Contents
Meningitis: all about this disease in infants
La childhood meningitis is generally benign. Indeed, nearly 70% of affected children recover spontaneously. This disease should not be taken lightly! Poorly taken care of, it can give rise to dramatic complications for the child. For the sake of the baby, it is therefore better to learn as much as possible about the meningitis.
How does a baby get meningitis?
La meningitis is an inflammation of the meninges and an infection of the fluid they contain. The meninges are membranes that protect the brain and spinal cord. This inflammation is usually a complication of a primary disease. Baby first has mumps, chickenpox, tonsillitis, otitis … Then the virus or bacteria responsible for the disease penetrates further into the body, causing baby meningitis.
7 to 8 in ten cases are due to a virus and are easily cured. The other cases are mainly bacterial meningitis, more worrying for baby. The main bacteria responsible are pneumococci and meningococci. Meningococcus C, responsible for meningitis C in babies, is the most formidable of these bacteria. The bacterial forms are very contagious, and are easily transmitted between children at nursery or at school. Bacteria can spread via saliva (sneezing, kisses), by contact with an infected object … Note: this is extremely rare in France, but babies can also contract a parasitic form of this disease, if their immune system is deficient. It is usually caused by a small parasitic worm, the nematode, and remains quite benign.
Meningitis: what are the signs and symptoms in children?
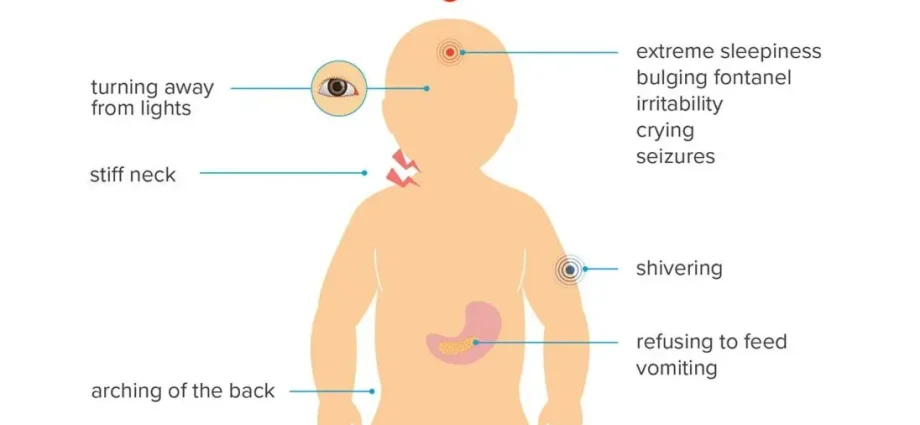
Regardless of the cause of the disease and the type of meningitis, the main symptoms of meningitis in babies remain similar. These are mainly photosensitivity (the child cannot stand the light), headaches, fever, and drowsiness. The nape of the neck is normally stiff, but not in a very young baby. Baby is cranky and sometimes has diarrhea as well. Warning: if the child suddenly has a high fever, loses consciousness and has small reddish spots on his skin, it is an emergency! These symptoms are those of a purpura fulminans, a very serious and rare complication of meningitis C potentially fatal outcome.
How to detect meningitis in babies?
Regardless of the type of meningitis, to confirm the diagnosis, the baby must go to the hospital for a lumbar puncture. Of cerebrospinal fluid contained in his spine is thus removed, usually under local anesthesia. A clear liquid indicates a viral origin: baby can go home for treatment. If the fluid is cloudy, purulent, this indicates a bacterial origin. Baby must stay in hospital for treatment. A bacteriological analysis of the cerebrospinal fluid makes it possible to determine which bacteria is responsible and which treatment is appropriate.
Treatment of meningitis in babies
La viral meningitis in young children has no specific treatment. It will indeed pass by itself in 7-8 days on average. On the other hand, it is possible to relieve the symptoms of the child: paracetamol against fever, painkillers for headaches …
For bacterial forms, it is first of all advisable to play the prevention card. Immunize baby with pneumococcal and meningococcal vaccines is particularly recommended, if not mandatory.
Remember that the vaccines against Haemophilus influenza type B (responsible for pneumonia and meningitis), against pneumococcus and against meningococcus of serogroup C are now part of the 11 vaccines are mandatory for infants born after January 1, 2018. As for the meningococcal type B vaccine, it is recommended in some cases, especially when there are cases within the community (school, nursery) attended by the child.
If the baby is already infected with one of these bacteria, let the hospital medical team do it. The treatment is essentially based onantibiotic injections.
In the rare cases of parasitic causes, treatment is mainly based on corticosteroids.