Contents
Violations in the work of the organs of vision cannot remain unnoticed by a person. Such a complication significantly reduces the quality of life and affects his work, study and daily activities.
Ophthalmology has made tremendous progress and has learned to rid people of most eye diseases that in past years seemed incurable. However, optic nerve atrophy is a pathology that is difficult to cope with. The functions of the eye suffer so much that it is not always possible to restore them. Many people become visually impaired for this reason.
Irreversible consequences can be prevented only if medical assistance is provided in the early stages of the development of the disorder. Therefore, it is so important to know the main causes and symptoms leading to optic nerve atrophy.
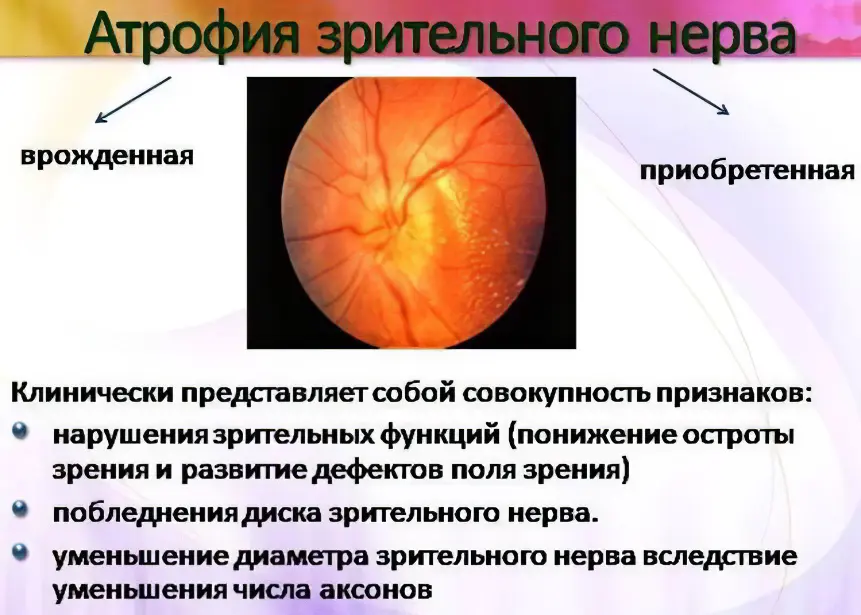
Optic nerve atrophy – what is it?
Atrophy of the optic nerve is a disease in which the tissues of the optic nerve suffer from a nutritional deficiency. This leads to the fact that the nerve stops performing its functions. The longer the nerve is in this state, the higher the probability of death of its cells. They do not die all at once, but if the pathological factor is not eliminated, then, ultimately, the nerve trunk will undergo atrophy completely. It will not be possible to restore vision in such patients.
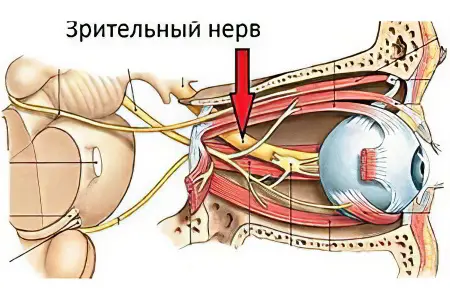
The optic nerve is represented by the second pair of cranial nerves. This pair inextricably links the brain and the eyeball. If the nerve cells die, it will not be possible to restore vision. It will be lost forever. Functionally, the optic nerve is divided into the right and left halves, along which impulses from the nasal and temporal regions of the retina are transmitted separately. They pass through the outer shell of the eye and are collected in a compact bundle. Therefore, if the nerve is damaged in the area where it left the orbit, this leads to disruption of the functioning of both eyes.
Causes of optic atrophy
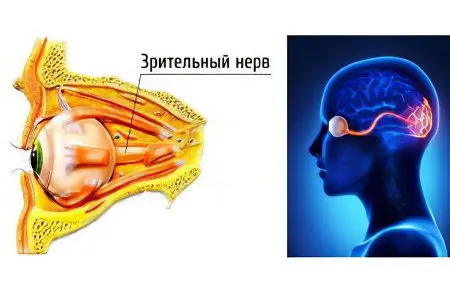
Optic nerve atrophy is most often the result of certain disorders in the body. To stop the death of nerve tissues, it is necessary to find out the cause of this pathological process.
The disease can originate from that part of the nerve trunk, which is located closer to the eye (before the intersection of the nerves). In this case, we speak of ascending atrophy. If the nervous tissue is affected above the decussation, but before entering the brain, then they speak of a descending form of atrophy.
Causes of ascending optic nerve atrophy:
Glaucoma. This disease is always accompanied by an increase in intraocular pressure. Nervous tissue begins to suffer from nutritional deficiencies, which leads to its atrophy.
Intrabulbar and retrobulbar neuritis. Neuritis is characterized by an infectious lesion of neurons in the cavity of the eyeball (intrabulbar inflammation), or outside it (retrobulbar form).
Toxic damage to the optic nerve. Nerve cells can be destroyed at an accelerated rate if they are affected by the following substances: methanol, large doses of alcohol or tobacco, lead, carbon disulfide. Toxic damage to the optic nerve may be the result of taking certain medications, provided that their dose is exceeded. These drugs include: Co-trixomazol, Sulfalen, Sulfanilamide, etc.
Tissue ischemiaaccompanied by a violation of blood flow to the optic nerve. A similar situation is observed with hypertension of the 2nd or 3rd degree, with any type of diabetes mellitus, with atherosclerosis.
stagnant disc, which is accompanied by edema of the initial part of the nerve trunk. Violation can be the result of a wide variety of pathological factors: traumatic brain injury, meningitis, hydrocephalus, spinal cord cancer.
Tumor of the optic nerveor tissues that surround it. In this case, the tumor should be up to the decussation. Atrophy develops due to the fact that the neurons of the nerve will be pinched by a growing neoplasm
Causes of the descending type of optic nerve atrophy:
Intoxication. The penetration of poisons into the body can lead to damage to neurocytes located after the cross. However, a similar situation is observed less frequently than in the case of an ascending type of disease.
Nerve tumors or surrounding tissues, which are located after the cross. The descending form of optic nerve atrophy most often develops precisely for this reason. Such tumors are very dangerous, as they affect brain structures. It is difficult to treat them.
Damage to nervous tissue by infectious agents. In this regard, neurosyphilis, tuberculosis of the nervous system, leprosy, herpes are dangerous.
Abscess of the cranial cavity. This severe inflammation most often develops after suffering meningitis or encephalitis.
Before proceeding with the treatment of optic nerve atrophy, it is necessary to find out the causes of its development.
Symptoms of optic atrophy
Depending on where exactly the lesion is concentrated (before or after the intersection), there are 2 main symptoms of atrophy – anopsia and amblyopia. The first condition is characterized by a loss of visual fields, and the second by a decrease in its acuity. The intensity of the symptoms depends on the severity of the course of the disease, which led to atrophy of the optic nerve.
Anopsia
Anopsia is a loss of visual fields. The field of view refers to the area that each person sees. To imagine it, you can simply cover half of your eye with your hand. The person will only see ? pictures, since the organ of vision does not perceive the rest of it. So, with atrophy of the optic nerve, such a loss of half of the image happens in ordinary life, when the eye is not covered by anything. Both left and right fields can fall out.
Neurologists distinguish between tympon and nasal anopia. In the first case, half of the image, which is located closer to the temporal part of the eye, falls out, and in the second case, half of the image, which is closer to the nose, falls out. Also, anopsia can be left and right, depending on the side from which the visual field is lost.
If optic nerve atrophy has just begun to develop, then such a symptom may not manifest itself, since the remaining intact neurons will transmit the resulting image to the brain. When atrophy permeates the entire nerve trunk, anopsia will definitely make itself felt.
Features of anopsia, depending on the degree of damage to nerve cells and the concentration of atrophy of the optic nerve:
Complete atrophy with damage to the entire nerve trunk, which is concentrated to the intersection (ascending atrophy), leads to the fact that the eye from the side of the damage completely ceases to perceive the picture.
Complete atrophy, concentrated after decussation (descending type), leads to the fact that the right or left visual field falls out in both eyes.
Incomplete atrophy, concentrated before the decussation and after it, leads to the fact that the field of view falls out in one eye (from the side of the lesion). Sometimes this symptom may not manifest itself.
Ophthalmologists and neurologists are able to determine the type of atrophy and its location by the nature of anopsia.
Amblyopia

Amblyopia, that is, a decrease in visual acuity, develops in all people with atrophy of the optic nerve.
There are 4 degrees of severity of amblyopia:
Mild degree disorders develop in the early stages of optic nerve atrophy. The person does not experience any discomfort. It can only occur to him when he tries to examine in detail an object located far away.
Average degree amblyopia develops when many neurons are damaged. Objects that are far away, the patient is not able to consider. Those objects that are located nearby, he sees well.
severe amblyopia indicates that atrophy is progressing. Vision is reduced so much that a person does not see objects that are next to him.
Blindness indicates that complete atrophy of the optic nerve has occurred.
Vision begins to fall unexpectedly for a person. If he does not receive treatment, then this process does not stop. As a result, the patient may become completely blind.
Diagnosis of optic nerve atrophy

Optic nerve atrophy does not cause difficulties in terms of diagnosis. The disorder is detected by ophthalmologists even at an early stage of its development. To do this, the doctor performs an eye examination.
Ophthalmoscopy, as a technique, is implemented in a dark room. The doctor examines the initial section of the nerve trunk using a special instrument (ophthalmoscope) and a light source. Also, the procedure can be carried out using a special apparatus. This improves the accuracy of diagnosis. A person does not need to prepare in advance for the procedure.
Ophthalmoscopy does not always make it possible to detect the onset of atrophy, since pathological changes in nerve cells can occur, but this is not manifested by external signs. Other diagnostic methods, such as urine and blood tests, cerebrospinal fluid sampling do not provide complete information about the disease, but are only clarifying.
Modern medical institutions have the following methods that allow you to detect atrophy of the optic nerve and clarify the cause of the disease:
FAG (fluorescein angiography). A contrast agent is injected into the patient’s vein, which penetrates into the vessels of the eye. The doctor illuminates the organ of vision with a special lamp and assesses its condition. This allows you to identify insufficient blood circulation of the eyeball and the initial signs of tissue damage.
HRTIII (laser tomography of the eyeball). This is a non-invasive method for evaluating the structures of the eyeball. It allows you to identify atrophy of the initial trunk of the optic nerve.
OCT (optical coherence tomography). The state of the nerve fiber is assessed using high-precision infrared radiation.
CT or MRI of the brain. These are high-precision techniques that are aimed at detecting the cause of atrophy. A similar study is prescribed for suspected tumor processes or other volumetric formations, for example, cysts or abscess areas.
Treatment is indicated for all patients immediately after contacting the doctor. Therapy will prevent the progression of atrophy.
Treatment of optic nerve atrophy
The phrase that “nerve cells do not recover” is hopelessly outdated. Recent studies prove that damaged neurocytes have the ability to grow. They increase the number of connections with tissues, and can also take over the functions that previously died nerve cells performed. However, neurocytes cannot multiply.
There is no cure for optic nerve atrophy. If the trunk was not completely affected, then vision can be restored, but only partially. It is not often possible to bring it back to normal and it is difficult to do it. If the process of transmitting impulses from the eye to the brain is disrupted, then the problem can only be dealt with in an operative way.
It is important to eliminate the cause that led to optic nerve atrophy. Otherwise, all efforts will be useless. If it is impossible to cure the underlying pathology, as is the case with some malignant tumors, then efforts should immediately be directed to restoring the functions of the eye.
How to restore the nerve?
Recently (10-15 years ago), vitamins and angioprotectors were prescribed to patients. Modern ophthalmologists assign these drugs only an auxiliary function. The therapy is based on taking medications that allow you to normalize metabolic processes in neurons (antihypoxants) and stimulate blood flow to nerve cells (nootropics, antiaggregants, etc.).
Drugs that are used for atrophy of the optic nerve:
Antihypoxants and antioxidants (Mexidol, Trimetazidine, Trimectal). These drugs allow you to restore damaged tissues and prevent further damage to nerve cells, eliminating hypoxia. If the patient is in the hospital, then the drugs are administered to him intravenously. At home, take tablet forms of medicines.
Microcirculation correctors (Trental and Actovegin). They are aimed at improving the metabolism in nerve cells and stimulating their nutrition. Medicines are available both in tablet form and in the form of a solution for injection.
Nootropics: Piracetam, Cerebrolysin, Glutamic acid. These drugs stimulate blood flow to nerve cells, thereby triggering their regeneration.
Drugs that reduce the permeability of the vascular wall (Emoxipin). They are aimed at protecting the optic nerve from damage. Emoksipin in ophthalmic practice has been used recently, it is administered parabulbarno. There is a drug in service only with large medical centers.
Vitamins B6, B12, PP, C. They are aimed at improving metabolic processes in neurons.
This is how the standard treatment regimen for optic nerve atrophy looks like.
Cortexin is injected subcutaneously into the temporal region, or intramuscularly. In this case, subcutaneous administration is preferred, since it allows you to create a high concentration of the active active substance in the right place. Retinalamin is injected into the parabulbar tissue.
If we combine the classical and peptide treatment regimens, then the probability of restoring visual function increases, although even such complex therapy does not always lead to positive results.
Physiotherapy
Two methods of treating optic nerve atrophy have received scientific confirmation of their effectiveness – these are UTIs and BT.
Pulsed magnetotherapy allows you to restore damaged cells and improve their functioning. Under the influence of magnetic fields, neurons thicken and better transmit impulses from the organs of vision to the brain.
Bioresonance therapy is aimed at improving metabolism in damaged tissues and normalizing the blood supply to the nerve through small blood vessels.
These methods are available in large clinics, as they are implemented on expensive equipment. Moreover, patients have to pay for such treatment on their own.
Operation
There are two types of surgery that are indicated for patients with optic nerve atrophy:
Operations to redistribute blood flow in the eye area. It is cut in one place, and in another it becomes more intense. Doctors may tie off some of the blood vessels in the face, allowing significant amounts of blood to flow to the eye. The operation is rarely performed, as it can cause severe complications.
Transplantation of revascularizing tissues. At the same time, tissues that are abundantly supplied with blood (muscles, conjunctiva) are transplanted into the area of atrophy. Thanks to this, new vessels begin to grow to damaged neurons and nourish them in a natural way. This operation is quite common.
In recent years, stem cell therapy has been actively used in Russia. However, such therapy is now prohibited by law. You can take the course in Germany and Israel.
Forecast
The prognosis is determined by the degree of damage to the nerve trunk and the timeliness of the therapy. Vision can be restored if only a few neurons are affected. When all the cells of the optic nerve are affected, a person will develop complete blindness. Sometimes surgery helps to cope with the problem, but no specialist will give a guarantee of success.
Answers to popular questions

Can optic nerve atrophy be a congenital pathology? This situation is rarely seen. The first symptoms of the disease are detected early, at the age of up to a year. The sooner the child starts receiving treatment, the better.
Can optic nerve atrophy be completely cured? No, this disorder is incurable, but therapy allows you to restore and maintain visual functions.
How often is optic nerve atrophy diagnosed in children?? In children, pathology is rarely diagnosed.
Are folk therapies effective?? No, non-traditional methods of treatment will not allow you to cope with the disease.
Does the person have a disability? The second group of disability is given to people with a decrease in visual acuity of 0,3-0,1 dp. With complete blindness, a person is recognized as a disabled person of the first group.
What is the duration of treatment? Treatment must be lifelong.









