestinal mucosa and begin treatment. The procedure also has a therapeutic focus, when there is a need to inject any drug directly into the intestines of the animal.
Treatment of blockage of the esophagus in a cow
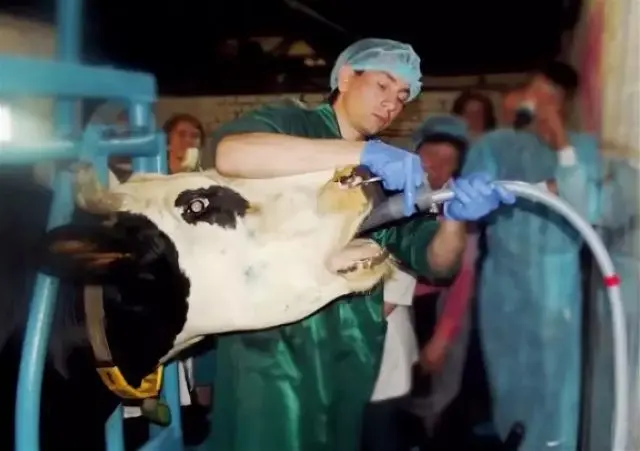
If the esophagus is blocked, she should be helped as soon as possible to prevent asphyxia. Treatment will depend on the form of the disease and the location of the foreign body in the esophagus.
First of all, you need to extract the item. All actions must be carried out in a certain sequence, only with trained assistants. You also need to take care of the precautions and proper fixation of the cow in advance. After that, a wedge is inserted between the molars of the animal. In the process of work, it is important to ensure that it does not fall out. Sometimes a probe is used for these purposes. The hand must be wrapped with a towel from the wrist to the elbow to prevent injury. Further, penetrating the hand into the oral cavity of the cow, try to remove the object.
The following method often helps: hands wrap around the cow’s neck in the area of the jugular groove. They make movements with their hands to the head, causing a gag reflex. As a rule, a foreign object comes out with vomit. Before starting the procedure, 100 ml of vegetable oil is poured into the throat of the cow, and during the procedure it is recommended to lightly pull the animal by the tongue.
If the foreign body is located in the region of the cervical or thoracic part of the esophagus, a 35 mm probe is used. By moving it along the esophagus, the object will be pushed forward. The procedure must be carried out carefully so as not to tear the esophagus. When the scar is swollen (tympania), a puncture is performed.
Traditional methods of treatment
Often folk methods help to start the stomach in cattle.
300-100 g of fresh yeast are diluted in 150 ml of warm water and left for half an hour. At this time, 100 g of sugar is diluted in 200 g of vodka. Diluted yeast is also added there. You should get 1 liter of tincture. It should be poured into the animal’s throat 2 times a day for 2 days.
Sometimes experienced farmers use hellebore tincture, which is diluted in 0,5 liters of boiled water. It is also poured into the animal’s oral cavity.
Various decoctions of herbs stimulate digestion well. For example, chamomile, a decoction of flax seed, yarrow. Prepare as follows: 30 g of raw materials are brewed in 1 liter of boiling water. The broth should be simmered in a water bath for about 30 minutes, then insist a little and carefully strain. Pour the animal warm for several days.
Prevention of blockage of the esophagus in cattle
With a cow’s history of esophageal obstruction, the cow should be protected from recurring problems of this kind.
The owner must carefully monitor what the animals eat. Large, rough food should be crushed to the right degree.
Pastures must be regularly cleared of debris, and cleanliness in the premises where cows are kept is also important. You can not drive the herd along the potato or beet plantations.
When cows are deficient in mineral supplements, they may lick plastered walls, eat earth and sand, and accidentally ingest foreign objects. Therefore, it is important to take care of vitamins and minerals by hanging special briquettes with useful components from the feeders.
Conclusion
Blockage of the esophagus in a cow is a serious disease that can lead to death. Many cattle owners have encountered this problem through their own fault. This disease occurs most often due to neglect of animals. You can avoid such a dangerous problem by competently caring for livestock, carefully monitoring their diet and providing all the necessary nutrients.









