Contents
Barberry Natasha is a plant that grows in its original form in the Far East. It was distributed to North America and Europe by gardeners who value culture for its high decorativeness.
Description of barberry Natasha
The plant is a deciduous shrub that can grow up to 2,5 m in height. When cultivated in specially created conditions, the barberry rarely exceeds 1 m.
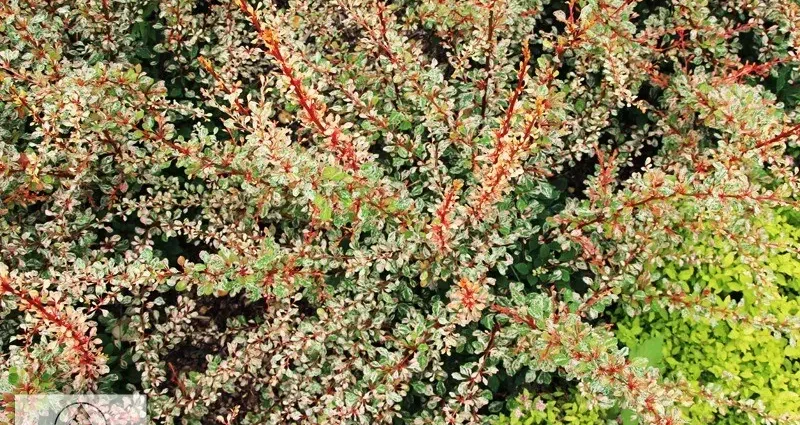
Description of barberry Thunberg Natasha: the plant has arcuate ribbed shoots, characterized by a bright red or red-orange tint. Gradually they change color to brown and brown.
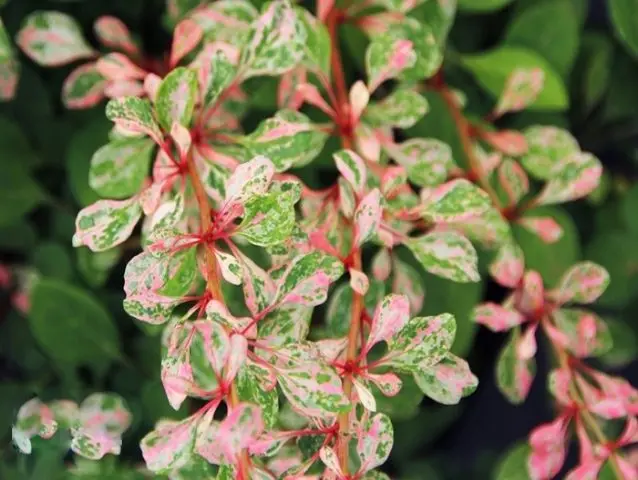

The kidneys of the barberry Natasha are reddish, ovoid in shape. Their length reaches 5 mm. Leaf blades are rhomboid-oval or rounded in shape, may be rounded at the top and resemble a wedge at the base.
Leaf plates are located on petioles, their maximum length is 2-3 cm, and their width is 1 cm. The upper side of the leaf has a juicy green tint, and the lower side is bluish in color. In autumn, they turn bright red or yellow.
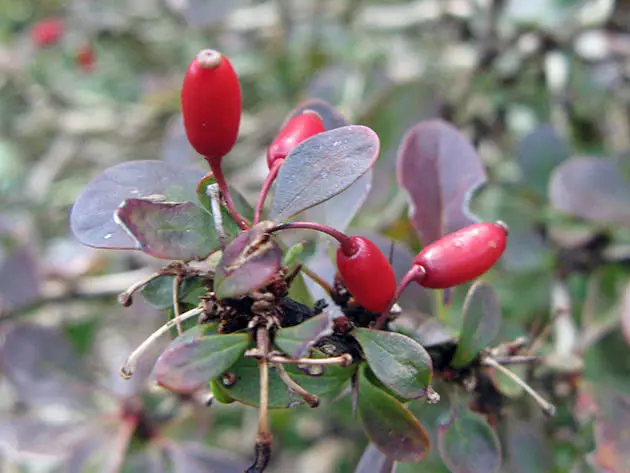
The branches of the plant are equipped with thin thorns. Flowers can be located both singly and form bell-shaped brushes in early May. In September-October, elongated fruits ripen, coral-red color.

Gardeners prefer Barberry Natasha, whose photo confirms the unusual appearance of the plant. The culture is popular and due to the fact that it is unpretentious in care, it gets along well with other representatives of the flora.
Planting and caring for a variety of barberry Thunberg Natasha
The optimal time for planting a plant is autumn. The seedling transferred to the ground before the onset of cold weather has time to take root and, after the snow melts, quickly starts to grow. If necessary, planting in the spring, the procedure is carried out before bud break.
If it is necessary to plant bushes separately, a distance of at least 1,5-2 m is left between them. To form a hedge, 4 bushes must be placed one after the other. Gradually, the barberry Natasha will grow and occupy the surrounding area.
Seedling and planting preparation
Barberry Natasha is characterized by unpretentiousness and high vitality, but compliance with the basic rules of agricultural technology will allow you to get a decent ornamental plant. The seedling prefers neutral soil, but grows well in acidic soil.
For the manufacture of soil mixtures, humus, garden soil and sand are mixed in equal proportions. If it is necessary to transfer the plant to acidic soil, the earth is mixed with limestone.
The preparation of the seedling consists in its acquisition and processing with a stimulant. The main requirement for barberry Natasha is a strong root system and the presence of buds on the branches.

Rules of landing
If you give preference to a sunny area, then the foliage will quickly acquire a yellow or red tint, when in darkened gardens the barberry Natasha retains a green tint of leaf plates.
Landing algorithm:
- Prepare a hole at least 0,5 m deep.
- Place the prepared substrate into the hole.
- Transfer the seedling to the hole, straighten the roots in a natural position.
- Fill the hole with soil, compact it tightly around the bush.
It is important to moisten the soil at the end of the process in order to activate the processes of growth and rooting.
Watering and top dressing
The basis of caring for barberry Natasha includes not only moistening the soil and fertilizing, but also loosening the soil, removing weeds.
Under favorable weather conditions with occasional rainfall, irrigation is not necessary. Intense heat causes the need for additional soil moisture. Watering is carried out with warm water under the root, it is necessary to avoid getting liquid on the leaf plates.
Keeping the soil moist is essential for newly planted shrubs until they take root.
Excessive watering or bad weather adversely affects the plant, increasing the risk of its death.
Bushes should be fertilized annually. Useful for barberry Natasha preparations containing nitrogen. When growing a crop for the sake of fruits, it is fed with potassium and phosphorus.
The best option for fertilizing is to use the Kemira-Universal solution, which is watered on the soil in early July.

Trimming
Shortening of shoots is an infrequent procedure that is carried out if necessary: disruption of shoot growth, its strong deviation from the crown. Be sure to remove damaged or dried branches. Carry out pruning before the start of sap flow.
Preparation for winter
Initially, all weeds are removed, the soil is mulched. To preserve the root system, it is recommended to leave fallen leaves under the bush, and in winter, cover the lower part of the plant with snow. The aerial part is pulled with ropes and wrapped with a cloth. The barberry bush Natasha can be left both in an upright position and bent to the ground.
Reproduction
There are several ways to breed barberry Natasha. One of them is seeds. To obtain them, ripe berries are harvested, the bones are separated from the pulp and placed in a solution of potassium permanganate, then dried.
In autumn, the seeds are placed in the ground to a depth of 1 cm and lightly sprinkled with earth. In the spring, after the appearance of 2-3 leaves, the plantings are thinned out and the bushes continue to be grown for 2 years. After the time has passed, they are seated.

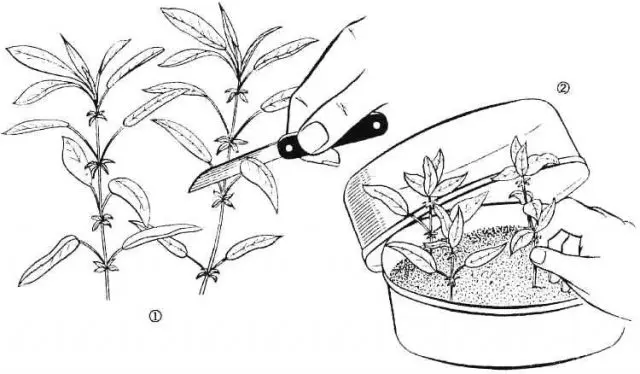
For propagation by cuttings, they are pre-prepared: they are cut in mid-July, the leaf plates are removed from the bottom, and the upper ones are shortened by half. After that, the plant is placed for 2-3 hours in a growth stimulator – this is Epin, Kornevin. At the end of the procedure, the stalk is washed and transferred to a moist substrate consisting of humus, peat and fertile soil.
A plastic dome is formed over the planted cutting, which is periodically removed to ventilate the plant. After the formation of the root system (the process takes about 2 weeks), all fences are removed. It is recommended to grow a young barberry in a greenhouse bed for 2 years, after which the bush is transferred to a permanent habitat.
Another method of reproduction is layering. In the spring, on the barberry bush Natasha, a strong one-year-old shoot is selected, which is bent to the ground and fixed. From above it is lightly sprinkled with soil, leaving only the top.
By autumn, the layering will form a root system that will allow you to separate the seedling from the mother bush and transplant it to a new place.
It is convenient to divide low bushes of 3-5 years of age into seedlings. To do this, the bush is dug up in the spring and cut into identical parts. To separate the roots of barberry, it is recommended to stock up on a saw, which should be carried out carefully, avoiding unnecessary trauma to the plant.
At the end of the work, the sections are treated with crushed coal and distributed among the plots. Bushes whose shoots branch above ground level are not suitable for dividing.
Diseases and pests
The main pests of barberry Natasha are aphids and moths. The plant is saved from the latter by treatment with Chlorophos or Decis. To get rid of aphids, it is recommended to spray the plants in the spring with folk remedies (300 g of soap per 10 liters of water, or 0,5 kg of shag per 10 liters of soap solution). If the procedures are ineffective, treatment is carried out with acaricides – Aktar or Aktellika.
When a whitish coating (powdery mildew) is detected on the leaf plates, the barberry bushes Natasha are sprayed with a sulfur-lime mixture. With a complete defeat of the shoots, they are cut and burned.
Spotting is characterized by the appearance of spots that provoke the drying of the leaf plate. To destroy a bacterial infection, a solution of copper oxychloride (30 g per 10 l of water) is used, which is treated with a spray bottle before and after flowering.
When affected by fungal diseases, the affected shoots are cut out, and the plant is treated with fungicides.
Often in spring, spots of rich orange color can be seen on the upper side of the leaf. On the reverse side of the plate, orange pads are formed, where spores are stored. This disease is called rust. As it progresses, the leaves dry up and fall off.
To destroy the bacteria, the barberry bush Natasha is treated with a 2% solution of Bordeaux mixture.

It is important to monitor the condition of the plant in a timely manner. With signs of complete infection of the bush, it is dug up and burned, and other barberries are prophylactically treated with antibacterial agents.
Conclusion
Barberry Natasha is an ideal plant for creating hedges, equipping picturesque corners for relaxing in the garden and implementing interesting landscape designs. Ease of care and strong frost resistance is an undoubted advantage of barberry.










