Contents
Blackcurrant Sevchanka is far from the most high-yielding and large-fruited variety. However, gardeners appreciate it for its “reliability”, general endurance and very good immunity. In addition, summer residents are attracted by self-fertility and good taste of berries. The variety also has other advantages, allowing it to successfully “compete” with the latest selection for several decades.
History of breeding
Blackcurrant Sevchanka is the result of free pollination of seedlings for a long time and well-known to gardeners variety Golubka by an “intermediate” selection result under the conditional name “hybrid form 32-77”. It was created by A. I. Astakhov and L. I. Zueva, specialists of the V. R. Williams FNTs VIK, at experimental stations in Bryansk.
Currant Sevchanka appeared in 1991, and entered the State Register of Breeding Achievements three years later. The necessary official variety trials were completed fairly quickly.
Description of the blackcurrant variety Sevchanka
The view of the Sevchanka currant is definitely not “outstanding”, it can well be described as “average”. There is nothing original either in the bushes or in the berries.
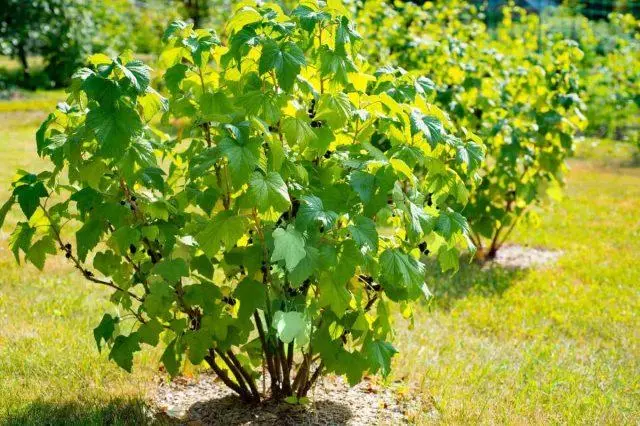
Bush
The bushes of the Sevchanka currant are quite high, characterized by rapid growth. But at the same time they are relatively compact, not sprawling: most of the shoots are upright or almost upright. Approximate dimensions – up to 1,5 m in height and 1-1,2 m in diameter.
The branches are “bare” (without edging), of medium thickness, often slightly bent. The leaves are medium-sized, leathery to the touch, with a strongly “wrinkled” surface. They are characterized by a slight bulge along the central vein and deep “cutouts”.

The crown is not prone to thickening, which greatly facilitates the care of the bush and harvesting.
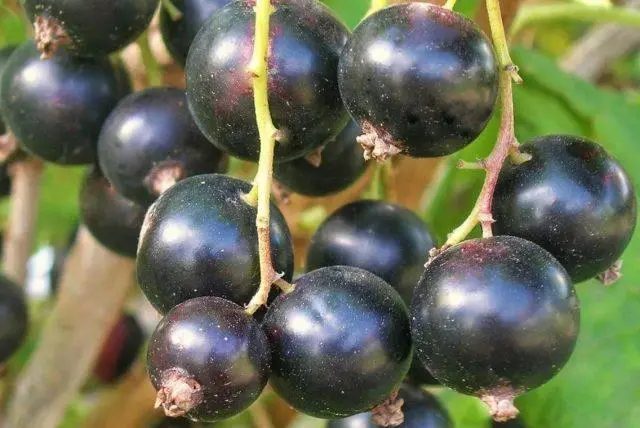
Berries
Sevchanka currant berries are quite large, different sizes (2-3,5 g), regular round shape. They are collected in medium-length and long brushes (8-14 pieces each) with a slightly curved “axis”. The skin is black, with a glossy sheen. It is thin (it is not felt when eating), but strong and elastic enough to provide the berries with good keeping quality and transportability for the culture.

On the “sunny” side of the bush, the berries are usually larger.
Characteristic of the variety
The main feature that gardeners appreciate in Sevchanka currant is its “stress resistance”. The endurance of the culture is successfully complemented by a very good taste of berries and stable fruiting.
Palatability
The official assessment of Sevchanka currant berries from professional tasters, recorded in the State Register, is 4,6 points with a maximum of five. The taste is characterized as “good”, but most gardeners who have tried the berries consider this definition unfair. In their opinion, Sevchanka’s currant can be called a dessert currant: the taste is very harmonious, sweet and sour. Also, the berries are characterized by a rich aroma.
Terms of maturation
In terms of ripening, currant Sevchanka belongs to early ripening varieties. In central Our Country, the crop is harvested in the last decade of June or in early July. Depending on the climate in the region and the weather, the ripening period can be “shifted” by 7-10 days forward or backward.
Productivity
The yield of currant Sevchanka, demonstrated by the variety during official tests, is 104 centners per hectare. In terms of bushes, this is approximately 1,6-2,2 kg from an adult plant. It reaches its “peak shape” by 3-4 years.
Fruiting is annual, without “rest” seasons. Berries on currant Sevchanka ripen together and “massively”.

Harvest is easy to harvest due to the dry separation of berries from the stalks
Frost resistance
The State Register recommends cultivating Sevchanka currant in the Central and Central Black Earth regions. But gardeners “by experience” quickly expanded its habitat, proving that it is quite capable of taking root and bearing fruit everywhere in central Our Country. Cold resistance down to -25-27 ° C allows it to successfully winter in a temperate climate.
Disease resistance
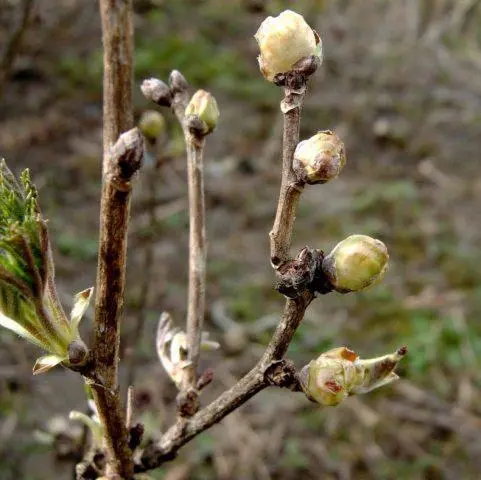
Currant Sevchanka has immunity against a whole “bouquet” of typical culture and dangerous diseases – real and downy mildew, rust, anthracnose. Other pathogenic microflora also rarely affects bushes, allowing gardeners to do without even preventive treatments with fungicides.
Also, Sevchanka currant has protection against bud mites, which can destroy a significant part of the crop already at the beginning of the season. In general, pests do not have a special “love” for her. Many of them do not like the pronounced aroma of the leaves, due to the high concentration of essential oils.

A kidney mite that eats out buds from the inside is one of the most dangerous pests of a crop.
Advantages and disadvantages
Currant Sevchanka is distinguished by a rather high content of ascorbic acid in berries (277 mg per 100 g). Harmonious taste is achieved by the presence of natural sugars in a concentration of about 7%.
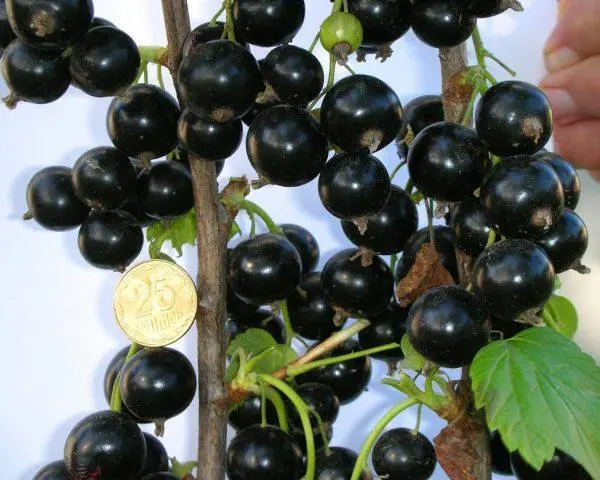

The versatility of the purpose of Sevchanka currant berries in the culinary plan is specially emphasized in the State Register
Pros:
- cold resistance sufficient for the European part of the territory of Our Country;
- the presence of immunity against certain diseases and pests typical of the culture;
- sufficiently high drought resistance;
- self-fertility;
- good keeping quality and transportability for currants;
- annual fruiting, “mass” ripening of berries;
- productivity, little dependent on the weather in spring and summer;
- comparative compactness of bushes;
- balanced, very pleasant taste, pronounced aroma of berries, their rather large size;
- lack of “tendency” of currants to shed after aging;
- versatility of the destination of the crop.
Cons:
- average yields.
Rules of landing
Most often, gardeners, given the characteristics of the temperate climate, plant Sevchanka currants in the spring, waiting for the likelihood of return frosts to be minimized. In principle, autumn planting is also possible, but there is a much higher risk that the seedling will not survive the first winter.
A place for a bush is chosen, taking into account the “requirements” of the culture:
- good lighting without direct sunlight during the hottest hours;
- normal air circulation;
- quite fertile, but loose substrate (loam, sandy loam);
- neutral or slightly acidic soil pH (5.0-5.5);
- lack of prerequisites for permanent waterlogging of the soil.

A place at the foot of a hill or a lowland is not suitable for a bush – melted, rainwater, humid air constantly stagnates there
A pit for planting Sevchanka currants has been prepared since autumn. Approximate depth – 50-60 cm, diameter – 60-70 cm. A drainage layer is required at the bottom (up to 8-10 cm thick). Fertile soil is covered over it.
When disembarking, you must be guided by the standard algorithm of actions. The main thing is to water the soil well before and immediately after the procedure. It is equally important to control the position of the root collar and roots.
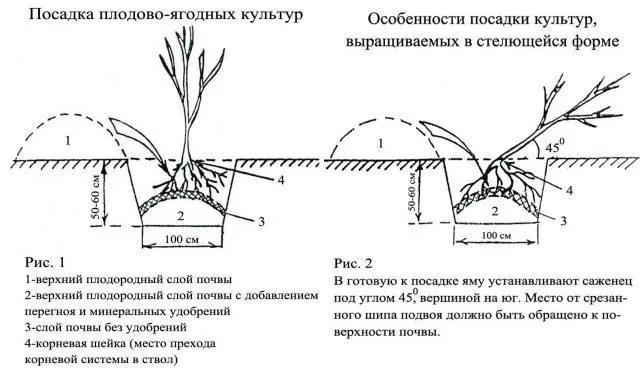
It is easier to plant seedlings with a closed root system, if the roots are “bare”, it is more convenient to work together
Features of care
Even an inexperienced gardener is able to provide Sevchanka currants with competent care. Agrotechnics is limited to the basic minimum of activities:
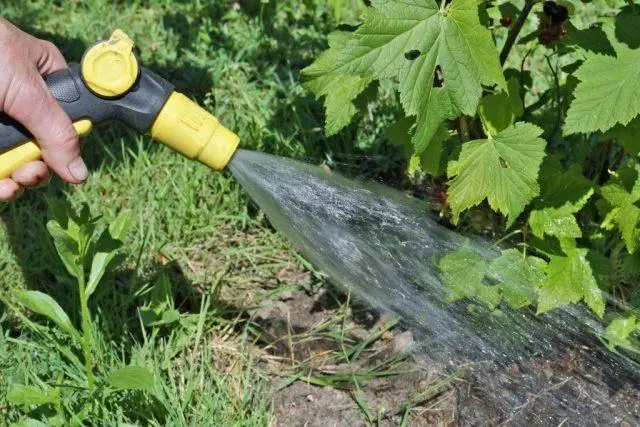
- Watering. Due to drought resistance, Sevchanka currant can do with rare but plentiful watering. The substrate must be moistened during the active growth of green mass, at the stage of flowering and the formation of fruit ovaries, and also about a month after harvest. If autumn is dry and warm, water-charging watering is also added.
- Loosening and weeding. To ensure normal air exchange, it is enough to loosen the soil every 1,5-2 weeks, while getting rid of weeds. Or you can save time on these procedures by mulching the trunk circle immediately after planting the Sevchanka currant.
- Top dressing. Fertilizers are applied according to the standard scheme: nitrogen shortly after “waking up” in the spring, complex preparations at the budding stage, 7-10 days after flowering and in late summer or early autumn.
- Pruning. Sevchanka’s currant is not prone to thickening the crown, usually the bushes have enough sanitary pruning at the beginning and at the end of the season. Plants older than 10-12 years old gradually rejuvenate, getting rid of 1-2 of the oldest branches in the spring.
- Preparing for winter. The cold resistance of currant Sevchanka allows you to do without a “capital” shelter in a temperate climate. It is enough to clean the trunk circle, loosen it deeply and cover it with fresh mulch (10-15 cm layer).
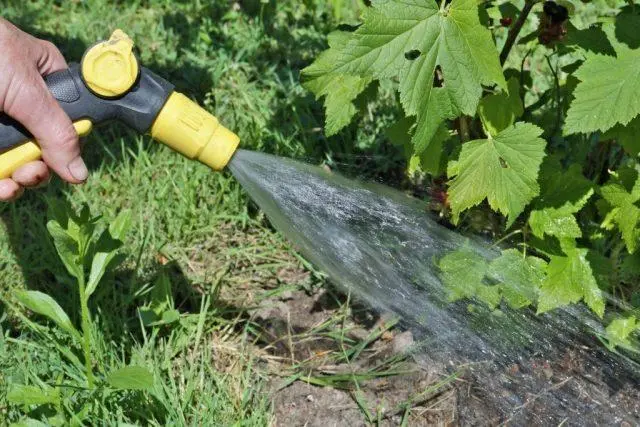

Leaving the bushes without watering, hoping for natural precipitation, is still not recommended.
Conclusion
Currant Sevchanka is a variety that requires minimal, standard care for the culture. The “return” from the plant far exceeds the time and effort spent on it during the season. Bushes have immunity against many diseases typical of the culture and protection from pests.









