Contents
Blackberry is a horticultural crop of North American origin, which is also grown with pleasure in Our Country. There are enough varieties of this berry that can grow safely and bear fruit well in conditions. For example, many gardeners plant Navajo blackberries in their gardens. Consider the features of this variety, its characteristics and the rules of cultivation.
History of breeding
The Navajo blackberry variety is just over 20 years old. It was bred in 1987 in the USA by scientists at the University of Arkansas, along with other varieties of this culture, a common feature of which is the absence of thorns on the shoots. The name of the variety – Navaho (Navajo) – comes from the name of one of the Indian peoples. Several varieties were chosen as parental forms for it: Thornfree, Cherokee, etc. Now the blackberry of this variety is popular not only in its homeland, but also in European countries and in Our Country.
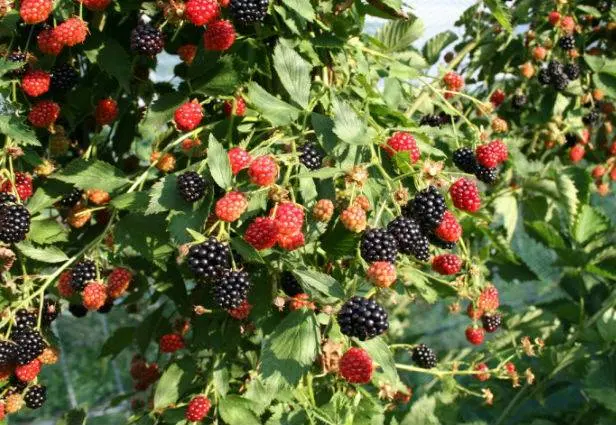

Description of berry culture
Blackberry is a subgenus of the genus Raspberry, in which there are 8 species, 2 of which are used in cultural breeding. These are semi-shrubs with flexible upright or recumbent shoots. Blackberries are grown for sweet or sour-sweet berries, which resemble raspberries in shape and appearance, but are not red, but dark blue or black.
General idea of the variety
The bush of this blackberry is powerful, with high (up to 2 m) upright shoots. They are quite strong, but can bend under the weight of the berries, so they need to be tied up after they reach a height of 1,5 meters or more. It has a strong shoot formation, therefore it forms a lot of overgrowth.
In addition to the classic Navajo variety, the Navaho Bigandearly hybrid derived from it is also known. This is not a full-fledged variety with characteristics different from the original form, but a hybrid form.. The authors of this creation claim that the hybrid Navajo blackberry variety produces taller shoots (up to 2,7 m) and larger berries that ripen faster and have a dessert taste. This is also evidenced by the name of the hybrid, which in translation means “big and early”.
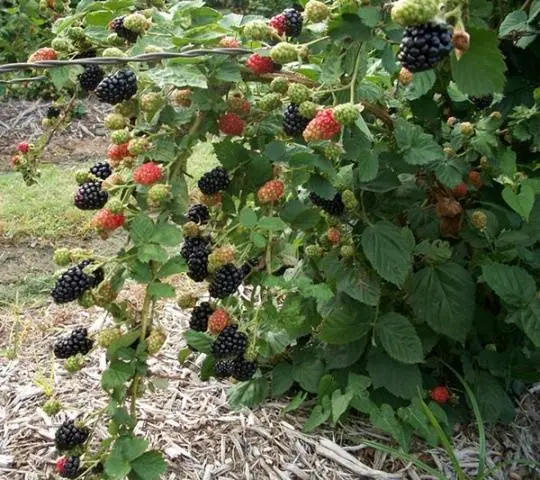

Berries
The berries of the Navajo blackberry are short-conical in shape, even in size and shape, relatively small (compared to other varieties of this crop) in size. Their weight is in the range of 4-7 g. But this feature is well compensated by the huge number of berries that ripen on one plant. For example, on 1 adult young bush there can be more than 0,5 thousand berries.
The berries of the Navajo blackberry are dark blue (in the phase of biological ripeness – rich black), shiny, have an excellent moderately sweet taste, which the tasters rated at 4,9 points out of 5 possible, and many gardeners call it almost a reference. Berries are able to retain their commercial and taste qualities for 5 days. The seeds of this blackberry are small, almost invisible, which is also considered an advantage of the variety and is appreciated by blackberry lovers. The berries are dense, so they withstand transportation well.
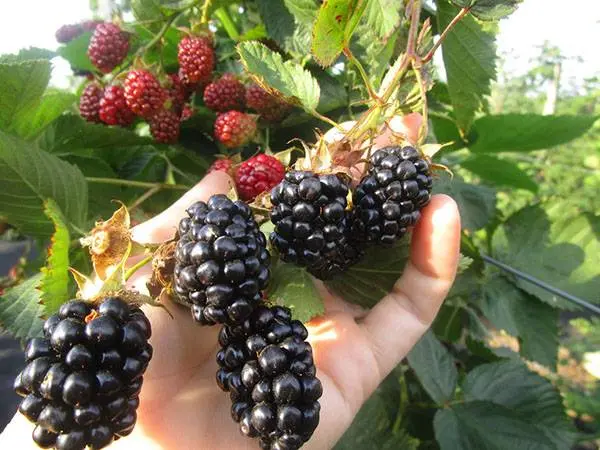

Characterization
The Navajo variety has qualities that attract many gardeners, both amateurs and professionals. That is why gardeners throughout Our Country are increasingly choosing it for planting on their plots.
Main advantages
Blackberry Navajo is considered an unpretentious variety that does not require special care. It tolerates drought well, can grow on almost any soil (but prefers fertile sandy loam and loam), has good frost resistance (up to -20 ° C), therefore, in regions where the temperature in winter does not fall below this indicator, it can grow without shelter. In the rest, the bushes will need to be covered. There are no thorns on the shoots of this blackberry, which greatly facilitates manual harvesting.
Flowering period and ripening period
The Navajo variety is of late ripening, and therefore it begins to bloom late – in the Central zone of the Federation, bushes throw flowers in the second half of June. Berries ripen, as stated in the characteristics of the variety, in August or September. This is influenced by the weather conditions of a particular season, the condition of the plants and, to some extent, the landing site (in a sunny or tennis place).
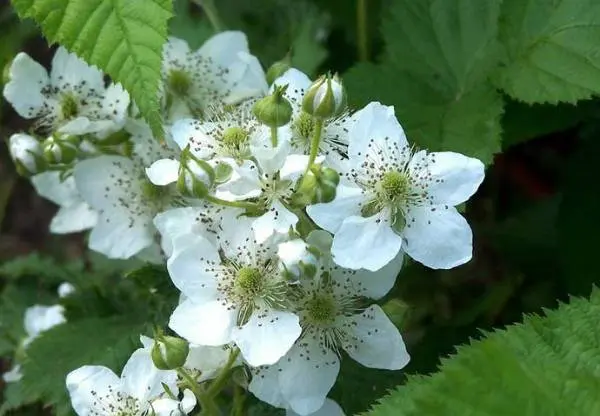

Yield indicators, fruiting terms
Due to the huge number of berries, the yield of Navajo blackberries is quite high and amounts to 9 kg per 1 sq. m. The fruiting of the bushes is stretched and lasts from 3 to 4 weeks.
Scope of berries
Most Navajo blackberries are eaten fresh, but they can also be used for homemade preparations. They make compotes, jam, jam, stuffing for wind pies, freeze in the refrigerator.
Disease and pest resistance
It is noted that the blackberry of this variety is not prone to diseases and pest attacks, therefore, it is not necessary to treat the bushes with pesticides, if this is not required. This reduces the cost, time and effort spent by the gardener on growing plants.
Advantages and disadvantages
The Navaho blackberry variety has many positive qualities, among them are:
- self-fertility (pollinators are not required for the formation of the ovary);
- high yield due to abundant fruit formation;
- undemanding to the conditions of cultivation;
- ease of care (bushes with upright shoots are easier to care for and easier to cut them);
- easy access to the berries during the picking process due to the absence of thorns and the fact that the berries are located in large clusters;
- good preservation of berries and their transportability (despite the fact that they are juicy, the berries remain elastic and do not flow for almost a week after picking);
- excellent dessert taste of blackberry.
The variety also has disadvantages. Those who grew it note that at high humidity and in cool summers, yields decrease, the amount of heat and light absorbed by plants affects the taste of berries. The disadvantage is also the need to remove excess shoots that thicken the bushes.
Methods of reproduction
Navajo blackberries are propagated by rooting the tips of the shoots and basal offspring. It is very simple to do this: when the young growth reaches about 0,6 m, the tops are cut off. After that, new shoots begin to grow from the axils of the leaves. Together with the shoot, they are pressed to the ground and dug to a shallow depth. In autumn or next spring, they are dug up, cut off from an adult plant and transplanted to a new place. Root shoots, when they reach a height of 0,2 m, are dug out together with a clod of earth and transplanted into new beds.
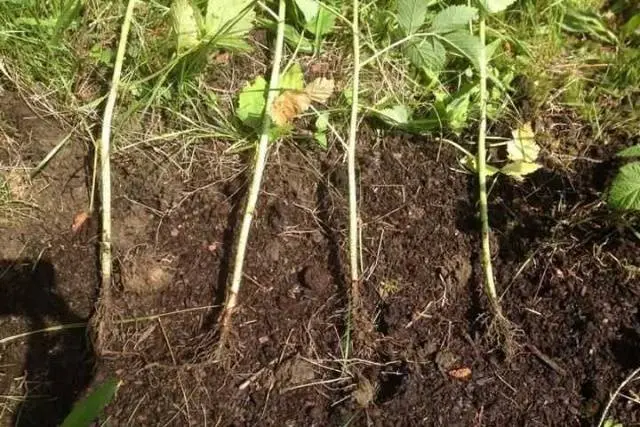

Rules of landing
With proper care, each blackberry bush can grow and fruit successfully for 10-15 years and it is greatly influenced by where and how it was planted. This is why planting and caring for Navajo blackberries in the spring is of great importance for the entire subsequent life of the plant and its yield.
Recommended dates
The best time for planting bushes is spring, in the northern regions they can also be planted in early summer. In autumn, blackberries are not planted, as young plants do not tolerate winter, especially long and cold.
Choosing the right place
A place for bushes is chosen sunny and warm, but partial shade is also acceptable. It is impossible to plant in a place that is too shaded: the plants will constantly receive less light and heat, from which the berries will be small and sour. You can place blackberries on an open flat area or on small slopes, near fences, outbuildings, as long as the plants are protected from strong winds and drafts.
Soil Preparation
The Navajo blackberry does not make special demands on the type of soil, but its quality must be high. The soil must be necessarily fertile, humus, light, loose and airy. Acidity – neutral, slightly increased is acceptable. The soil is preferably moisture-intensive, but not swampy: too high humidity is contraindicated for the culture, plant roots can rot in wet soil.
You can prepare a plot for blackberries in the fall or in the spring. To do this, it is cleaned of plant residues, dug up and fertilized with organic matter or mineral fertilizers. Shortly before planting, the soil is leveled with a rake and holes are made.
Selection and preparation of seedlings
Navajo blackberry seedlings should be healthy, free from damage, signs of disease, and well developed. They should have strong roots and strong shoots with green (not pale) leaves. Plants with dry roots or poorly growing shoots are not suitable for planting. Before planting a blackberry, its roots are moistened and placed in a solution of a root formation stimulator, such as Kornevin, for the time specified in the instructions for use of the drug.
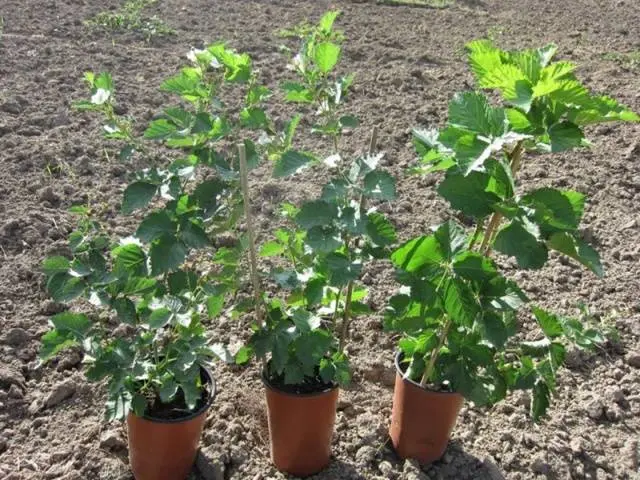

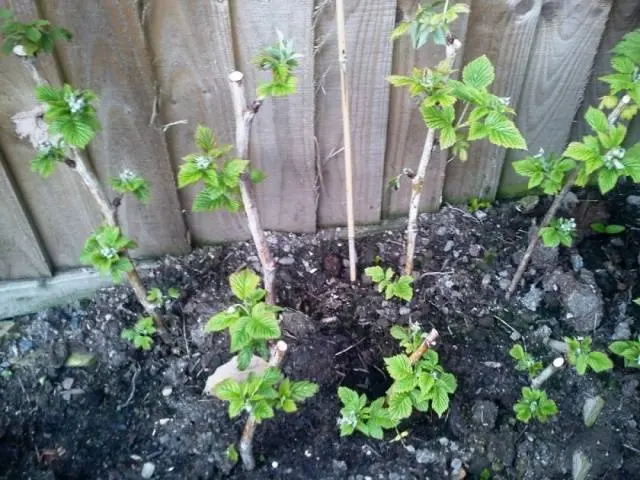
Algorithm and landing scheme
The distance between placed young plants should be at least 1,5-2 m. The holes for them should be voluminous: at least 0,6 m in diameter and depth. In each of them, when planting, pour 1 bucket of humus and 2 tbsp. ash. From above, fertilizers are covered with a layer of earth so that the roots do not touch them.
Navajo blackberry seedlings are planted in the following sequence:
- Moisten the soil in the holes.
- The bush is placed in the middle and its roots are straightened.
- Cover it with earth up to the growth buds.
- Shoots are cut with secateurs, leaving 2-3 buds on each.
- The soil surface is mulched with hay, sawdust or straw, non-acidic peat.
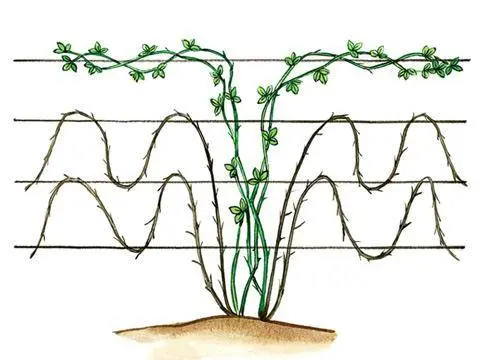
A strong support is placed near each bush, to which long shoots will be tied. The second option: the supports are installed along the edges of the row, and 2-3 rows of wire are pulled between them, which will support the bushes.

Culture aftercare
The cultivation of the thornless Navajo blackberry is quite simple. If you plant it correctly, then the next season the first berries will appear on the bushes, and starting from the 4th year you can expect a bountiful harvest. The main task for the gardener at this time should be to provide the plants with the necessary amount of moisture and fertilizer, form bushes and prepare them for winter.
Growing principles
It is desirable to tie up the bushes of this blackberry, although it does not belong to tall varieties. They are grown on trellises, but as an alternative, special pruning of the main and side shoots on the bush can be used.
Necessary activities
Cultivation of Navajo blackberries involves the implementation of a set of standard agricultural works: watering, loosening (or mulching), weeding. Water the bushes abundantly, especially during the period when the blackberry blooms and sets fruit. But it is not necessary to fill in the blackberry, it does not tolerate too wet soil. With a small area occupied by a crop, a drip irrigation system can be installed on the site. It will evenly distribute water and save it. After watering or rains, the soil is loosened, weeds are weeded, or a layer of mulch is laid on the soil, which prevents it from drying out quickly. Moisture-charging irrigation is carried out only if the autumn is dry.
shrub pruning
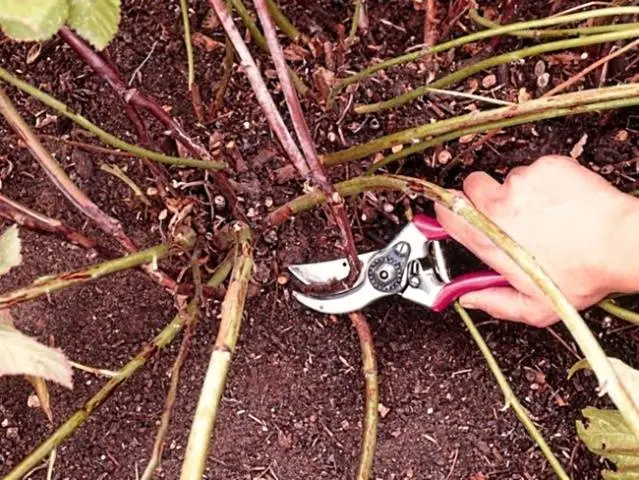
The Navajo blackberry is distinguished by the fact that it gives a strong shoot, so it is pruned starting from the second year of life. In late spring, young shoots, which branch to 1 m, cut off the tops. From this, side shoots begin to grow, the volume of the bush increases, and fruit formation increases.
The formation of the Navajo blackberry bush continues in the fall, as it bears fruit on last year’s shoots, which produce berries for only one year. For this reason, they need to be cut. This is done in the fall, cutting them with a pruner at the root. Leave 3-4 new shoots, while shortening them.
Preparation for winter
For the winter, blackberry bushes need to be covered. To do this, the shoots, when the foliage falls from them, are removed from the trellis, tied together and bent to the ground. From above they cover with covering material: synthetic or vegetable, for example, spruce branches. Under such protection, blackberries tolerate the winter cold well.

Diseases and pests: methods of control and prevention
All blackberry varieties of American breeding, to which Navajo belongs, are considered resistant to pests and diseases. It has been established that even aphids and gall midges rarely settle on its bushes. But, nevertheless, this culture can be affected by spider and blackberry mites, raspberry beetle, powdery mildew, seproriosis and anthracnose. When insects or signs of disease appear, blackberries should be treated with an appropriate insecticide or fungicide.
Conclusion
Navaho blackberry is considered the most unpretentious, therefore it is popular with gardeners. With proper care, it is able to give an excellent harvest for many years and delight its owner.
Reviews
Gardeners who grew this blackberry leave their reviews about the Navajo variety.
Video about the Navajo blackberry:









