Due to the complexity of the process, high labor costs, thermal energy and time, not many amateur distillers make moonshine from barley. But those who have successfully prepared this drink at least once do not want to return to raw sugar. Grain distillate is much softer and more aromatic, however, it requires a special approach. We will take a detailed look at all the technology from beginning to end, so that anyone can reproduce it at home.
The proposed recipe is suitable not only for barley, but also for other cereals: wheat, rye, corn, millet, or mixtures of different grains in certain proportions.
Theory
Yeast only converts simple sugars into alcohol, which are not originally present in the grain, so you can’t just add water and yeast. Sugar can be obtained from cereals by splitting starch with enzymes released after the germination of grains. The process is called “saccharification”.
From this it follows that in order to prepare barley mash, it is first necessary to germinate some of the grains (activate enzymes), then, to extract sugar, the sprouted barley (malt) is mixed with unsprouted cereals under special temperature conditions. Only after this, the mash can be put on fermentation.
On average, 1 kg of malt can saccharify 4-5 kg of ordinary grain, but if possible, I advise you to germinate the whole barley or as much as possible, this contributes to the complete breakdown of starch, increasing the yield of distillate.
Fans of absolutely natural drinks prefer moonshine from barley without yeast, replacing artificial dry and baker’s yeast with pre-prepared grain sourdough. The advantage of the method is that even with errors in the distillation technology, moonshine will not have a characteristic yeast odor. The disadvantage is that “wild” yeast does not always remain on the surface of the grain, often the leaven does not ferment or infects the wort with pathogenic microorganisms, such as mold. In the recipe, we will separately consider the method of preparing grain sourdough, but I still advise beginners to use ordinary yeast.
To increase the yield, you can put barley mash with sugar. The addition of regular beet sugar slightly offsets the grainy aroma and mild taste of the distillate for which it is so prized. The more sugar added, the less “bread” notes remain in the moonshine, but the drink is more. This is a compromise between quantity and quality, let everyone find the optimal proportions for themselves.
In theory, with 1 kg of barley, you can get up to 800 ml of moonshine with a strength of 40%, but in practice the starch content in grain is usually lower, along with losses during saccharification, which beginners very often experience, and distillation, the real yield of moonshine from barley is 5-20 % below the estimated. With 1 kg of sugar, 1,1-1,2 liters of distillate (40%) is obtained, the result here is more predictable, losses are possible only in case of negligence – if the yeast does not process all the sugar into alcohol, or with inept distillation.
barley mash recipe
For barley moonshine, only high-quality grain is suitable that has been aged for at least 2 months (preferably 5-6), but not older than 3 years, since old cereals have a lower germination ability.
Attention! Saccharification with malt requires strict adherence to the temperature regime, an error of 2-3 degrees is allowed, so a thermometer is required. To determine the temperature “by eye” will not work.
Ingredients:
- barley grain – 6 kg;
- water – 27 liters;
- sugar (optional) – 1 kg;
- yeast (optional) – 12 grams dry or 60 grams pressed.
Technology
1. Prepare the sourdough (only for moonshine without yeast). It is done on the day of the beginning of work with grain. Rinse 100-150 grams of barley twice with an interval of 10-15 minutes in cold water, removing floating particles, dirt and husks. Spread the grains in an even layer of 2-3 cm in a plastic or metal container. Add water (should cover a layer of barley by 1-2 cm). Cover the container and transfer to a dark place at room temperature.
After 1-2 days, sprouts will appear, you need to add 50-75 grams of sugar, mix with your hands. If the mass is very thick, add some water. Bandage the neck of the container with gauze and leave for 7-8 days. When foam, hissing and a slight smell of fermentation appear, the grain sourdough is ready. To prevent souring, it is better to put the fermented sourdough under a water seal until the fermented sourdough is added to the mash.
2. Pour at least 1 kg of peeled and sifted barley (based on the proportions in the recipe) into a soaking container – an enamel pan or a plastic bowl. Fill with water 3-5 cm above the grain level. After 8 hours, remove the floating debris and replace the water. Repeat the water change procedure twice more. The total soaking time is 24 hours.
3. Completely drain the water, the grain should be damp but not wet. Spread barley for germination in a layer of 5-10 cm. From above, to speed up the process, you can cover with a damp cloth. The recommended germination temperature is 12-20°C, ventilation is desirable.
Swollen and sprouted grain increases in volume, this must be taken into account when choosing a container, the stock must be at least 15 cm in height.
Stir every 8-12 hours with your hands so that carbon dioxide does not accumulate inside the layer. Spray dry grain as needed, but water should not accumulate at the bottom of the container.
Germination of barley (other cereals) lasts 6-10 days until the length of the sprouts reaches 5-7 mm and they begin to intertwine. When biting, the finished grains should be bittersweet, a slight cucumber smell may appear.
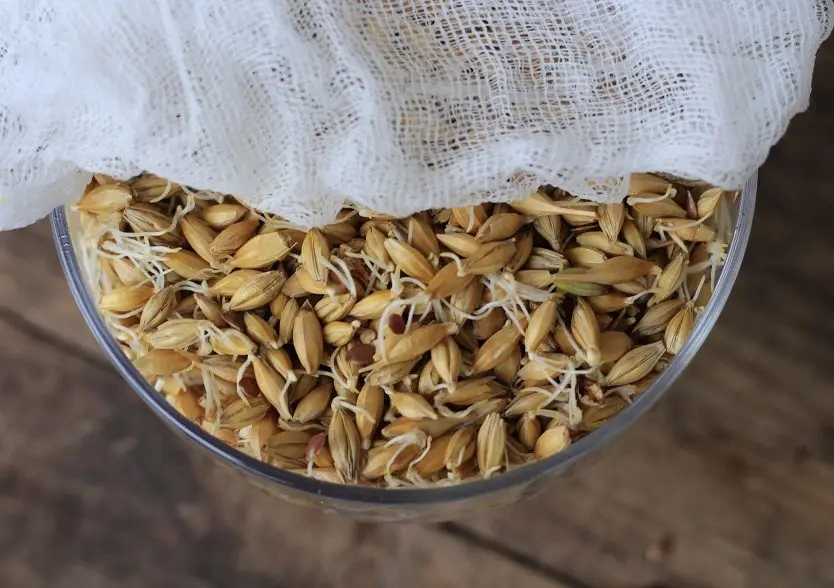

The resulting “green malt”, which is best suited for saccharification, must be used within three days (preferably immediately), otherwise the activity of the enzymes will be greatly reduced.
To increase the shelf life, green barley malt can be dried at a temperature not exceeding 40°C and the sprouts removed. The moisture content of the dried grain is not higher than 3%. In a tightly closed container, the resulting “white” malt can be stored for years, but its saccharification efficiency is 20% lower than that of green. This must be taken into account when choosing proportions.
4. Grind the resulting malt (green with sprouts) as finely as possible in a meat grinder or in another way. Add water heated to 26-29°C (3 liters per 1 kg of malt). The result is a “malted milk” that must be used within a day.
When working only with pure malt (without flour), after adding water, heat the mixture to 63°C and follow the sequence of actions described in the 9th step (skip steps 5-8).
5. Grind unsprouted barley (regular grain) to a state of flour. It should be a maximum of 5 times more than malt (according to the recipe 5 kg). You can immediately take ready-made barley or other flour.
6. Pour the flour into the cooking container – a saucepan or a bucket. Pour water heated to 50 ° C (4 liters per 1 kg of flour) in a thin stream, stirring constantly so that lumps do not appear.
7. Heat the mixture on the stove (by any other method) to 55-60°C, maintain the temperature in the specified range for 15 minutes. Then increase to 62-64°C, maintain for another 15 minutes. After that, bring the wort to a boil and cook for 1,5-2 hours, stirring every 15 minutes so that the mixture does not burn from below. The lower the quality of barley and the coarser the grinding, the more time it takes to boil, the mass should become homogeneous.
8. Cool the wort to 65°C and add the malt milk prepared in the fourth step. Pour in a thin stream, stirring constantly. Cover the container with a lid, heat the mass to 63 ° C.
9. Maintain a stable temperature of 120-55°C for the next 65 minutes, stirring every 20-30 minutes. At the end of the process, the wort should become sweet.
If the temperature exceeds 70°C, the enzymes will be destroyed and the saccharification will stop without the possibility of recovery!
10. Ready for fermentation barley wort as soon as possible (so as not to infect with pathogenic microorganisms) cool to 28°C. The easiest option is to lower the container into a bath of cold water.
11. Pour the cooled wort into a fermentation tank, add sugar and water if desired (4 liters per 1 kg of sugar). Fill the container to a maximum of 75% of the volume. Add yeast at the rate of 2 grams dry or 10 grams pressed per 1 kg of raw materials or sourdough. Mix. Yeast can be pre-diluted according to the instructions on the label.
Put a container under a water seal or a medical glove with a hole in your finger (made with a needle). Transfer to a dark room with a stable temperature of 18-27°C.
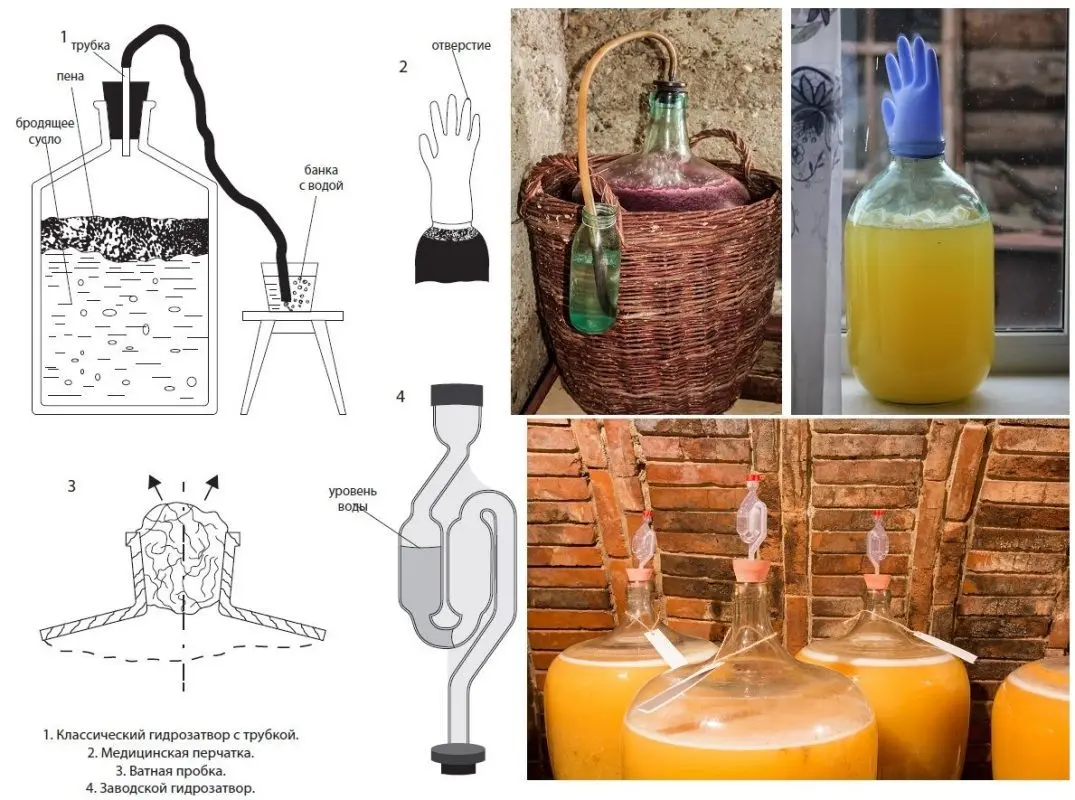
12. Depending on the quality of the yeast and the temperature in the room, barley brew ferments on average 4-7 days. Then the water seal stops emitting gas (the glove deflates), the mash becomes lighter, and a layer of sediment appears at the bottom. The taste is sour-bitter without sweetness.
Obtaining barley moonshine
13. Drain the mash that has won back without sediment and filter through cheesecloth (so as not to burn) into a distillation cube.
14. Overtake the first time without fractionation. Finish selection when the strength in the jet falls below 25 degrees. The distillate may be cloudy, this is normal.
15. Measure the strength of barley moonshine of the first distillation. Determine the amount of pure alcohol using the formula: alcohol u0,01d strength * volume * 5. For example, if there are 50 liters of 2,5%, then the pure alcohol content is 5 liters (50 * 0,01 * XNUMX).
16. Make a second distillation. The first 8-15% of the yield from the amount of absolute alcohol (in our example 220-375 ml) is collected separately. This is a harmful fraction (“heads”) that should not be drunk. It usually has a strong unpleasant odor.
17. Finish collecting the main product (“body”) when the output strength (in the jet) falls below 45%.
18. Dilute the prepared moonshine from barley to 40-45 degrees and insist 2-3 days before use in a hermetically sealed glass container in a dark, cool place so that all reactions are completed when mixed with water. After that, you can proceed to tasting or pour the drink into barrels for aging. In the second case, you get something similar to whiskey.










