Contents
Vaginosis – This is a condition in which there is a violation of the microflora of the vagina. The average age of patients with vaginosis is 20-45 years. The incidence of the disease in this group is 80%. Based on these data, we can conclude that eight out of ten women suffer from vaginosis at least once in their lives.
The disease does not pose a danger to a woman’s life, but can adversely affect her reproductive function. Often, even after the onset of pregnancy, patients with vaginosis have miscarriages. If she bears a child, then the disease threatens with intrauterine infection of the fetus, complications after delivery. Therefore, you need to know the main causes and symptoms of the disease, as well as be able to cope with it.
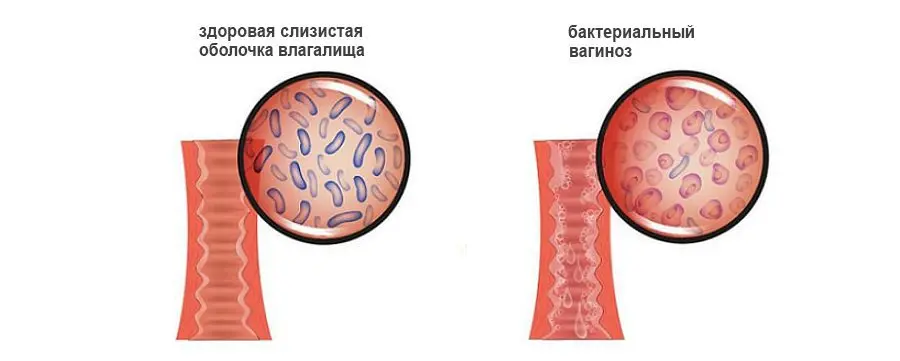
The mechanism of development of vaginosis
Man and microbial flora exist in indivisible tandem. There are microbes that, in the process of evolution, have adapted to live in the human body and even benefit it. This process is called biocenosis. Such flora is represented by a stable bacterial composition. Some bacteria inhabit exclusively the dermis, others live in the mouth, and others in the gastrointestinal tract. Such bacteria benefit the human body by destroying the harmful flora, producing vitamins and stimulating the work of its immunity.
Lactobacilli live in the vagina. They look like small thick sticks. The bacteria break down glycogen, which is found in the epithelium that lines the vagina. During this process, lactic acid is released. Due to which the acidic environment is maintained in the vagina. Pathogenic microorganisms die in it, which is the norm. In the biocenosis of the vagina, lactobacilli account for 95-98% of all beneficial microflora.
Sometimes it happens that lactobacilli are destroyed. Then other microbes take their place. The acidic environment of the vagina changes, which creates favorable conditions for pathogenic microorganisms to enter it. They can be sexually transmitted, or they can reproduce on their own. In the latter case, they speak of nonspecific vaginosis. Lactobacilli are replaced by flora, which inhabits the perineum, urethra, perianal folds. Microbes begin to multiply rapidly, but such flora is not able to perform the functions of lactobacilli.
A change in the biocenosis of the vagina leads to the fact that not only metabolic, but also immune processes fail in it. The production of immunoglobulin A decreases. It is this substance that prevents pathogens from attaching and penetrating deep into the epithelial wall of the organ. The epithelium itself tries to cope with bacteria, which leads to excessive desquamation of its particles. This explains the increase in the volume of vaginal discharge in vaginosis. Lactobacilli are replaced by anaerobic bacteria. This is the name of microorganisms that are able to maintain their vital activity in an oxygen-free environment. Some of them produce amino acids and volatile fatty acids. They are broken down in the vagina to volatile amines. These amines have an unpleasant odor that resembles the smell of fish.
The vaginal environment changes from acidic to alkaline. The metabolism of fats, proteins, minerals and carbohydrates is disturbed, the epithelium produces more mucus. This is the first sign of developing vaginosis. At the same time, the walls of the vagina themselves are not inflamed. All changes are purely physiological in nature.
Causes of vaginosis
Bacterial vaginosis cannot be called a sexual infection, since there are no infectious representatives of the flora in the vagina. This disease is called nonspecific vaginosis. The main reason for its development is a change in the vaginal environment, which further leads to an imbalance in the microflora.
A wide variety of microbes are capable of replacing lactobacilli.
Microorganisms such as:
Peptococcus.
Bacteroid.
Megaspheres.
Peptostreptococci.
Aptopobium.
Leptotrichia.
Mycoplasmas.
Gardnerella.
Bacteria with disturbed microbiocenosis of the vagina begin to multiply rapidly, in 1 ml of secretion their number can reach 1010. In this case, for the development of bacterial vaginosis, there must be appropriate conditions. Therefore, there are 2 groups of causes that can become an impetus for the development of the disease. They are divided into internal and external.
Internal factors include:
Hormonal imbalance in the body of a woman with excessive production of progesterone.
Atrophy of the vaginal mucosa.
Intestinal dysbiosis.
Deterioration of immunity.
External factors that affect the development of the disease:
Long-term use of antibiotics.
Treatment with drugs that adversely affect the immune system. First of all, this applies to cytostatics and immunosuppressants.
Radiation therapy for cancer.
The presence of a foreign object in the vagina, such as a tampon, pessary, diaphragm to prevent unwanted pregnancy.
Use of spermicides.
Douching that is done too often.
Errors in intimate hygiene.
Any of these reasons leads to the fact that the microbiocenosis of the vagina is disturbed. In the future, this can provoke vaginosis.
During pregnancy, vaginosis develops mainly due to hormonal imbalance. In order for a woman to be able to bear a child, the level of progesterone in her body rises. This hormone helps to reduce the level of glycogen in epithelial cells. Lactobacilli will have nothing to eat, they begin to die, which provokes a change in the acidic environment of the vagina to alkaline. Another effect of progesterone is a decrease in immunity, which creates a favorable environment for the reproduction of pathogenic microflora.
Symptoms of vaginosis

Vaginosis is not a sexual infection, but its symptoms often resemble STDs. In addition, vaginosis often occurs after a change of sexual partner. About a day after intimacy, a woman has the first signs of discomfort. This happens on the condition that intimacy occurred without the use of a condom.
When the cause of vaginosis is the intake of antibacterial drugs, menopause or another factor, then sexual life does not have any effect on its development.
Symptoms of acute vaginosis can be identified as follows:
An increase in the volume of secretions from the genital tract. They become grayish in color, have a uniform consistency. They start to smell bad. The discharge becomes more after intimacy, after menstruation, after using irritating intimate hygiene products.
Pain that occurs during intimacy.
Itching and burning in the vulva. Sometimes this symptom is absent altogether.
Some patients complain of pain during bladder emptying.
Also, pain can occur in the pubic area.
If vaginosis haunts women for 60 days or more, and the treatment does not bring the desired relief, then they talk about the chronic form of the disease. In this case, a woman is most often diagnosed with a hormonal imbalance. A complication of sluggish vaginosis is atrophy of the mucous membranes of the vagina.
Diagnosis of vaginosis
To confirm the diagnosis, you need to visit a gynecologist. The doctor will take an anamnesis, find out the main complaints of the woman. The next stage of diagnosis is an examination on the gynecological chair. In the course of its conduct, the doctor collects mucus.
Facts that allow you to make a preliminary diagnosis of “vaginosis”:
The age of the patient. Vaginosis most often develops in women 20-45 years old.
Recent change of sexual partner or surgery.
Recent use of antibiotics.
The presence of symptoms characteristic of vaginosis.
During a gynecological examination, the doctor evaluates the external and internal genital organs. If the disease develops due to the reproduction of opportunistic flora, then the color of the vagina does not change, its walls remain of a uniform tone, there are no signs of inflammation.
Allocations are distributed unevenly along the inner wall of the vagina. If the disease is in the acute phase, then the color of the discharge is grayish, an unpleasant odor emanates from them.
Chronic vaginosis is characterized by yellow or green discharge. They are thick, viscous and can form into curd lumps or clots. Sometimes the discharge foams.
During the examination, the doctor evaluates the acidity of the vagina. He does this with the help of an indicator strip. If a woman has vaginosis, then the indicator exceeds 6.
To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor performs a rapid test. A smear from the vagina is applied to the glass and mixed with caustic potassium at a concentration of 10%. At the same time, a sharp fishy smell begins to emanate from the collected mucus. In this case, the test is considered positive.
Another swab from the vagina is sent to the laboratory. Epitheliocytes will be found in it. These are cells of the vaginal mucosa that contain gram-variable microbes. The cells themselves do not have a clear outline, they become granular. The level of lactobacilli in the smear is significantly reduced. At the same time, streptococci, bacilli and other pathogenic flora in significant quantities will be found in it.
Bacterial sowing of a smear with suspected vaginosis is rarely performed, only when it is necessary to find out exactly which representatives of the pathogenic flora inhabit the vagina.
If there is a suspicion of sexual infections, a PCR test is performed.
Differential diagnosis of vaginosis is carried out with diseases such as trichomonas colpitis, nonspecific colpitis, candidiasis, gonorrhea.
The effect of vaginosis on the process of conception and pregnancy

With bacterial vaginosis, a woman can become pregnant, since the disease does not cause any pathological changes in the genital tract. Male sperm itself is alkaline. Once in the vagina with vaginosis, nothing happens to the spermatozoa.
After pregnancy, opportunistic microflora can enter the uterine cavity and lead to infection of the fetus. In this case, the child will lag behind in development, will not gain the desired body weight.
Sometimes vaginosis causes miscarriage, early rupture of amniotic fluid, the birth of a premature baby.
There is also an increased risk of blood poisoning during childbirth. The danger is especially high for those women who have undergone a caesarean section.
Treatment of vaginosis

Vaginosis is treated by a gynecologist. However, if a woman has diseases of other organ systems, then she can be referred for a consultation with an endocrinologist or gastroenterologist. Treatment is carried out at home, the patient is not placed in the hospital.
The therapy is aimed at destroying the pathogenic flora in the vagina and restoring normal microflora in it, that is, lactobacilli. It is important not only to eliminate the symptoms of vaginitis, but also to get rid of the cause that provoked its development. As practice shows, the passage of one-stage treatment leads to the fact that in 35-50% of cases the disease recurs. To prevent this from happening, you must strictly adhere to the timing of therapy, which should be phased.
First, the patient is prescribed antibiotics. They allow you to destroy the pathogenic flora that inhabited the vagina. For this purpose, drugs such as: Metronidazole, Clindamycin, Tinidazole can be used. All these agents are destructive to anaerobes.
Doctors point out that with an uncomplicated course of the disease, it is better to give preference to local antibiotic therapy. This will avoid many of the side effects that such drugs have on the body as a whole.
Therapy is selected by the doctor on an individual basis:
Metronidazole. The drug is used in the form of a gel with a concentration of 0,75%. It is inserted into the vagina once every 24 hours. The course of treatment should last no more than 5 days.
Clindamycin gel with a concentration of the main active ingredient of 2%. The drug is injected into the vagina 1 time in 24 hours. The course of therapy is a week.
Tablets Tinidazole 2 g. They are taken 1 time in 24 hours. The course of treatment is 3 days.
Clindamycin suppositories 100 mg. They are inserted into the vagina once every 1 hours. The course of treatment should last 24 days.
Tablets Metronidazole 2 g. The drug is taken orally once.
If vaginosis develops in a pregnant woman, then antibiotics are prescribed to her no earlier than the 2nd trimester. They are used in tablet form. Treatment should last 7 days, but no longer.
During the course of therapy, it is important to exclude any alcoholic beverages. This applies even to small doses of alcohol. Drugs that are used to treat vaginosis react with ethyl alcohol and cause severe intoxication of the body. Its symptoms are similar to those of a hangover. The woman’s weakness increases, there is a tremor of the arms and legs, blood pressure rises, intense headaches occur. The patient is nauseated and vomits.
The composition of the drug Clindamycin contains fat, which can damage the integrity of the condom. You need to enter any means into the vagina before going to bed. This will allow the drug to remain inside the woman’s body for a long time and not leak out.
If a woman has an individual intolerance to antibacterial agents, then antiseptics are prescribed for the first-stage therapy.
These can be tools such as:
Hexicon. It will be necessary to enter 1 candle every 12 hours. The course of treatment is 10 days.
Miramistin. Irrigate the vagina with this solution once a day. The course of treatment lasts a week.
The second stage of treatment of vaginosis is reduced to the use of drugs containing lactobacilli. They allow you to normalize the microflora of the vagina. They begin to be used 2-3 days after antibiotic therapy is completed.
For this purpose, drugs such as:
Candles Acilact. They are inserted into the vagina 1 piece 2 times a day. The course of therapy lasts 5-10 days.
Bifiliz drug. It is taken orally 5 doses 2 times a day. The course of treatment lasts 5-10 days.
Candles containing an antifungal component are not prescribed for women. They can be used only when the disease is accompanied by pathogenic growth of fungi of the genus Candida. In this case, use the drug Clotrimazole. It is inserted into the vagina once every 1 hours. Treatment will have to continue for 24 days.
Experts strongly do not recommend self-medication. If you choose the wrong dose, this can lead to resistance of pathogenic microflora. It will be more difficult to cope with such a disease, as well as with a chronic form of the disease. Therefore, at the first symptoms of vaginosis, you need to go to an appointment with a gynecologist.
Video: gynecologist Yulia Fakhradinova Balatskaya about bacterial vaginosis:









