Contents
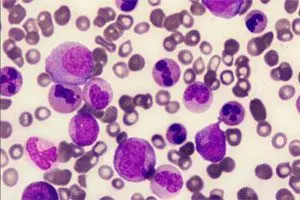
Basophilia is an excess of basophils in the blood. By itself, this condition is not a disease. It accompanies other pathologies that can sometimes pose a threat to life. In the blood test form, basophils are referred to as BA or BASO.
Basophils are a type of white blood cell. They are produced in the bone marrow and help the body fight various infections. Basophils are the smallest cells among the rest of the leukocytes (neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes) of the granulocytic series.
Basophils are small. Immediately after their birth in the bone marrow, they enter the tissues. There is no reserve in the body. The life span of basophils is no more than 7 days.
Basophils carry receptors for immunoglobulin E, they also produce histamine and other substances that are involved in the process of blood clotting. Thanks to their work, the anticoagulant heparin is produced in the body.
In tissues, basophils are represented by mast cells, which are called mast cells. Basophils are present in the skin, in the connective tissue that surrounds the capillaries, and also in the serous membranes. The level of basophils in the blood is 0-1%, but if the body needs them, then these values u1bu0,65bwill increase rapidly. So, the excess of relative values of basophils by 10% and absolute values of more than XNUMX * XNUMX9/l indicates the development of an inflammatory or allergic reaction.
Causes of basophilia
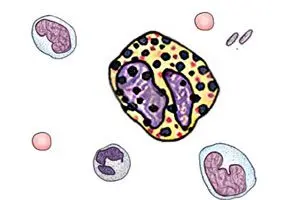
Basophils are an integral part of the immune system. They are involved in the formation of an allergic reaction, their level rises in response to the penetration of helminths into the body. At the site of allergic inflammation, the level of basophils, eosinophils and immunoglobulin E will simultaneously increase.
The causes of basophilia can be as follows:
Acute infectious diseases provoked by cold or chicken pox viruses.
Allergic reaction of the body.
Infection of the body with helminths.
Donor blood transfusion.
Inflammatory reaction in the body: tuberculosis, ulcerative colitis, sinusitis, hepatitis, nephrosis.
The period of ovulation in a woman.
Hypothyroidism, diabetes mellitus, increased blood estrogen levels and other endocrine pathologies.
Taking drugs for the treatment of thyroiditis and taking estrogens.
Anemia with low levels of hemoglobin in the blood.
Emotional turmoil.
Postponed surgery to remove the spleen.
Diseases of the hematopoietic system: myeloid leukemia (acute and chronic), polycythemia vera and erythremia.
Autoimmune diseases: rheumatoid arthritis and dermatitis.
Hodgkin’s disease.
The introduction of a vaccine into the human body.
There is no such thing as a “low basophil level” in medicine. Basophils may be present in the blood, either normal (0-1%) or elevated. Moreover, the jump in their level often occurs instantly.
Many blood parameters in a person undergo changes with age, but this rule does not apply to basophils. Moreover, in newborn children, they are most often not found at all. However, when the baby starts to cry, when he is given the first complementary foods, or he is sick, the level of basophils in the blood rises.
If in the general analysis of human blood there is a significant excess of basophil values, then this, first of all, makes one think that a foreign antigen has entered the body. As a result, an immune response develops, which consists in an increase in the number of basophils in the blood. Moreover, this response can be very rapid and even life-threatening (anaphylactic shock).
Women with basophilia should first check their hormonal status. Often, an increase in the level of basophils in the blood indicates developing thyroiditis. Other symptoms of this disorder are: decreased performance, hearing impairment, obesity, swelling of the eye orbits.
Radiologists who regularly receive minimal doses of radiation will also have increased levels of basophils in the blood.
Basophilia is not always a sign of any disease. It may indicate a high level of estrogen in the blood during ovulation. Also, the values of these blood cells increase in the first trimester of pregnancy.
Allergic reaction and basophilia
An increase in the level of basophils in the blood will be observed with an allergic reaction of an immediate and delayed type.
An immediate allergic reaction is a life-threatening condition that requires emergency medical attention. It develops very quickly and is characterized by damage to the body’s own tissues. An example of such a reaction is anaphylactic shock, angioedema, urticaria.
An allergic reaction of a delayed type is formed over several days. It can be manifested by contact dermatitis, asthma, autoimmune diseases.
Basophilia develops in response to an increase in the concentration of immunoglobulin E in the blood, which reacts to allergen antigens that have entered the body. At the start of anaphylactic shock or another immediate type of allergic reaction, the level of basophils in the blood decreases, as all cells rush to the pathological focus. Compensates for their lack of bone marrow quickly. With a delayed-type allergic reaction, basophils will be produced for several days.
In adults, allergy is most often characterized by a chronic course, manifested by hay fever, conjunctivitis, bronchial asthma, and dermatitis. In this case, the level of basophils in the blood will be in the range of 1-2%.
Symptoms of basophilia
There are no specific symptoms that would indicate an increase in the level of basophils in the blood. They depend largely on what exactly led to basophilia.
If an infection has become a provoking factor, then it is her symptoms that will come to the fore. A person’s body temperature rises, general well-being worsens. Other symptoms depend on the type of pathogen.
If basophilia is the result of an allergen entering the body, then the patient has the following complaints:
Sneezing
Flow of mucus from the nose.
Burning and itching in the eyes.
Rashes on the skin.
Swelling of tissues.
Asthmatics often have asthma attacks.
Anaphylaxis is the most severe allergic reaction in which a person loses consciousness, his blood pressure drops sharply. Medical care must be provided urgently, otherwise the person will die. Anaphylactic shock develops in a few seconds.
If basophilia is a consequence of intestinal diseases, then a person has the following symptoms:
Cramping and pain in the abdomen.
Diarrhea.
Flatulence.
The appearance of blood in the stool.
The presence of chronic inflammation in the body, accompanied by an increase in the level of basophils in the blood, is expressed by the following symptoms:
Muscle aches.
Swelling of tissues.
An increase in body temperature to subfebrile marks.
Numbness of the limbs.
Skin rashes.
In myeloproliferative disorders, a person develops the following symptoms:
Weakness increases.
There are headaches.
Eyesight deteriorates.
There are bruises on the skin.
Bones begin to ache.
However, the main reason for the increase in basophils in the blood is still an allergic reaction, which gives the corresponding symptoms.
An increase in the level of basophils in a child
Normally, the level of basophils in a child is slightly lower than in an adult. Their values do not exceed 0,5%. However, this difference is conditional. In childhood, an increase in basophils in one milliliter of blood up to 1% is not considered a pathology.
If a child is still diagnosed with basophilia, then most often this indicates a helminthic invasion, or an allergic reaction of the body. If blood sampling was carried out after the next prophylactic vaccination, then basophilia is a normal reaction of the body.
Diagnosis of basophilia
To determine the level of basophils in the blood, it is necessary to perform its clinical analysis. Modern devices most often calculate the leukocyte formula. At the same time, basophils are in the MID group – medium cells or in the GRN group – granulocytes. If the indicators of these populations do not go beyond the normal range, then the number of basophils is not counted separately.
When there are deviations in the leukocyte formula, the doctor may prescribe a second blood test with smear microscopy. High-tech devices are able to distinguish between all 5 types of leukocytes. Basophils will be designated in the data interpretation as BA (BAS).
What to do if the level of basophils is elevated?

Most often, an increase in the level of basophils in the blood does not require any specific treatment. Moreover, there is no therapy for basophilia. After all, this condition is not an independent pathology, but only a consequence of some disturbance in the body. Therefore, treatment should be aimed at its elimination. After the inflammatory or other reaction is stopped, the level of basophils will return to normal.
Treatment of an allergic reaction involves the elimination of the allergen, the use of antihistamines, the use of glucocorticoids. In anaphylactic shock, the patient needs an emergency injection of adrenaline.
Rheumatoid arthritis is treated with anti-inflammatory drugs and immunosuppressants.
Bacterial infections require antibiotics. With helminthic invasion, it is necessary to take anthelmintic drugs.
If basophilia is a consequence of iron deficiency anemia, then a person needs to revise his diet to include more red meat, liver, and eggs. You may need to take iron supplements to increase your hemoglobin levels.
Rarely, basophilia is a sign of blood cancer. However, in addition to basophils, a blood test will reveal a decrease or increase in the level of leukocytes, platelets and erythrocytes. Suspicion of blood cancer requires consultation of an oncologist and hematologist with a comprehensive diagnosis. Treatment involves stem cell transplantation, chemotherapy or radiotherapy.
As for the prognosis, with a mild course of infection, basophils return to normal fairly quickly. You just have to wait for the body to recover. Be sure to get more rest and spend time outdoors.
Allergies and inflammation of the internal organs often become chronic and recur periodically. At the same time, the level of basophils in the blood will increase.
Severe oncological diseases require an individual approach and long-term treatment.
So, basophilia is not a disease, but a symptom of a disease. Therefore, efforts should be directed to the treatment of the cause that led to the increase in the level of basophils in the blood.










basophils ki