Contents
Cultivation of cattle (cattle) is a profitable occupation. Animals from the class of mammals give milk, meat, skins. In some regions, bulls are used as a draft force. In order to profit from cattle, it is necessary to know the economic and biological characteristics of cattle.

Features of the constitution and exterior of cattle
The constitution and exterior of cattle depend on the breed and the conditions in which the animals are kept. There are several classifications to help understand the biological characteristics of cattle.
Classification according to P. M. Kuleshov
Pure cattle species are rare. Most often, groups are mixed or intermediate:
- Rude. This group is represented by working and primitive cattle. Animals are distinguished by a large head and powerful horns. The skeleton is massive. On dense skin, thick and coarse hair. Since the cattle of this group is intended to perform work associated with physical activity, the animals have well-developed muscles, and there are few fat deposits.
- Gentle. Animals of this group have their own biological characteristics. Cattle are distinguished by thin skin, delicate wool. The muscles are moderately developed, the skeleton is light. Such a structure can be found in dairy and meat cattle.
- Dense or dry. Cattle of this group are highly productive and viable. Animals are distinguished by thin and elastic skin. The biological feature of this group of cattle is a small fat layer and fiber under the skin. Animals of this group are especially appreciated by farmers involved in the production of milk and meat.
- Loose or raw. Cattle in this group have their own biological characteristics: thick skin, well-developed subcutaneous fat. Despite the fact that the skeleton is weak, the muscles are quite voluminous, but its tone is lowered. Cattle grow quickly, gaining weight in a short time. Farmers directly involved in the production of meat most often pay attention to the biological characteristics of cattle. But you can’t count on getting milk.
Systematics of KRS according to Yu. K. Svechyn
This scientist, classifying cattle, took into account such a biological feature – the growth rate of the calf. He divided the cattle precisely on this basis, singled out the following types of constitution:
- individuals with rapid growth;
- animals forming at an average speed;
- slowly growing.
Other features of the constitution and exterior
Adult cattle belonging to different sexes differ in exterior. For example, sires are 30-40% heavier than cows (the same age of animals is taken into account). Gobies are much taller than their girlfriends, they are also distinguished by a well-developed front part of the body.
Immediately after birth, calves have long hind limbs, the body is short and flattened. The back of the body is slightly raised. Looking at a newborn calf, according to biological features, one can estimate what an adult cattle animal will be like (subject to proper care):
- body weight – 6-8% of the weight of an adult bull or cow;
- leg length – about 70%;
- height at the withers – 55%;
- chest width – 30%;
- calf length – 40%.
As they grow older, the exterior of the cattle changes as the skeleton, organs and tissues are formed.

The most important biological features of cattle
The choice of animals will directly depend on the direction of cattle breeding: dairy, meat and dairy or meat production. That is why it is necessary to understand the biological characteristics of cattle.
First you need to understand the benefits:
- Due to the biological features of the digestive system, animals are able to digest a large amount of grass, various combined feeds.
- The ability of cattle to produce offspring occurs at 6-9 months.
- Breeding bulls can be kept up to 9 years, as they successfully retain their function.
- Dairy cows have their own biological feature: they never get fat.
- Cattle have hereditary characteristics, so they rarely suffer from brucellosis and tuberculosis.
Cattle also have their own biological disadvantages that future agricultural producers need to know about:
- It will not work to get a large offspring, which means to quickly increase the herd, since every year a cow has only one calf. Twins and triplets are very rare, this is one of the features of the physiology of cows.
- Despite the early maturity, it is desirable to allow heifers to breed at the age of 1,5-2 years. In this case, you can count on healthy viable offspring.
reproductive organs
Speaking about the biological characteristics of cows, you need to figure out how the reproductive organs are arranged.
The reproductive system of gobies is represented by testes. They produce sex cells and testosterone. This hormone is responsible for reflexes and regulates the formation of spermatozoa.
The reproductive system of cows consists of ovaries. In them, eggs mature, sex hormones are formed. The growth of female cells responsible for reproduction occurs due to the production of estrogens and progesterone. The sexual cycle and metabolic processes in the cow’s body depend on the development of these hormones.
Progesterone has a beneficial effect on the development of a fertilized egg. Testosterone is produced in the ovaries, due to which follicles are formed that regulate the sexual desire of cattle.
Digestive system
The physiological characteristics of cows include nutrition. The digestive system of ruminants has its own characteristics. Cows are able to eat and digest a lot of food of plant origin, because they have a multi-chambered stomach. It grinds roughage rich in fiber.
The oral cavity of cattle is limited by the lips. Inside is a tongue with taste buds, thanks to which cows determine the taste of food.
The lower jaw of cattle has incisor teeth only in front. During feeding, pressing the grass to the incisors, the animals tear it off. Primary grinding occurs in the oral cavity, where food is combined with saliva, after which it passes into the scar.
The digestive system of cattle consists of several departments:
- scar;
- grids;
- books;
- to the mouse;
- 3 chambers called proventriculus.
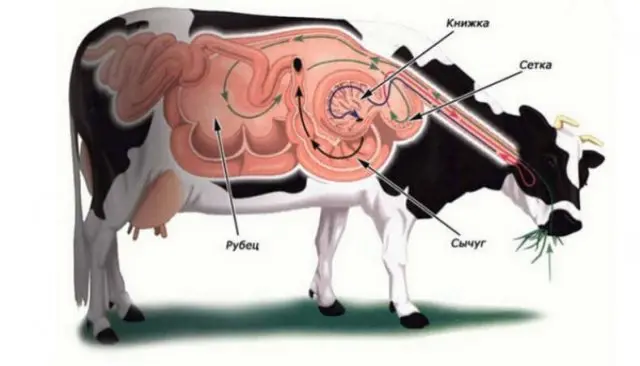
Biological features of the digestion of cattle:
- In the oral cavity, the grass is not crushed finely, large particles fall into the scar. Then from the scar, the food passes into a mesh with a shell similar to honeycombs. They have large food items on them.
- These unground particles press against the mesh wall, causing the animal to burp. Then the chewing gum starts again. Fermentation begins in the scar and mesh, so the eructation has a specific smell.
- But small particles of food, similar to gruel, are sent to the book, then to the proventriculus, where the mechanical processing of the food takes place.
All other processes of nutrient absorption are no different from animals in which the stomach is single-chamber:
- From the proventriculus, the mass moves into the abomasum, where there is hydrochloric acid and pepsin. Thanks to these substances, further splitting occurs.
- The resulting slurry is in the small intestine. Its villi absorb nutrients.
If a farmer dreams of getting quality products from cattle, he should know that he cannot do without a strong forage base. In addition to natural grass, cows need grain and succulent supplements. As additional feed you need to use:
- compound feed;
- beets;
- makuhu;
- potatoes;
- pumpkin crops:
- silage;
- various grains.
Fresh water should always be in sufficient quantity. After simple substances enter the bloodstream, it is water that promotes them to the liver. And from there, with the blood, nutrients enter the heart, lungs and all organs. The main absorption of nutrients occurs in the large intestine.
Excretory system
Since cattle have large dimensions, which is due to biological characteristics, animals require a lot of feed, this refers to the physiology of cattle. The digestive system processes a portion of food for 2-3 days. The fact is that the intestines are 20 times longer than the torso. The average length of the digestive system is about 63 m.
After the prescribed time, cows excrete feces. Depending on age and weight, healthy animals excrete 15-45 kg of feces. The kidneys produce up to 20 liters of urine per day.
It is also necessary to understand the characteristics of the intestines of cattle, located in the right hypochondrium. It consists of the following intestines:
- thin;
- duodenal;
- skinny.
Fiber is broken down and absorbed in the large intestine. The rest of the feces go into the rectum and out through the anus.

The urinary system consists of:
- 2 kidneys;
- ureters;
- Bladder;
- the urethra.
The kidneys are sponges and are an excellent filter. They cleanse the blood of various harmful substances, as a result, urine is formed. Urine moves through the ureter to the bladder.
Organs of perception
Information about the world comes to cows through the organs of sight, hearing.
The eyes have the following structure:
- Eyeball. It has 3 membranes: vascular, reticular, fibrous.
- protective organs. They are the lacrimal apparatus, muscles, eyelids.
- subsidiary bodies. Thanks to the long eyelashes, foreign objects do not get into the cow’s eyes. They are also analyzers. Eyelashes help determine the length of the herbage, branches on trees and shrubs.
The organs of perception also perform an important function. Excellent hearing of cows is an important biological feature of cattle. Animals can distinguish not only voice and sounds, but also different music.
The hearing aid consists of the outer, middle and inner ear. The outer ear is like a shell, able to move thanks to muscle tissue and cartilage. The middle ear contains the ossicles and the tympanic membrane.
Economic features of cattle
Cows are bred in the private sector and on farms. In private farms, as a rule, animals are raised for milk and meat. Therefore, preference is given to cows of mixed origin, dairy and meat direction.
Farmers, depending on the purpose of production, breed different breeds: meat, dairy or meat and dairy. Some farms prefer only breeding animals.
Cultivation of cattle has its own economic features:
- Animals are distinguished by endurance, unpretentiousness. They are able to eat various feeds that can be grown in specially allocated areas.
- The possibility of obtaining important dairy and meat products containing complete animal protein.
- There is no tax on cattle.
Features of the behavior of cows
Livestock owners should understand the economic and biological characteristics of cattle and the behavioral reactions of their wards. When raising animals, it should be understood that a sharp change in living conditions can cause stress and depression. And this negatively affects productivity, can cause serious diseases.
Young growth also reacts negatively to adverse conditions. Keeping animals in the cold reduces growth by almost a quarter, and dairy cows produce less milk.
Conclusion
As you can see, the biological characteristics of cattle are important to know for owners of personal and farm enterprises if they want to receive a sufficient amount of dairy and meat products. Cows are sensitive and affectionate animals that will thank their owners.









