Contents
In line with its mission, the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony makes every effort to provide reliable medical content supported by the latest scientific knowledge. The additional flag “Checked Content” indicates that the article has been reviewed by or written directly by a physician. This two-step verification: a medical journalist and a doctor allows us to provide the highest quality content in line with current medical knowledge.
Our commitment in this area has been appreciated, among others, by by the Association of Journalists for Health, which awarded the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony with the honorary title of the Great Educator.
Autism is a condition that belongs to the group of symptoms known as withdrawal, i.e. avoiding contact with the outside world – with people and the environment. It is considered to be a brain disorder that may have a genetic component. However, despite the identification of many factors that increase the risk of autism, its cause has not yet been fully understood.
What is autism?
Autism, also known as Kanner’s syndrome, after the psychiatrist who first described an autistic child in 1943. Autism is a neurological disorder that affects the brain and is most often of a genetic nature. The first symptoms appear already at the stage of childhood and last for the rest of life.
Autism is characterized by the child’s lack of response to commands, lack of play with peers, difficulties in expressing emotions or communicating with both gestures and speech. We often perceive the behavior of an autistic child as strange.
Autism is understood as a spectrum. This means that autism is different for each person. People diagnosed with autism spectrum disorders have very different severity of behaviors and traits resulting from autism.
This disorder has many varieties, it happens that the child simply develops slower – which is often mistaken for autism. Although there are many factors that increase the risk of autism, the specific causes of autism are still unknown.
The word “autism” comes from the Greek word autos, which means “alone.” This concept was introduced to psychiatry by Eugen Bleuler in 1911 to describe the inability to maintain relations with the environment. According to this Swiss psychiatrist, real relationships were replaced by dreams or delusions by people with autism.
What is World Autism Awareness Day and when is it? Read: World Autism Awareness Day
The causes of autism
It is not fully known what causes autism, but it is believed to be the main factor in the development of this disorder genetics (a large number of genes responsible for autism have been identified) and the environment.
Studies with autistic patients have shown some abnormalities in several regions of the brain. In addition, other research suggests that people with autism have poor levels of serotonin and other neurotransmitters in the brain. All of this may suggest that disturbances in fetal brain development at an early stage of development and abnormalities in genes may contribute to the development of autism.
- You’re pregnant? Remember about regular checkups. We recommend Testing during pregnancy – a blood test package that also allows you to collect blood at the patient’s home.
About 15-20 percent. autistic children have a genetic mutation that increases the risk of developing the disorder. Certain genetically determined diseases, such as Fragile X Syndrome and Rett Syndrome, are well known to increase the risk of autism.
If parents already have one autistic child, the risk that the other will also be born with this disorder is close to 20%. – groundbreaking research by scientists from the University of California at Davis proves it. In the event that parents have two children with autism, the risk that the third will also be autistic is as high as 32%, comments the author of the study, Sally Ozonoff.
A number of studies have reported that an anticonvulsant drug (valproic acid) may increase the risk of autism in children who have been exposed to it before birth.
On the other hand, another study found a higher risk of this disorder among children exposed in utero to anti-depression drugs.
In contrast, prenatal vitamin use has been associated with a lower risk of autism. That is why a pregnant woman should supplement vitamins and minerals. We recommend, for example, Pregnancy Complex – Viridian pregnant woman.
To sum up, four factors dominate the causes of autism: genetic, developmental, infectious, as well as factors related to pregnancy and childbirth.
Genetic factors influencing the development of autism:
- Fragile X chromosome syndrome is a condition present in 2-3% of people with autism spectrum disorders. When this cause of autism was discovered, it was believed that it would solve the problem of autism. However, later studies showed that it is only observed in autistic boys with a frequency of 2,6%;
- tuberous sclerosis – a condition present in approximately 2% of people with autism spectrum disorders;
- ADA2 gene mutation – is associated with abnormal metabolism of purine bases and occurs in approximately 20% of children on the autism spectrum;
- mutations in some regions of chromosome 2 and chromosome 7 – which was found in studies that included 150 pairs of siblings.
Developmental factors in the structure and functioning of the brain influencing the development of autism:
- increased levels of serotonin in the blood;
- changes in the GABAergic system;
- mTOR-related synaptic plasticity abnormalities;
- increased brain volume in autistic children until they are 4 years old;
- hyperactivity of the amygdala;
- different perception of human faces – paying more attention to the mouth area and less to the eye area;
- differences in the activity of the right temporal lobe of the brain in activities requiring the recognition of experiences and emotions of other people;
- lower left frontal lobe activity on tasks involving memory and language skills;
- enlargement of the ventricles of the brain.
Infectious factors influencing the development of autism:
- Immunological causes of autism are possible, such as maternal antibodies to fetal tissues, especially nervous tissue.
Factors related to pregnancy and childbirth influencing the development of autism:
- increased prevalence of autism in the group of children with genetic predisposition who experienced complications perinatal;
- bleeding during pregnancy;
- diabetes in pregnancy;
- fetal hypoxia;
- umbilical cord complications;
- delayed development of the fetus;
- low birth weight;
- low Apgar score at the fifth minute postpartum;
- birth defects;
- blood group incompatibility between mother and fetus in AB0 and Rh group systems – serological conflict;
- high levels of bilirubin in a newborn;
- advanced age of the child’s father;
- advanced age of the child’s mother.
You can read more about the causes of autism here: Autism – causes
Myths about the causes of autism
Despite numerous studies and studies on autism, it is commonly believed that you can still encounter myths related to the causes of autism. Among them, it is mainly indicated:
- MMR vaccination and autism – There is currently no scientific evidence that measles, mumps and rubella vaccines affect the development of autism. There is also no evidence that the organomercury preservative present in MMR vaccines, thimerosal, would contribute to the onset or development of autism. The concentration of this compound in vaccines ranges from 0,003% to 0,01%, which means that in preparations containing 0,01% thiomersal there are approx. 25 μg of mercury per 0,5 ml dose. This misconception about a cause-and-effect relationship between vaccination and autism is the result of a coincidence in time between the vaccination schedule and the appearance of the first symptoms of autism in children;
- parent-child relationship and autism – the original assumptions of Leo Kanner, an Austrian-American psychiatrist, who in 1943 was the first to describe a set of symptoms that make up early childhood autism, turned out to be inaccurate. He believed that the emotional coldness of parents led to the development of childhood autism. Comparative studies of parents of autistic and non-autistic children did not reveal any significant differences between the two groups.
If you want to learn more about MMR vaccines for autism, read on: The MMR vaccine causes autism?
Autism – symptoms
In typical forms, symptoms of autism appear before the age of 3. The first symptoms in a child are usually observed by parents – in some cases already in infancy. They are worried that the child is too polite, calm, does not flinch at the noise, does not focus his eyes on people entering, and that when you pick it up, it stiffens. In addition, the child stares at one point for hours, e.g. a ticking clock, does not babble or develop speech. It also happens that the child’s development is normal at first and that unusual behaviors appear unexpectedly.
How does an autistic child behave?
An autistic child closes itself in its own world. It is a bit distorted, but so absorbing that the child does not see the need to talk to people around him.
There is a comprehensive development disorder. The child avoids contact with peers and family. He stops talking to his mother for no reason and treats everyone around him like air. She doesn’t allow herself to be touched and stiffens when you pick them up, doesn’t feel like doing anything. He doesn’t ask his parents for super toys. Doesn’t respond to pain. She is not happy when her beloved aunt drives by. When he gets his favorite ice cream – he doesn’t show that he likes it very much.
Gentle signs (grimace, other people’s gestures) do not matter much to him. You can smile at him with the most sincere tenderness, and he will not pay attention to it or find it nice.
An autistic child stops talking, and if he does, he / she speaks in a disturbed, illogical way, repeating words or slogans from TV commercials over and over again. Instead of “I”, he says “you”, uses incomprehensible phrases.
Behavior of a child with autism is stereotypical – he is waving his arms or going in circles. He becomes overly attached to certain items. And if someone takes them from him, he panics. He doesn’t like when someone changes his or her previous habits. He likes to walk the same way, eat from the same plate, clean with the same brush. He does not tolerate changes in his daily activities.
Children with autism spectrum disorder often have a very selective and limited range of interests, which is why they are experts in narrow areas. Sometimes they show extraordinary memory, which, however, they do not use in everyday life, at school, and in contact with people.
Autistic children are often anxious and easily aggressive, with disturbed sleep.
The diagnosis of the autism spectrum is made by a team consisting of a psychologist, a special educator and a psychiatrist. If you need help, book a consultation with an Arkmedic child psychiatrist.
Summary of symptoms in autistic children. Child with autism disorders:
- does not participate in playing with peers;
- likes loneliness;
- he smiles very rarely;
- he is more interested in contact with objects than people;
- has facial expressions that do not express many emotions;
- usually avoids eye contact with another person;
- can be hyperactive and impulsive;
- does not react to his name;
- often becomes aggressive for no apparent reason;
- He hardly speaks at all, and if he does, uses meaningless words;
- introduces objects in a uniform rotary motion;
- he nods, turns in one place without stopping;
- has difficult contacts with other people;
- if he is talking – it is on one topic;
- is hypersensitive to sounds and touch;
- sometimes it is unresponsive to pain;
- does not jump;
- there are no spontaneous reflexes.
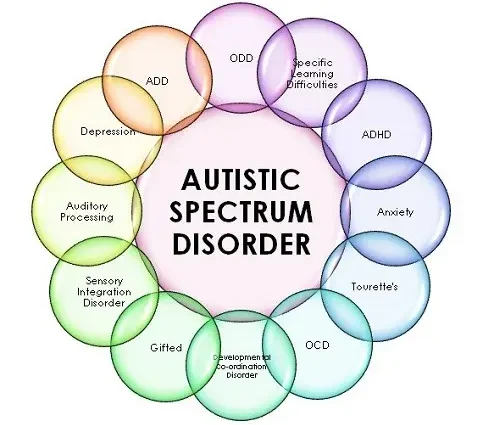
It is also worth mentioning that children with autism spectrum disorders often have comorbidities. Among the disorders that often coexist with childhood autism, the most frequently mentioned are: intellectual disability, epilepsy, insomnia, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder ADHD, food allergies, frequent symptoms from the digestive system and minor infections in childhood.
If you notice disturbing symptoms in your child, you can make an appointment quick on-line consultation with a psychiatrist.
Autism – diagnosis
There are no unambiguous medical tests that will immediately answer the question of whether a child suffers from autism. Blood or urine tests cannot diagnose this. In the diagnosis of autism, specialists primarily focus on observing the child’s behavior and its development.
Autism diagnosis is divided into two stages
1. Child development study: the specialist carries out a test to show whether the child has basic skills for a given period of life, or whether he or she has some delays. During this examination, the doctor asks the parents a number of questions, for example whether the child is learning well, how to speak, how to behave, whether he is moving well.
This is important because a delay in any of these areas may indicate developmental disorders. Each child that is referred to a specialist is examined for developmental delay and disability at the age of 9 months, 18 months, 24 or 30 months, respectively.
When it is suspected that a child is at high risk of developmental disorders due to the fact that other people in the family have autism, premature delivery or low birth weight – additional screening tests are performed. Screening tests during the control should be performed on children aged 1,5-2 years.
2. Comprehensive assessment of the child – this is the second stage of diagnostics. The assessment of the child includes the child’s behavior and an interview with the parents, in addition, neurological and genetic tests and other medical tests may be performed. More specifically, the child’s assessment is usually made by:
- neurologists – assessing the work of the brain and nerves;
- developmental pediatricians – assess the child’s development;
- child psychologists or psychiatrists – they have knowledge of the human mind and use it in examining the patient.
Whenever you suspect that your child is not developing properly, see a specialist! Most often, parents report to psychologists or educators.
You can also make an appointment for a psychological consultation online. An e-visit to a child psychologist gives you the opportunity to present current problems without traveling to the clinic.
In diagnosing autism, it is important to distinguish whether we are dealing with autism, common disorders (problems with hearing or vision) or disorders of one of the development zones, e.g. speech. There are certain diseases that can resemble autism, so it should be ruled out with proper testing. Observing the child and talking to the parents / guardians are important elements in making a diagnosis. Educational capacity is tested by a multidisciplinary team.
summarizing: based on the experience of parents and their observations, it is worth performing the following tests:
- blood and urine test;
- ENT examinations – to exclude problems with the speech and hearing apparatus;
- examination for toxoplasmosis and cytomegaly;
- hearing tests – to rule out hearing problems;
- neurological examinations – performed in order to exclude other neurological disorders;
- ophthalmological examinations – to exclude vision problems;
- genetic or metabolic testing – often performed by parents to rule out other autism-like diseases.
In order to complete one of the first steps in assessing your baby’s health, you can start with a laboratory test. Basic tests to diagnose a child’s health in one package is the initial information for specialists conducting diagnostics.
Autism – diagnostic criteria
According to the ICD-10 classification, the criteria for childhood autism are divided into 3 subgroups.
First, autism shows abnormal or impaired development clearly evident before age 3 in at least one of the following areas:
- linguistic understanding and expression used in social communication;
- development of selective social attachment or mutual social interaction;
- functional or symbolic play.
In order for the adjudicating panel to be able to make a diagnosis of the autism spectrum, there must be a total of at least six symptoms from among those listed in items I, II and III, with at least two from item I and at least one of items II and III each.
I. Qualitative irregularities in mutual social interactions, manifested in at least two of the following areas:
- insufficient use of eye contact, facial expressions, body posture and gestures to adequately regulate social interactions;
- insufficient development of peer relationships, including mutual sharing of interests, activities and emotions;
- lack of socio-emotional reciprocity, manifested by impairment or different responses to other people’s emotions, lack of modulating behavior in accordance with the social context, poor integration of social, emotional and communication behaviors,
- no spontaneous need to share joys, interests or achievements with others.
II. Qualitative irregularities in communication, manifested in one or more of the following areas:
- delay or complete lack of spoken language development that does not involve an attempt to compensate with gestures or facial expressions as an alternative means of communication;
- the relative scarcity of initiative and perseverance in a conversation in which there are feedback reactions to another person’s messages;
- stereotypical and repetitive idiosyncratic use of words and phrases;
- lack of spontaneous variety in pretend play or social role play.
III. Restricted, repetitive and stereotypical patterns of behavior, interests and activities manifested in one or more of the following areas:
- preoccupation with one or more stereotypical interests of inappropriate content and focus or one or more abnormal interests because of their intensity and limitation, and not because of content and focus;
- expressively compulsive attachment to specific, non-functional routines and ritualized activities;
- stereotypical and repetitive movement patterns, including tapping or twirling the fingers; or complex movements of the whole body;
- focus on the partial or non-functional properties of play items.
In addition, autism can be diagnosed if the current clinical picture cannot be explained:
- other symptoms of pervasive developmental disorders;
- specific developmental language comprehension disorders with secondary socio-emotional difficulties;
- reactive attachment disorder or disorder of attachment selectivity;
- mental retardation with some features of emotional and behavioral disorders;
- early-onset schizophrenia
- Rett syndrome.
There are also other classifications determining the criteria for the diagnosis of autism, such as DSM-5 or DSM-IV, but the ICD-10 criteria are most often used in the diagnosis of the autism spectrum.
How to recognize autism? Check: What are the symptoms of autism?
Autism – Can This Disorder Be Treated?
Autism can vary in severity from child to child. The child requires constant care. Treatment consists of various forms of psychotherapy – it should apply to the whole family.
The sooner we implement the therapeutic process, the greater the chances of improving functioning.
Treatment for autism can take several dimensions. There are therapeutic, pharmacological and dietary treatments.
Therapeutic treatment is usually based on behavioral therapy, rehabilitation and special education. Therapy and classes take place in centers that specialize in the treatment of autistic children. During the therapy, there are classes on communication and behavioral disorders as well as social skills training. The effectiveness of this type of therapy depends on how early the child is referred to such a specialist center. The sooner, the better the results.
Children with autism spectrum disorders are more and more often offered music therapy, hippotherapy and dog therapy. dolphin therapy, art therapy, but also jogging, dancing and martial arts
Pharmacotherapy, especially antipsychotics such as risperidone and aripiprazole, are recommended only in cases of persistent difficult behavior.
It is not uncommon for autistic patients to receive methylphenidate or atomoxetine. These drugs help reduce the symptoms of ADHD. Administration of antiepileptic drugs has not shown very positive results so far.
It is worth mentioning that the studies conducted so far indicate the lack of usefulness of SSRI drugs, such as fluoxetine, fluvoxamine and citalopram.
Proper diet is also important in the treatment of autism. It turns out that a significant proportion of people with autism may have gastric and intestinal problems, but their relationship to this disorder is still unclear.
As an auxiliary in the treatment of autism, it is worth using weighted blankets that support the fight against anxiety and sensory disorders. Weighted blankets available at medonetmarket.pl have different sizes and loads. You will find minky cotton duvets for children, as well as year-round duvets for adults.
How to Treat Autism? Check: Is There A Cure For Autism?
Autism – Tips for Parents
Consult your doctor if your child:
- has impaired speech development, does not communicate with the environment;
- does not make social contacts;
- does not respond to the name.
It is extremely important to start treatment as early as possible.