Contents
No one will argue with the statement that the rose is the queen of flowers in the garden. Each of her flowers is a miracle created by nature, but with the help of the caring hands of the grower. Roses require careful care and, with the exception of a few species, are not able to endure frosty winters without reliable shelter. What do garden roses expect from a grower in the fall? The main task is to properly prepare them for wintering and provide protection from frost.

Preparing roses for wintering
A feature of roses is that they are unable to independently stop the growing season by autumn. Therefore, the grower will have to encourage the rose to do this. And the process should begin long before the onset of cold weather. What do I need to do?
- Already in August, stop feeding the bushes with nitrogen-containing fertilizers, and it is better not to do this from mid-July. But feeding rose bushes with superphosphate and potassium salt is an indispensable part of care. In mid-August, pour a teaspoon of superphosphate and potassium sulfate under each bush and lightly bury them in the ground. Potassium chloride is not suitable for these purposes – chlorine greatly inhibits the root system of roses.
- With the beginning of September, do not loosen or dig the ground under the bushes.
- Do not allow new shoots to grow and inhibit the growth of old branches so that they mature. To do this, stop pruning faded shoots of roses. Let the seeds form. And if the shoots suddenly decide to bloom, do not cut them out so as not to stimulate growth, but simply bend the bud at the base and then the growth of the shoot will stop and there will be no flowering. It is useful to pinch actively growing shoots of roses.

- Reduce watering rates. It is possible only when the weather is dry for a long time. If autumn is rich in rains, stretch a film over the bushes and this will stop the access of moisture. You can also dig drainage grooves near the bushes.
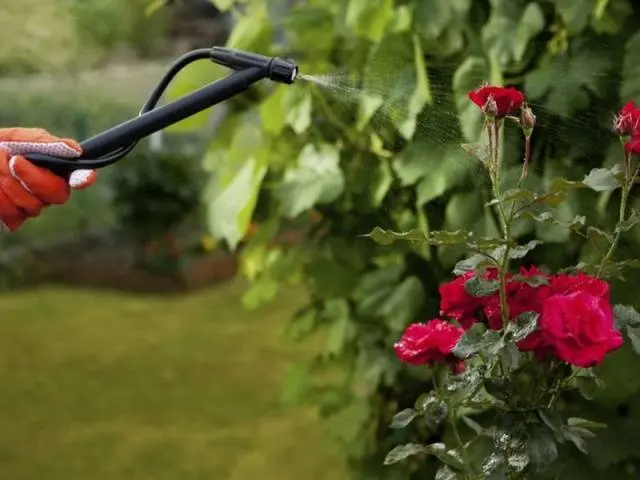
- Free rose bushes from accumulated parasites – aphids, sawflies and other pests by applying an insecticide. You need to spray the bushes in dry and calm weather.

- Care of roses at this time also consists in removing diseased leaves and shoots. Healthy leaves from the bushes are removed immediately before shelter, so as not to provoke the growth of new leaves from dormant buds.
- If weeds appear under the rose bushes or flowers remain that were specially planted, they must be removed.
- It would be useful to spray the shoots to the entire height of the future hilling with copper-containing preparations. Grab some of the shoots a little above this level as well.

With the beginning of October, the first frosts usually come. If the temperature does not drop below minus 6 degrees, there is nothing to worry about. Such a frost will not harm garden beauties, but will even be useful. A rose before shelter must undergo a certain hardening. But the approach of a serious cold snap is a signal that the time has come to create shelter for the roses for the winter. We will tell you how to do this step by step.
Stages of winter shelter of roses
Different types of this delightful flower relate to frost in different ways. The most persistent roses are Canadian selection and park roses. Manufacturers recommend only to sprinkle the base of the rose bush for insurance, declaring frost resistance up to -40 degrees. But in fact, it will not be superfluous to organize a minimum shelter for these varieties. The rest of the species need a thorough warming.

Traditionally, roses are covered with spruce branches. But practice has shown the unreliability of this shelter in the event of severe frosts with a small amount of snow. Yes, and now there are so many roses planted that you can simply lime the coniferous forests, breaking off the prickly paws. The abundance of modern covering materials makes it possible to do without the barbaric extermination of pines.
How to start sheltering roses for the winter?
- We remove all leaves and unripened shoots, they can be recognized by their bright green color and soft structure. It is better to do this in several stages, starting from the bottom of the bush, so as not to weaken the plant.
- Whether it is necessary to cut healthy shoots from a rose – each grower decides for himself. There are many supporters and opponents of this operation. Everyone has their own reasons. One can only say about the pros and cons of pruning rose shoots. Pros: Cut bushes are easier to cover, more nutrition accumulates in the remaining part and protection against infection is improved. Cons: pruning stimulates dormant buds and, with a strong thaw, they can bloom, and with further cooling, they can die.
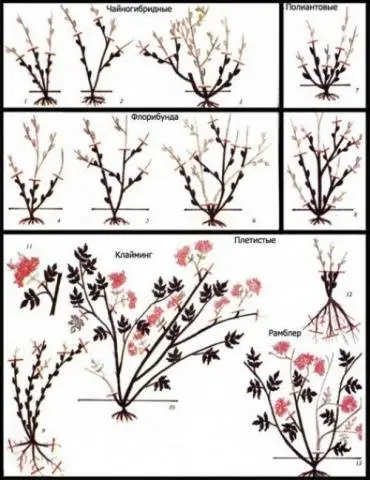
- If you still decide to cut, then you need to know that hybrid tea and polyanthus roses, floribunda are cut to half the height of the bush. In climbing and semi-climbing roses, the branches are only slightly shortened, since the main flowering next year will be on last year’s shoots. The hardest thing is with scars. If you do not want to cut them to 40 cm, you will have to gradually bend the shoots to the ground. Severe pruning of scrubs will delay their flowering next year. Polyanthus and miniature roses do not need pruning at all, you just need to clear the bushes of leaves and wilted flowers.
Pruning scheme for different types of roses
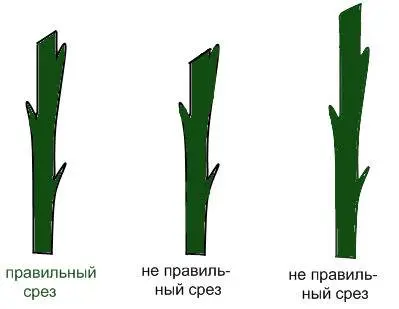
- The timing of pruning rose bushes depends on the temperature outside. It is undesirable to do this in frost – the shoots become brittle. The weather should be dry, preferably sunny.
- Cutting technique: the cutting tool must be sharp, disinfected with alcohol, the cut is made at an angle of 45 degrees.

- The cut points are covered with pitch, and the plant itself is sprayed with a solution of copper sulphate.
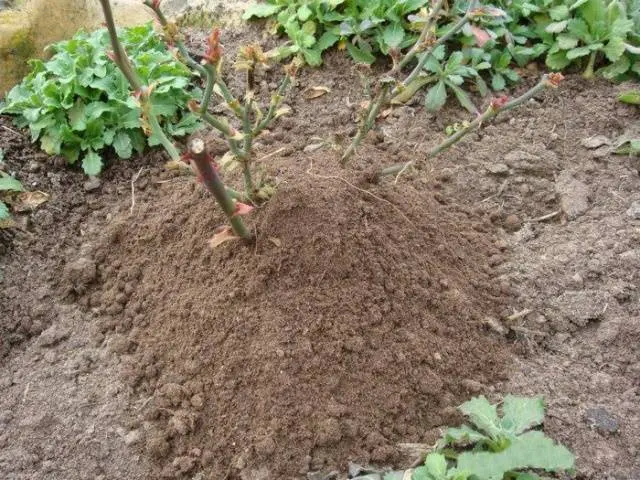
- We fall asleep rose bushes to a height of up to 30 cm with any of the following materials: earth, peat, humus, sand so that a hill forms at the stems. Low cut rose bushes fall asleep completely. The substrate for backfilling should only be dry and loose. Make sure it stays that way all the way to cover.

- Gradually, in a few days, we bend the thick shoots to the ground. It is impossible to do this in frost – the branches become brittle and can break.
- Rose shoots should not just lie on the ground. Under them, you need to put a material that does not allow moisture to pass through so that the bushes do not rot. Boards, plywood, plastic or foam sheets are suitable.

- When the rose bushes are fully prepared and stable frosty weather has been established with slight negative temperatures, a dry air shelter is built. First, the bushes are covered with any non-woven covering material, then arcs or wooden frames are placed and a film is thrown over them. In areas with a harsh climate, you can additionally insulate the structure with cardboard. There should be a gap of about 10-15 cm between the film and the covering material for air circulation. Be sure to leave holes at the bottom so that the structure can be ventilated during light frosts and thaws.

Autumn pruning can be combined with the propagation of roses.
Do not be surprised, roses can be propagated in the fall. Of course, the best results are obtained if this is done in the middle of summer. But at this time, you have to cut off the flowering stem, which affects the decorativeness of the plant. In autumn, after pruning, many unnecessary shoots remain, from which it is easy to cut into excellent cuttings for propagation. From such cuttings you can grow beautiful own-rooted seedlings of roses. True, care and attention to these bushes in the first three years of development require increased, but the plant itself will be more resistant and durable.

What roses can be propagated by cuttings
There will be the least attacks if you take cuttings for propagation from miniature, polyanthus and ground cover roses. Suitable for this and climbing roses, but only with small flowers. The situation is worse with floribundas – only half of the planted cuttings will take root. And it’s really bad with the survival rate of cuttings of hybrid tea, park and large-flowered climbing roses. But you still need to try. Perhaps you are the lucky one and in the end you will be able to propagate beautiful and rare varieties of roses.
How to cut the cuttings correctly
Choose only healthy shoots as thick as a pencil or thinner. The length of the cuttings should be about 20 cm. The presence of 3-4 buds on each cutting in the upper part is mandatory. Sections are made with a sharp knife, which should be disinfected. The top cut is always straight, and the bottom cut is at a 45 degree angle.

Autumn reproduction of roses
For him, cuttings are planted immediately or kept until spring. You can do this in several ways.
- The simplest thing is to leave the cut shoots under the bushes, and in the spring cut them into cuttings. Under winter shelter, they are well preserved. But the risk of losing the cuttings is quite high, besides, in the spring, all planting procedures will have to be done very quickly.
- A more reliable way is to build a special greenhouse for cuttings – cuttings. We make a hole in the ground with a depth of about 30 cm. We put a layer of fresh grass in it, 20 cm thick, which will provide heating of the stalk from below. Grass, rotting, gives warmth. We cover it with a layer of rotted compost mixed with peat. The top layer about 1 cm thick is river sand. In a well-moistened soil, we stick the cuttings 2/3 of the length at an angle of 45 degrees. We build a small frame from improvised materials and tightly cover it with a film. There should be no gaps between the film and the soil. For insurance, we cover the greenhouse with spruce branches.
- If there is no time for such a structure, you can do it differently and keep the cuttings just in the ground until spring. To do this, we make a recess of the desired size in it. Its depth should be about 15 cm. We put covering material in the recess, even the old one will do. It should be of such a size that the cuttings can be covered from above. We lay out the cuttings so that they do not touch each other and cover from above with the ends of the covering material, sprinkle with earth. Be sure to mark the storage location of the cuttings with a peg.
Spring planting cuttings
If the cuttings were not planted in the cuttings in the fall, in the spring this should be done immediately, as soon as they were taken out of the shelter. As a rule, during this time, callus has formed in the cuttings, so there will be no problems with rooting.

If well-preserved cuttings did not form it, they need to be helped and speed up the rooting process with a root stimulator. To do this, the cutting is dipped with the lower end into a root formation stimulator or kept for several hours in its solution. Plant them in good soil, choosing partial shade. The cuttings should be 2/3 submerged in the soil and planted at a 45 degree angle with a slope to the north.

Further care for the planted cuttings consists in daily airing and keeping the soil moist. After rooting, the shelter is removed. It is better to transplant young roses to a permanent place next spring. Such seedlings require attention and careful care, aimed at the speedy formation of a strong root system.
A rose is a flower worthy of being in every garden. If you take care of her properly: feed, water, cut and shelter for the winter, she will thank with amazing flowering. There are no ugly roses, each is good in its own way.