Contents
Leukoplakia of the bladder is accompanied by inflammation of the walls of the organ, but there are no obvious clinical signs of the disease. Therefore, women suffering from this pathology can visit various specialists for a long time, and the diagnosis remains unclear.
Leukoplakia of the bladder – what is it
Leukoplakia of the bladder – this is the degeneration of normal epithelium into a flat one with the formation of areas of keratinization. It will be possible to detect these pathological changes only after a biopsy with a histological examination of the collected tissues.
Leukoplakia can affect various organs in which transitional epithelium is present. Leukoplakia of the bladder and its neck is a serious disease that most often affects women of reproductive age. Pathology is accompanied by intense pain, which negatively affects the patient’s well-being. Painful sensations arise for the reason that the altered tissues are sensitive to the effects of the acid contained in the urine.
Leukoplakia of the bladder has a chronic course.
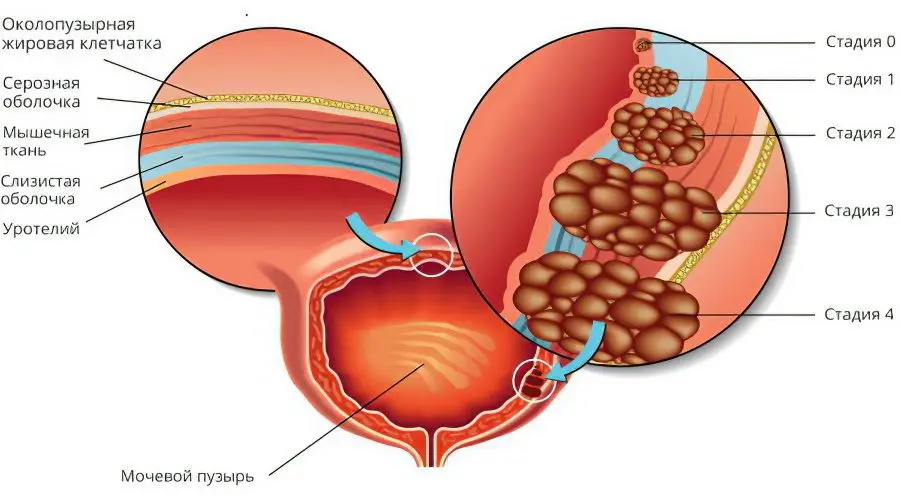
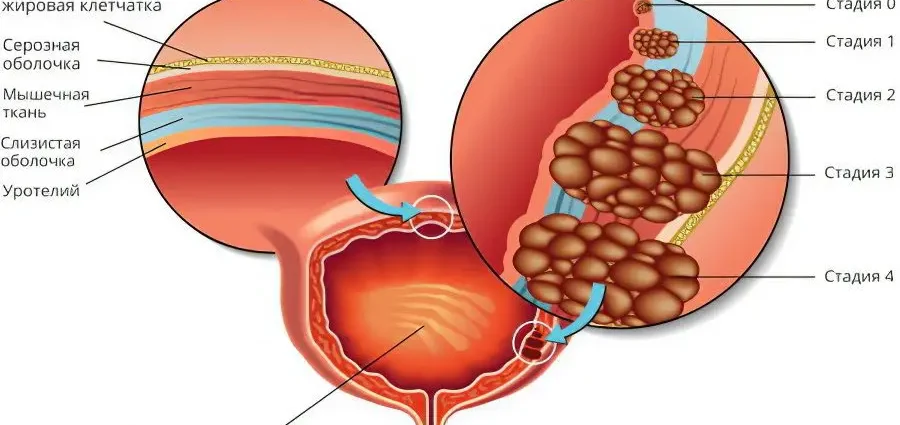
The disease develops in stages:
Squamous transformation. At this stage, the transformation of the single-layer transitional epithelium into a squamous stratified epithelium occurs. The cells themselves do not undergo any changes.
Squamous metaplasia. At this stage, apoptosis is observed, that is, a change in cells in the transformed stratified squamous epithelium.
Formation of plaques and keratinization of cells.
Causes
Scientists cannot accurately name the causes of the development of this pathology. Most experts are of the opinion that leukoplakia is the result of abnormal intrauterine development. This means that the walls of the bladder are formed with certain defects even while the fetus is in the uterus. The proof of this theory is the fact that the pathology is diagnosed in patients with anomalies in the development of the bladder.
In addition, there are risk factors that can increase the likelihood of developing the disease.
These include:
Diseases of the endocrine system. This applies to disorders in the work of the hypothalamus, pituitary gland and ovaries. If the values of estrogens are increased in a woman’s body, then this stimulates the epithelium to metaplasia. Sometimes the disease develops against the background of taking hormonal drugs.
Cystitis and organs adjacent to it. Leukoplakia can be provoked by a chronic form of cystitis, stones in the bladder, past injuries of the organ, as well as the ingress of foreign objects into it.
The presence of a chronic focus of infection in the body, for example, carious teeth or inflamed tonsils.
Long-term effects of stress on the body, reduced immunity.
If the organ is healthy, then its epithelium will produce mucopolysaccharides. They prevent bacteria from sticking to the surface of the bladder. These same substances protect cells from the damaging effects of uric acid.
When the epithelium of an organ transforms into a flat one, its protective properties weaken. This facilitates the penetration of pathogenic flora into the cell walls. The woman develops chronic inflammation. A kind of vicious circle is formed. Cystitis causes leukoplakia, and it, in turn, stimulates the inflammatory process.
Bacteria enter the bladder most often ascending, that is, from the external genitalia.
Therefore, pathogenic microorganisms such as:
Gonococci
Trichomonas.
Chlamydia.
HPV and herpes virus.
Through the blood and lymph, the infection enters the bladder less frequently. In this case, other organs can become a source of pathogenic flora: palatine tonsils, kidneys, intestines, uterus, ovaries. In such a situation, leukoplakia develops due to the penetration of staphylococci, streptococci, Escherichia coli, etc. into the bladder.
Symptoms of leukoplakia of the bladder

There are three forms of bladder leukoplakia:
Flat shape.
Warty form. Areas of tissue keratinization are expressed to a large extent.
erosive form. The epithelium is covered with ulcerative defects.
Flat leukoplakia may not manifest itself for a long time. With a warty and ulcerative form, a woman suffers from severe symptoms of the disease. If the neck of the bladder is damaged, then the patient’s health deteriorates significantly.
The main symptoms of bladder leukoplakia resemble the clinical picture of cystitis:
Pain in the pubic region. It is pulling and radiates to the lower back.
The urge to empty the bladder becomes more frequent.
When the organ is empty, the woman experiences pain and burning.
In the urine, flakes are noticeable, blood can be visualized.
During intimacy, a woman experiences discomfort.
Diagnosis of leukoplakia of the bladder
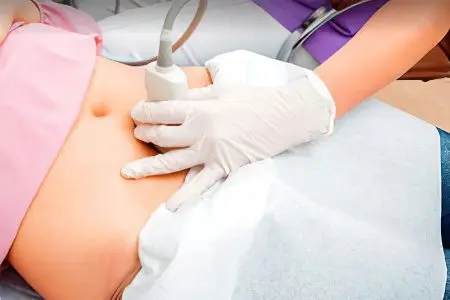
The doctor can make a diagnosis only after a comprehensive examination. A mandatory procedure is the histology of organ tissues.
To confirm the disease, diagnostic measures such as:
Collection of anamnesis. The doctor should clarify how often a woman has seizures, whether she has other diseases of the internal organs. It is important to find out all possible predisposing factors of the disease.
Vaginal examination. It allows you to assess the sexual health of women.
Donation of blood, urine and a smear from the vagina for analysis.
Carrying out a biochemical blood test. It is important to clarify the level of creatinine and urea.
Study by PCR and ELISA. These diagnostic procedures allow you to identify hidden infections.
Collection of urine and smear from the vagina for bacterial culture.
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs and kidneys.
Urodynamic examination (cystometry and urometry). It is carried out in the case when the patient indicates a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder. The study allows you to assess the tone of the organ and its contractility.
Endoscopic examination of the bladder with a biopsy. This study is highly informative. It makes it possible to assess the size of the lesion, the form of the disease, the state of the tissues of the organ. Based on the data obtained, a treatment plan is drawn up. The lesions may appear as flat, whitish areas, as yellow plaques, or as erosions.
The clinical picture of bladder leukoplakia may resemble the symptoms of other diseases, so it is important to make a differential diagnosis with pathologies such as:
Chronic cystitis. The symptoms of this disease are similar to those of leukoplakia. They can be distinguished only after cystoscopy with biopsy. In patients with cystitis, the mucous membrane of the organ is inflamed, but there are no low areas on it.
Bladder cancer. Often this disease does not give any symptoms at all, but as the pathology progresses, clinical signs appear that resemble leukoplakia. During cystoscopy, ulcerative defects and altered areas of the epithelium will be detected on the mucous membrane. However, cells in bladder cancer will have an atypical structure.
Treatment of leukoplakia of the bladder
Treatment can be either conservative or surgical.
Conservative therapy
To cope with the pathology, an integrated approach is needed:
Prescribing antibacterial drugs. Antibiotics are used in long courses that can last up to 3 months. In the course of treatment, drugs are changed, choosing the optimal drug. The course is stopped only after the bacterial culture of urine three times gives negative results. The drugs of choice are: Norfloxacin, Ciprofloxacin and Levofloxacin. They have minimal side effects and are able to effectively eliminate the pathogenic flora in the bladder.
Drugs for the relief of inflammation. If it is severe, corticosteroids such as prednisone may be used.
Immunity Boosting Drugs: Interferon, Lavomax.
Installations. The bladder is irrigated with mucopolysaccharide analogues. They allow you to protect the mucous membrane of the body from the damaging effects of uric acid and microbial flora. Such funds are injected directly into the organ using a catheter. Treatment should be long-term. Its specific timing depends on how affected the walls of the bladder. For installations, Heparin, Hyaluronic acid and Chondroitin sulfate are used.
Physiotherapy treatment. It allows you to speed up recovery, reduce the degree of inflammation, prevent the formation of scars and adhesions. The most effective methods of treatment are: laser therapy, electrophoresis with hormonal preparations, magnetotherapy, microwave therapy.
Surgery
If conservative therapy does not achieve the desired effect, the patient is prepared for surgery.
Indications for its implementation are:
Persistent inflammation, accompanied by a violation of the contractility of the bladder.
Leukoplakia stage 2 or 3, which was confirmed by histological examination.
Severe pain that cannot be relieved by medication.
presence of abnormal cells. This condition threatens with a cancerous tumor of the organ.
Types of surgical intervention:
TUR (transurethral resection of the bladder). During the procedure, the affected areas of the mucous membrane are removed. To do this, use a special loop. The device is inserted through the urethra using endoscopic equipment for this purpose. This procedure allows not to violate the integrity of the bladder.
Laser coagulation of the bladder. During the operation, only mucous structures damaged by the disease are removed. The muscle layer of the organ is not touched, that is, healthy tissues do not suffer with this type of intervention. The patient recovers quickly, the rehabilitation period is a month.
laser ablation. In this case, the tissues of the organ do not cauterize, the thermal effect is not aggressive. The impact is pointwise, healthy tissues do not suffer. The likelihood of complications is minimal. Rehabilitation after such a procedure is fast.
On the second day after the operation, the woman is allowed to go home. The process of urination returns to normal within 7 days. During this time, a woman may experience pain and discomfort.
Diet

To increase the effectiveness of treatment, the patient must follow a diet. Foods and drinks should be selected in such a way that they do not irritate the mucous membranes of the organ. Food is steamed or boiled.
Products recommended for use:
Sweet fruits fresh.
Fresh and boiled vegetables. White cabbage, cauliflower, tomatoes, garlic, onion, sorrel and radish are removed from the menu.
Low-fat fish and meat.
Milk and dairy drinks.
Porridge.
You need to drink about 2 liters of water per day. This will allow you to quickly remove bacteria from the bladder and reduce the effect of uric acid on the walls of the organ. You can drink herbal teas, black and green tea without sugar, fruit drinks with lingonberries and cranberries, pure water, mineral water without gas.
It is forbidden to eat:
Condiments.
Spicy dishes.
Marinades and pickles.
Rich soups.
Smoked meats.
Fried foods.
Strong tea, coffee, spirits.
Complications
After undergoing treatment, a woman will need to be tested regularly. From time to time, she undergoes a cystoscopy of the organ. This will prevent recurrence of the pathology.
Possible complications include:
Malignancy with the development of a cancerous tumor.
Loss of normal bladder function. The tissues of the organ stop contracting and cannot hold urine.
Renal failure. With the development of this complication, a woman may die.
Leukoplakia of the bladder during pregnancy

Leukoplakia can complicate the course of pregnancy. If the disease worsens in the early stages, then the risk of miscarriage or abnormalities in the intrauterine development of the fetus increases.
When the disease occurs in the second half of pregnancy, it threatens with premature birth, placental abruption and intrauterine infection of the fetus. If a woman’s health worsens significantly, then antibiotics are prescribed to her. The rest of the treatment can be carried out only after childbirth.
Chronic cystitis can lead to leukoplakia, as well as provoke its development. These pathologies are closely related. Therefore, with frequent exacerbations of the disease, you need to go to an appointment with a urologist and undergo a comprehensive examination.