Contents
Prostatitis is a fairly common inflammatory disease of the prostate gland. Without treatment, prostatitis can become chronic, or even cause infertility. We will deal with an expert how bacterial prostatitis manifests itself, what causes it, how it is treated and whether this problem can be avoided.
What is bacterial prostatitis
Bacterial prostatitis is a disease that is caused by various pathogenic microorganisms. Most often it is E. coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, gonococci and chlamydia1. Some of these bacteria belong to opportunistic microflora, which is always present in the human body and causes disease only in the presence of predisposing factors.1.
Causes of bacterial prostatitis in men
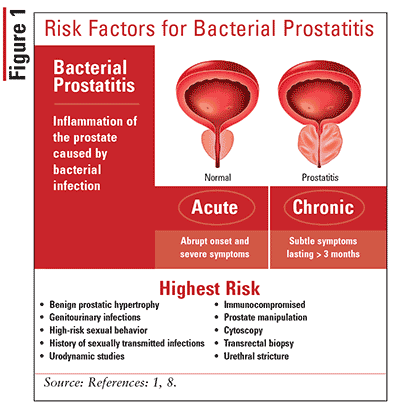
As a rule, for the development of bacterial prostatitis, in addition to the penetration of bacteria into the gland tissue, other reasons are necessary. It would be more correct to call them risk factors. The chance of getting bacterial prostatitis will be higher in men who:
- suffer from immunodeficiency conditions;
- underwent a biopsy or surgical intervention on the genitourinary organs;
- lead a promiscuous intimate life;
- have a history of gastrointestinal diseases, which are accompanied by diarrhea and constipation.
Lifestyle is also important. The results of some studies confirm that the development of prostatitis can be provoked by night work, smoking, alcohol abuse, spicy and fatty foods.1.
Symptoms of bacterial prostatitis
The clinical manifestations of acute and chronic bacterial prostatitis differ significantly from each other. In chronic prostatitis, the symptoms are minor and can only appear during periods of exacerbation. Most often, men with chronic prostatitis complain of discomfort in the perineum and frequent urge to urinate.2.
In acute bacterial prostatitis, the symptoms are pronounced:
- frequent urination (more often at night);
- pain in the sacrum, scrotum, bladder and perineum;
- burning in the urethra and discharge from it;
- difficulty urinating.
Sometimes these symptoms may be accompanied by fever, erection instability and pain during ejaculation.2. Most often, acute bacterial prostatitis develops rapidly, symptoms appear and increase sharply on the first day, which leaves no doubt when making a diagnosis.
Treatment of bacterial prostatitis
The main treatment for bacterial prostatitis is aimed at suppressing pathogenic bacteria and treating complications. Mild forms of prostatitis can be treated on an outpatient basis. If the course of the disease is accompanied by high fever, intoxication and a general deterioration in well-being, hospitalization and more intensive therapy are necessary.
Diagnostics
In the acute form of the disease and exacerbation of chronic prostatitis, there are usually no difficulties in making a diagnosis. The patient complains of characteristic symptoms, and the prostate gland is swollen and enlarged, which is easily determined by palpation. For laboratory confirmation of the diagnosis, a complete blood and urine test will be required.3. Bacteriological seeding of prostate secretion will reveal the type of bacteria that caused inflammation and their sensitivity to antibiotics. PCR research will help to find or exclude infections that are sexually transmitted.
During the examination, an additional set of studies may be needed:
- transrectal ultrasound of the prostate;
- tests for the detection of oncology;
- spermogram to determine the threat of infertility.
Therapies
Treatment for bacterial prostatitis in men is usually complex, including medication, physical therapy, and diet.3.
Medication
The means of drug treatment, first of all, include antibiotics, to which the pathogen is sensitive. The result comes quite quickly – within a few days, but the treatment lasts at least 4 weeks. During this period, it is usually possible to completely defeat pathogens and avoid the transition of the disease to the chronic stage. If necessary, antibiotic therapy is extended up to 6 weeks or longer.
If you have difficulty urinating, alpha-blockers are prescribed. Also, the doctor may prescribe non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, drugs to improve blood circulation, and in some cases, antidepressants.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is used after the end of the acute period of the disease. Prostate massage, therapeutic baths, acupuncture are prescribed. Laser therapy shows good results.
Diet
Diet is of great importance for the restoration of the gastrointestinal tract, since constipation is the most common cause of relapses.
Alcohol, fatty, spicy and smoked foods are categorically excluded from the diet. Showing foods high in fiber, rich in vitamins and trace elements. Food should be easily digestible and stimulate the bowels. Drinking water is important to prevent dehydration.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies are good only as an addition to the main treatment. With the help of decoctions and infusions of herbs, you can relieve stress, stimulate the immune system, and normalize bowel function. Many herbs and fees have an anti-inflammatory effect. Do not forget to consult with your doctor before using folk remedies. Remember that self-treatment does not always lead to the desired result and can complicate the situation.
Prevention of bacterial prostatitis
The main goal of preventing bacterial prostatitis is to prevent infection from entering. The most effective way is to lead a healthy lifestyle. Eat well, do not forget about physical activity. Personal hygiene and safe sex practices minimize the possibility of infection. Do not overcool, monitor the state of immunity. Doctors recommend, starting from the age of 30, to regularly undergo examination by a proctologist and urologist.
Remember, it is much easier to prevent a disease than to treat its consequences.
Popular questions and answers
We asked our expert general practitioner Mikhail Lystsov answer the most frequently asked questions about bacterial prostatitis.
How to understand that prostatitis is bacterial?
Why is bacterial prostatitis dangerous?
What can not be done with bacterial prostatitis?
The main thing that can not be done is to delay the moment of going to the doctor after the first symptoms appear. The sooner treatment begins, the more effective it will be.
Sources of:
- Medical encyclopedia. Astrel, 2009. https://search.rsl.ru/ru/record/01000718460
- Smirnov V. A. Drug therapy of chronic prostatitis. Pharmindex-Practician, No. 10, 2006. https://www.pharmindex.ru/practic/10_urology1.html
- Chronic prostatitis. Gorilovsky L.M., Dobrokhotov M.M. Medical advice. M., 2010.