Contents
Bacterial burn of an apple tree (also called bacteriosis) is a dangerous infectious disease that manifests itself by blackening of leaves, ovaries, secretions on the bark, as well as fruit mummification. Often leads to the complete death of the tree, spreads to neighboring plantings. Treatable only in the early stages. For treatment, chemicals belonging to the group of antibiotics are used.
Causes of appearance
The disease has an infectious nature. It is caused by bacteria from the genus Erwinia amylovora. They are distributed in different ways:
- with raindrops;
- wind;
- with irrigation water;
- aphids;
- bees;
- gall midges;
- birds.
The pests overwinter in the plant tissues of the infected tree. With the onset of spring, they activate and parasitize the apple tree again, and can spread to neighboring plantings. The disease develops in relatively warm (temperatures from 18 degrees) and humid weather (from 70%).
Signs and symptoms
Bacterial burn affects the entire aerial part of the apple tree. The main symptoms of the disease are the following signs:
- The leaves are deformed, begin to curl up. Then they turn black, but do not fall off.
- Trees look like burnt ones.
- The bark on young branches swells due to the large influx of fluid.
- Then the liquid begins to flow down the bark.
- At first, the discharge has no color, then it darkens and solidifies in the form of drops of yellow or brown color.
- Apple blossoms quickly wither and turn dark.
- Shoots dry out and die.
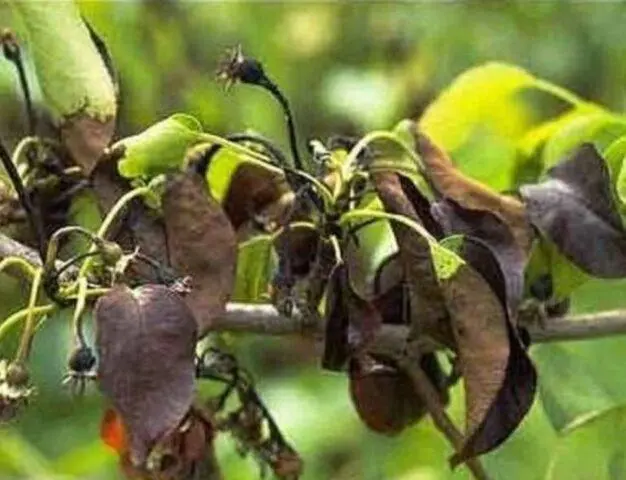

An apple tree affected by a bacterial burn can be identified by blackened foliage.
The disease is ubiquitous. Bacterial burn affects not only apple trees, but also pears, as well as quince, mountain ash, rose, raspberries, strawberries and other crops. Exacerbation of the disease is observed up to three times per season:
- In the second half of spring, when flowering occurs.
- At the beginning of summer (June), during the period of intensive growth of shoots.
- In late August – early September, when secondary growth of annual shoots is observed.
What can be confused with a bacterial burn
Diagnosing a bacterial burn of an apple tree is quite simple. But it can be confused with bacterial cancer, i.e. cortical necrosis. This is also a bacterial disease caused by Pseudomonas syringae.
The main signs of this pathology:
- Sudden wilting of young leaves that appear in spring.
- Dark spots without plaque form along the edge of the leaf plate.
- The leaves do not fall off and continue to remain on the tree.
- Flowers and buds that have not blossomed also darken and remain on the apple tree.
- Cracks in the form of wedges form on the bark. They separate diseased tissues from healthy ones.
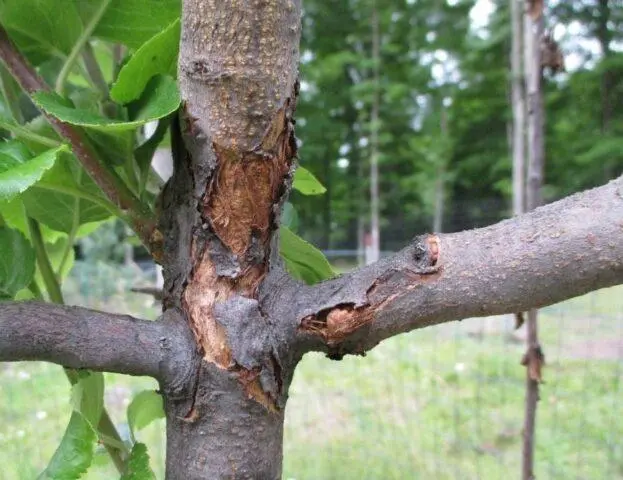

Cancer of an apple tree is diagnosed visually
The symptoms of fire blight resemble damage caused by drought. The comparison is presented in the table.
Sign | Bacterial burn | Drought damage |
Leaf condition | Red patches between veins | Brownish areas on the edges of the leaves. Damage does not affect the veins |
State of shoots | Wither like a “shepherd’s crook” or “whip” | Branches remain straight when withering |
The development of lesions | Top down | |
bark condition | Raw, sticky. White discharge gradually turns brown | The bark is dry. There are no selections |
Flowers, ovaries | The buds become dark brown and die off, remaining on the branches. The ovaries darken and do not grow | Do not change color, do not fall off |
Fruit condition | Covered with secretions, then mummified. Remain on branches, hibernate | May become wrinkled, but do not mummify. Fall to the ground |
This is a fungal disease that affects leaves (they do not fall off even in winter) and bark (longitudinal cracks, ulcers). At the same time, the bark noticeably lags behind on skeletal branches, and on young ones it only peels off.
Treatment of an apple tree from a bacterial burn
Treatment is carried out by complex methods – chemical and biological preparations are used simultaneously. As an additional measure, you can use folk remedies.
Chemical preparations for bacterial burn of an apple tree
To treat pathology, gardeners use chemicals – antibiotics:
- “Ampicillin” – 1 ampoule is diluted in 1 liter and the tree is sprayed throughout the season.
- “Fitolavin” – 20 ml per 10 liters. They process the apple tree and the near-trunk circle.
- “Streptomycin” (1 ampoule) and “Tetracycline (3 tablets) – dissolve in 5 liters and carry out treatment from a bacterial burn before flowering, during and after it.
- “Gentamicin” – 1 ampoule per 1 liter. Moisten the gauze and tie the damaged areas (they are cleaned first).
- “Ofloxacin” – 1 tablet per 1 liter. Moisten the bandage and also tie the damaged area. You can also dissolve 2 tablets in 10 liters and treat the apple tree from a bacterial burn before flowering and after it.
Ampicillin and other antibiotics are used to treat burns.
But this is only an additional, and not the main means of treatment.
Biopreparations
Biological agents are not used to treat bacterial burns. They are used only to increase immunity simultaneously with the chemicals described above. Among the most effective drugs are the following:
- “Stimix Concentrate” – diluted 100 ml in 10 liters. Water the tree after harvest.
- “Stimix Standard” – 50 ml per 10 liters. Leaves are processed seven times over the summer with a break of two weeks.
- “Stimix Fitostim” – 50 ml per 10 liters. Processing is carried out once a month.
- “Baikal EM-1” – 10 ml per 10 liters. Three sprays are carried out per season.
- “Shining-1” – 10 ml per 110 liters, treatment is carried out in the spring (watering the apple tree).
Folk remedies
Folk remedies will not help cure a bacterial burn. But they can be used as an additional means of treatment, as well as for prevention. With the help of treatment with solutions, an acidic environment is created – in such conditions, the spread of infection is difficult. Also, home remedies can be used as an additional top dressing of an apple tree to increase its resistance to diseases.
Basic recipes (for 10 liters of water):
- Boric acid – 10 g.
- Succinic acid – 10 tablets.
- Wood ash – 200 g.
- Dry yeast – 10 g.
- Sugar – 2 tablespoons (must be dissolved in warm water).
All solutions are used to treat an apple tree from a bacterial burn in the late evening or early morning. They can be alternated with the main drugs (interval 3-5 days).
It is placed in the trunk circle as a mulch (layer 5-7 cm). It destroys bacteria and also contributes to the saturation of the soil with valuable nutrients (phosphorus and potassium).

Boric acid and other folk remedies can only be used as an auxiliary measure.
preventive measures
Bacterial burn is a very dangerous disease that often leads to the death of a tree. Therefore, gardeners need to know not only about methods of treatment, but also about preventive measures:
- Always observe the watering rate – a young apple tree is given no more than three buckets of water, an adult – no more than eight. It is better to take water from the water supply, previously settled at room temperature.
- To facilitate the treatment of a bacterial burn of an apple tree, in the fall, all plant residues are carefully removed and burned. If the tree has already been damaged, all affected parts must be removed, including mummified fruits.
- Do not neglect potash and phosphorus top dressing, especially during flowering and the formation of ovaries, as well as during the treatment of a tree from a bacterial burn.
- Carefully inspect the seedlings when buying. Purchase them only from trusted suppliers, in nurseries.
- Plant apple trees at a distance of at least 4 m from each other.
- Regularly trim the crown, especially if the variety is prone to active shoot formation.
- During pruning, disinfect garden tools with potassium permanganate or other preparations.
- Every spring, carry out preventive treatment from pests. In summer, you also need to monitor the appearance of aphids and other insects. If necessary, treat with an insecticide, for example, “Aktara” or “Fitoverm”.
Common mistakes in treatment
Beginners and even experienced gardeners often make mistakes in the treatment of a bacterial burn of an apple tree. They are associated with both incorrect diagnosis and the procedures themselves. The main inaccuracies are:
- If you make the wrong diagnosis, then the treatment will be wrong. For example, a gardener may think that an apple tree has been hit by a drought and will over-water it, causing the disease to spread even more.
- Treatment with fungicides. These drugs are used to kill fungi, and bacteriosis is treated by other means, including those described above.
- Also, gardeners can leave mummified apples on the branches, especially if they grow at a height that is difficult to reach. And they need to be completely removed and burned, since it is in such parts that pathogens overwinter.
- Another common mistake is that summer residents avoid the use of chemicals, and for a long time they are treated with folk remedies. This measure will not help – the disease will continue to develop. Therefore, it is better to immediately use chemical and biological agents.
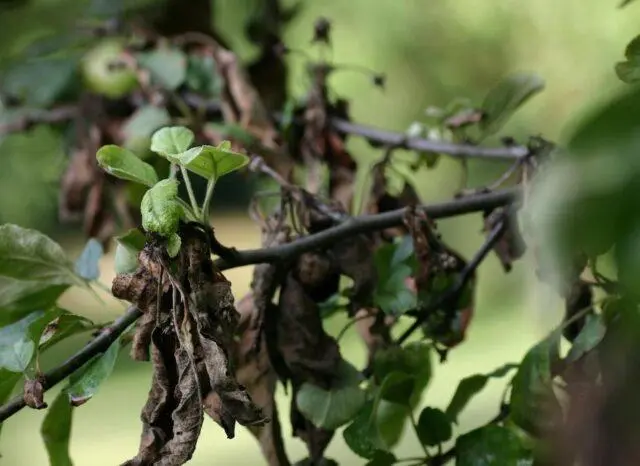

For successful treatment, it is necessary to learn how to accurately diagnose the disease.
Conclusion
Bacterial burn of an apple tree is quite dangerous, and it is not always easy to deal with it. Therefore, it is recommended to follow general preventive measures and learn how to diagnose the disease by external signs. Antibiotics are mainly used for treatment. Biological preparations and folk remedies can only be considered as an additional measure.









