Contents
Growing blackberries in home gardens has not been exotic for a long time. High yields and excellent taste contributed to the rapid growth in the popularity of this fruit shrub. The article deals with one of the varieties of English selection – Helena blackberry.

History of breeding
Blackberry Helen (Helen) is an early-ripening hybrid obtained in 1997 by Derek Jennings (Great Britain) as a result of crossing the Silvan variety and unidentified Western American numbered forms. As of 2017, the Helen blackberry variety is not registered in the State Register.
Description of berry culture
Blackberry of early ripening Helena belongs to dewberries – creeping varieties. It is a medium sized shrub resembling a raspberry. Unlike the latter, it contains much more vitamins and microelements in its fruits. Description of the variety, photo, reviews of blackberry Helena are presented below.
General idea of the variety
Characteristics of the Helen blackberry variety are shown in the table:
Parameter | Value |
Culture type | creeping shrub |
Shoots | Powerful, with short internodes, 1,5–1,8 m high, sometimes up to 2 m, with well-developed lateral branching |
foliage | strong |
Sheet | Green, matte, elongated heart-shaped, with characteristic serrated edges, leaf blade with clearly legible veins, slightly hairy |
Number of replacement shoots | 1–2 pcs. |
Root system | Superficial, well developed |
The presence of thorns on the shoots | None |
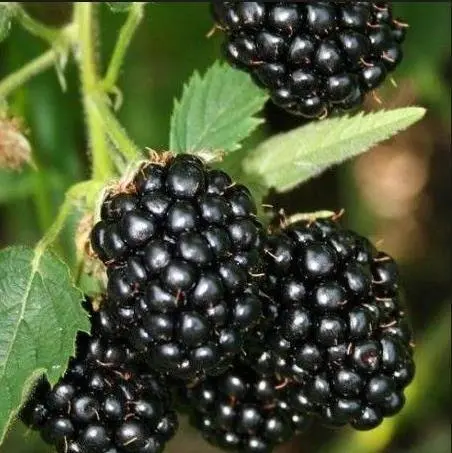
Berries
Black shiny Helena blackberries do not leave anyone indifferent. The main data on the fruits are given in the table:
Parameter | Name |
Variety assignment | Dessert |
fruit color | In the initial stage – ruby, in the stage of full ripeness – black, glossy |
Size | Large |
Mass of berries | Up to 10 gr. |
Form | Rounded, oblong |
Taste | Sweet, with cherry aftertaste and deep aroma |
juiciness | Very high |
Bones | Complex, small, poorly felt |
Tasting assessment | 4,3 |
Transportability | Low |
Characterization
Main advantages
There are few of those. The advantage of Helena blackberry is its original taste, but it is much inferior to many other varieties, and according to the tasting data, Helen is not even in the top ten. The positive point is almost the earliest ripening period among black varieties, friendly ripeness of fruits and the absence of thorns on the shoots.
Flowering period and ripening period
Blackberry Helena blooms late, in June. Thanks to this, the flowers do not suffer from spring frosts. Certain difficulties can only arise if the plant is frozen in winter. In this case, the affected fruit buds bloom with difficulty and are poorly pollinated. Below is a photo of Helen’s blackberry during flowering.
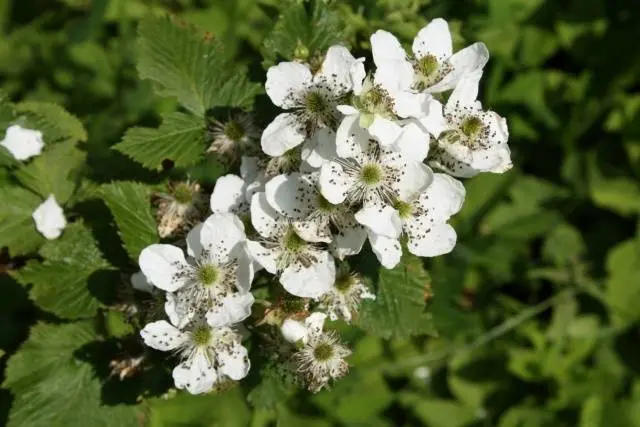

Fruiting blackberry Helena friendly, begins in the first decade of July. Ripening is not extended in time.
Yield indicators
Among other varieties of blackberries, Helen shows very average yields. This is partly due to the weak growth of replacement shoots, and also due to the low winter hardiness of the plant. Data on the full first fruiting of some varieties of blackberries are shown in the table.
Blackberry variety | Productivity from 1 sq.m, kg |
Chester | 10,0 |
Black Satin | 8,2 |
loch tay | 5,7 |
Clea Helena | 3,0 |
The given figures are the statistics of field trials of the Research Institute of Horticulture in Skiernowice (Poland). In addition to low yields, Helena blackberry shows a very modest subsequent increase in productivity – about 200 gr., While other varieties – from 0,5 to 1,5 kg.
Scope of berries
The Helena blackberry variety is a dessert variety, therefore it is consumed fresh. It can also be used for making jams, compotes, fruit drinks. Due to the low yield and low keeping quality of ripe berries, the question of industrial processing, as a rule, does not arise.
Disease and pest resistance
Blackberry Helen does not have stable immunity and is subject to the same characteristic diseases as other varieties. Therefore, it is imperative to take preventive measures.
Advantages and disadvantages
Blackberry Helena ripens early and will please the gardener with large ripe berries in early July. This is where her virtues end. Helen’s blackberry has many more disadvantages, here are just the main ones:
- low yield;
- a small number of replacement shoots;
- tendency to chlorosis;
- weak frost resistance;
- no immunity to diseases;
- poor portability.
Thus, the planting of Helen’s blackberry in the garden plot cannot be unambiguously recommended as promising.
Methods of reproduction
You can propagate Helena blackberries in any traditional way. These include reproduction:
- layering;
- shoots;
- offspring;
- root and green cuttings;
- seeds.
The first method is the most optimal. Its essence is as follows. In early August, two grooves 15 cm deep are dug from the bush, into which healthy annual shoots are laid, fixed with a wire or load and covered with earth.
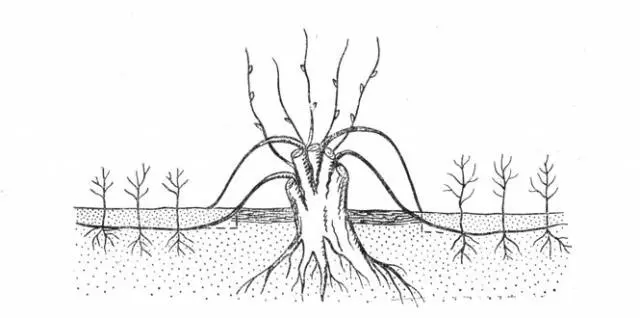
The soil is mulched with sawdust and watered regularly. After about two months, the Helena blackberry shoots will take root and give rise to shoots. At this time, they can be cut off from the mother branch and transplanted to a new place along with a clod of earth.
Rules of landing
When planting Helen’s blackberries, consider the effect the bushes will have on the garden. And also whether the shrub itself can grow and develop normally in the proposed conditions.
Recommended dates
Blackberry Helen can be planted in both spring and autumn. In regions with different climatic conditions, the timing for spring planting may be different, you need to consider the following:
- The air temperature is not less than +15 degrees.
- The soil warmed up by at least 20 cm.
- The buds haven’t opened yet.
In the middle lane, this is the end of April – the beginning of May, in the southern regions – April, in the Far East – the first decade of May.
Planting Helen blackberry seedlings in the fall should be done in such a way that at least a month remains before the first frost.
Choosing the right place
Helen’s Blackberry will grow well in a sunny, wind-sheltered spot. The ideal place would be to plant on the south or southwest side along the fence. Avoid places with possible stagnant moisture, as well as with groundwater levels above one and a half meters. It is preferable to plant Helena blackberries on loamy and sandy soils.
Soil Preparation
Pits for planting Helen’s blackberries need to be done in advance, nutrient soil, which will fill the roots of the seedlings, too. Usually they are prepared a month before planting, so that the soil and substrate are saturated with air.
The pits should be at least 40x40x40 cm. They are made at a distance of 1,5–2 meters from each other.
Selection and preparation of seedlings
When planting Helena blackberries, it is better to use your own seedlings obtained from the mother bush. In this case, the process will be with a clod of earth and will easily transfer the transplant to a new place.

If the roots are open, then they should be wet. Such Helen blackberry seedlings should be soaked for several hours in a root growth stimulator before planting.
Algorithm and landing scheme
Prepared pits are 2/3 filled with nutrient soil. It should include:
- compost or humus – 5 kg.
- superphosphate – 120 g.
- potassium sulfate – 40 gr.
The components must be mixed with soddy soil. Helena blackberry seedlings are planted vertically, deepening the root collar by 2–3 cm and covered with soil. The soil around the plant must be compacted and poured with 5 liters of water, and then the trunk circle should be mulched with sawdust or peat.
Culture aftercare
The planted plant should be watered regularly for 40–50 days. Then the frequency of watering can be reduced and guided by the weather. Also, Helen’s obligatory blackberry care activities include pruning, tying on trellises, feeding, watering and shelter for the winter.
Growing principles
Blackberry Helen must be tied up on the trellis. Usually, two or three rows of wire are pulled for this, at a height of 0,7, 1,2 and 1,7 meters. The principle of the garter is fan. The side shoots are tied to the lower trellis, the central ones to the middle and upper ones.
Necessary activities
Helen’s blackberry needs watering only when the fruit is ripe. Too much moisture is bad for her. After watering, the earth can be loosened and mulched with sawdust or straw.
Feeding Helena blackberries is done in two stages. In the spring, nitrogen fertilizers are applied (ammonium nitrate – 50 grams for each bush) to stimulate the growth of annual shoots. In the autumn, after the end of fruiting, the bushes are fed with superphosphate and potassium sulfate (100 and 30 grams, respectively), applying fertilizer along with humus to the trunk circles during their digging.
shrub pruning
Helen’s blackberry pruning is done in the fall and spring. In autumn, two-year-old shoots that bear fruit are cut out under the root, in the spring sanitary cuttings are made of broken and dead branches during the winter.
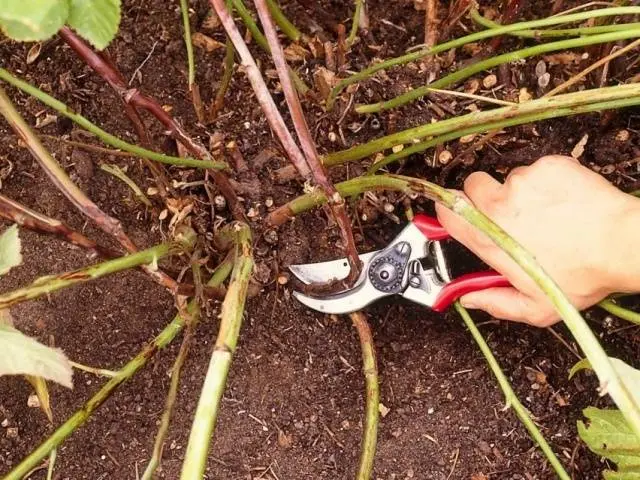

Preparation for winter
For Helena blackberries, shelter for the winter is a must. The shoots are removed from the trellis, tied together, bent to the ground and covered with two layers of agrofiber.
Diseases and pests: methods of control and prevention
Helen’s Blackberry is not inherently immune to disease. The table shows the most common diseases.
Disease | What is manifested in | Prevention and treatment |
Root cancer | Growths of green, and then brown color on the roots and root collar | Not treated. Affected plants are burned. The site is treated with Bordeaux mixture. |
Curly | Weak growth, the leaves become bright green, wrinkled, bent inward. Flowers are not pollinated | Not treated. A diseased plant must be burned. |
Mosaic | Chaotic yellow spots on the leaves, thinning shoots. Frost resistance is greatly reduced | There is no cure. The plant must be dug up and burned. |
yellow netting | The leaves turn yellow, the veins remain green. shoots stop growing | The virus is carried by aphids, the diseased plant is destroyed along with the aphids. |
Antraknoz | Gray spots on leaves, rarely on shoots. Gray ulcers on berries | Not treated. The diseased plant is destroyed. For prevention, bushes are treated with fungicides three times a season. |
Septoria (white spot) | Round brown spots with a thin border on the leaves, black dots of the fungus. Mucus appears on the berries, they rot | Not treated. Prevention is the same as for anthracnose |
Didimella (purple spotting) | Drying of leaves, wilting of shoots. Purple spots on the stem. | Thinning plantings, spraying with 2% Bordeaux mixture |
Botrytis (gray rot) | Berry and shoots are affected by a gray fleecy coating, later rot | Treatment of bushes with fungicides, with a change after repeated application |
In addition to diseases, Helena blackberry bushes can be attacked by pests. The table shows the main insects that are dangerous for this variety.
Pest | What strikes | Control and prevention |
Tick of the web | Leaves, a thin cobweb appears on the affected bushes | Cleaning and burning of all old leaves. Triple treatment with fungicides (Actofit, Fitoverm, etc.) with an interval of 7 days after the opening of the first leaves |
blackberry mite | Berries, affected fruits do not ripen and remain red | Treatment of bushes with Envidor, BI-58 preparations before bud break |
Raspberry fly | The tops of the shoots, the larvae of flies gnaw their moves inside them, then descending along the shoot down to wintering | There are no chemical methods, the tops of the shoots are cut off and burned immediately after wilting is detected. |
crimson beetle | All parts, from roots to flowers, gnawing holes in them | Digging the soil, cleaning the rot. A week before flowering, the bushes are treated with Iskra, Fufagon, etc. |
Conclusion
Unfortunately, the facts do not allow us to unequivocally recommend the Helen blackberry variety as promising for cultivation. Low yield, not the best taste with a pronounced tendency to freezing. It is more suitable for a change, as an addition to the main crops of the garden. Helena blackberries are not suitable for commercial production.
To better decide on the choice of variety, you can watch the following video about Helen’s blackberry
Reviews
Reviews about Helen’s blackberry are contradictory.









