Contents
- Causes of atrial fibrillation
- Risk factors for the development of atrial fibrillation
- Types of atrial fibrillation
- Symptoms of atrial fibrillation
- Complications of atrial fibrillation
- Treatment of atrial fibrillation
- Types of surgery for atrial fibrillation
- Emergency care for patients with an acute attack of atrial fibrillation
- Forecast for life
- Prevention of atrial fibrillation
Cardiac arrhythmia is a violation of the conduction of electrical impulses, which causes the organ to contract abnormally and irregularly. There are several types of arrhythmia, but the most dangerous of them is atrial fibrillation. It is characterized by a high risk of death and the most unfavorable prognosis.
Atrial fibrillation got its name because of the clinical features of its course. During an attack, the muscle layers of the heart begin to shake and twitch. Their movements can be compared to the uncontrolled flickering of light.
The atria are the chambers of the heart located below the ventricles. Blood accumulates in them, after which it is thrown into the upper sections of the heart. If the atria do not work properly, then the heart is not supplied with blood and nutrients as it should be in the norm. Such a failure in 35% of cases leads to the development of hypoxia and the death of sections of the heart muscle. To minimize the likelihood of developing a myocardial infarction against the background of an attack of atrial fibrillation, you need to seek medical help as soon as possible. Therefore, it is so important to know the main symptoms of the disorder and be able to distinguish them from other pathological manifestations. This is especially true for people at risk for heart disease, as their atrial fibrillation often leads to serious consequences.
Causes of atrial fibrillation

Atrial fibrillation develops against the background of cardiac pathologies. Diseases can be congenital or acquired during life.
The most common pathologies that can lead to the development of atrial fibrillation are:
primary hypertension.
Heart disease.
Damage to the heart valves.
Atrial septal defects.
Cardiomyopathy of unspecified etiology.
Atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries.
Sinus tachycardia.
Cardiac ischemia.
Acute or chronic heart failure.
Atrial fibrillation often develops after suffering pericarditis or myocarditis. Also, surgical interventions on the heart or on the coronary arteries can provoke the development of a violation.
Increases the likelihood of developing atrial fibrillation apnea. Risks increase when sleep apnea develops in combination with high blood pressure and diabetes. Apnea leads to an increase in pressure in the atria, negatively affects their size, disrupts the functioning of the autonomic nervous system.
Risk factors for the development of atrial fibrillation

Separately, risk factors that increase the likelihood of developing atrial fibrillation can be identified.
These include:
Alcohol abuse.
Smoking.
Drug addiction.
Poisoning with toxic substances.
Therapy with antibiotics, cardiac glycosides, corticosteroid hormones, dopamine blockers. Atrial fibrillation will develop when the treatment takes place without proper medical supervision.
Private stress and nervous strain.
Age. The older a person is, the more likely they are to develop an arrhythmia. This is associated with a decrease in the number of cardiomyocytes, as well as with violations of intercellular connections in the myocardium, which negatively affects the conduction of impulses.
Excessive physical and mental stress.
Obesity and diabetes.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Leading a sedentary lifestyle.
Nutritional errors. Arrhythmia can develop if a person receives little potassium and magnesium from food. It is these trace elements that the heart muscle needs to maintain health.

To exclude the possibility of developing heart pathology in patients who are forced to take medicines for a long time, it is necessary to regularly undergo an ultrasound scan of the organ.
There are also products that must be present on the menu of each person. They saturate the body with useful substances and allow you to maintain normal heart function.
These products include:
Leafy salads such as arugula, lettuce, and Chinese lettuce.
Any herbs: rosemary, dill, parsley, cilantro.
Eggplant, tomatoes, cabbage, spinach.
Potatoes boiled or baked. You need to cook the vegetable in the peel.
Dried fruits compote.
River fish.
Nuts. Brazil nuts and pine nuts are very good for the heart.
Cod liver.
Seafood.
Legumes: lentils, peas, beans.
Dairy products.
Types of atrial fibrillation
Specialists identify 5 types of arrhythmia, which differ not only in symptoms, but also in the duration of the attack:
Paroxysmal.
Persistent.
Prolonged persistence.
Constant.
Non-valvular.

During the diagnosis, it is important to correctly determine the type of atrial fibrillation, since the success of therapy depends on this.
Most often, patients have a paroxysmal form of atrial fibrillation. It lasts no more than a week. If an attack has not been stopped in 2 days, then it will not stop on its own, but the likelihood of developing systemic thromboembolism is extremely high. In such situations, doctors talk about chronic or persistent arrhythmia.
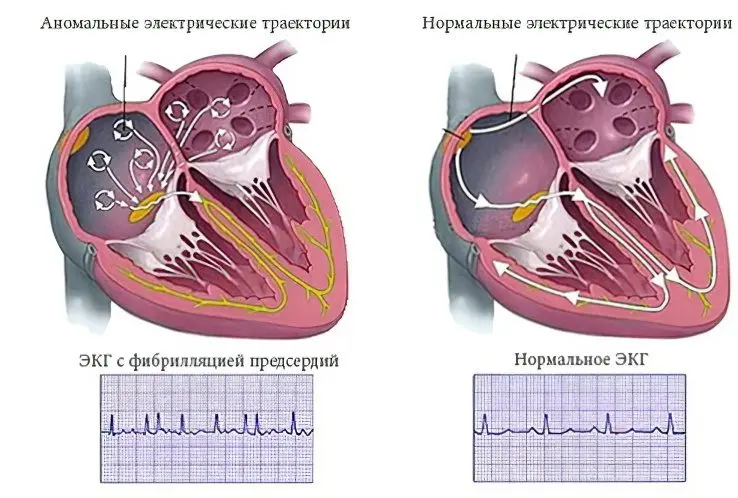
Depending on the heart rate, the following types of arrhythmia are distinguished:
Heart rate greater than or equal to 90 beats per minute – tachysystolic arrhythmia.
Heart rate 60-90 beats per minute – normosystolic arrhythmia.
Heart rate less than or equal to 60 beats per minute – bradysystolic arrhythmia.
Persistent atrial fibrillation may not resolve on its own. It lasts over 7 days. To cope with the violation, medical assistance is needed.
Long-term persistent arrhythmia is said to be when it lasts more than a year. In this case, drug therapy is an obligatory direction of treatment. The ablation method can also be applied.
Permanent atrial fibrillation is said to be when it can be preserved, or when previous drug treatment or surgery has been unsuccessful.
Symptoms of atrial fibrillation

Symptoms of atrial fibrillation will vary in different categories of patients. The age of the patient, his lifestyle, the form of the disorder, and the state of health are important. Although there are still common symptoms of this cardiopathology.
They include:
Pulse instability. A person can independently understand that the heart is beating irregularly, but an ECG in 12 leads is required to confirm the diagnosis. The first signs of atrial fibrillation can be considered ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack.
Heartache. During an attack, patients indicate pain in the region of the heart. She always focuses on the left side. The pain may be dull, sharp, or stabbing, burning, or pressing. The patient is always able to clearly describe the location of the pain, since it does not spread to other parts of the body.
Respiratory failure. Patients with atrial fibrillation complain of shortness of breath. Many patients report that they experience heart pain when they try to breathe. If the patient begins to move, then the painful sensations gain strength.
Shortness of breath develops regardless of the level of physical activity of a person. It can happen at night when he is at rest.
If the heart rate exceeds 100 beats per minute, shortness of breath can become very intense and even provoke asthma attacks in the patient. An asphyxiation attack lasts 5-7 minutes, so most people do not go to the doctor about this. This should not be done, since a neglected violation can result in arrhythmogenic shock and even cardiac arrest.
Convulsions and tremors in the limbs. Seizures and tremors are two different things. If a person has convulsions, then he has an involuntary contraction of the muscles. In this case, the limbs do not move. When a patient has a tremor, shaking of the affected areas is always observed.
If we consider convulsions and tremors in the extremities against the background of arrhythmia, then patients most often complain of symptoms such as:
Cramps in the calves. Most often they develop at night, during sleep.
Tremor of hands, feet, neck, head.
Tingling and numbness of the limbs.
After drug therapy is started, tremor and convulsions cease to disturb the patient.
Muscle weakness. Muscle weakness very often accompanies various forms of arrhythmia. Its degree of expression varies widely. The upper and lower extremities are primarily affected. Sometimes it is difficult for the patient to dress himself, wash the dishes, he can drop objects. More than half of the people point to cottony feet and a decrease in the sensitivity of the feet.
Increased sweating. Even with minor physical exertion, a person will sweat a lot. A similar situation occurs with emotional stress. The patient sweats during the day and at night when he sleeps. Sweat is liquid, not sticky. It has the same temperature as the human body temperature.
Increase in the amount of urine excreted. As a rule, increased separation of urine is observed no longer than 1-2 days. Daily diuresis increases to 1,8-2 liters, while normally these figures are 1,5 liters maximum. Severe arrhythmia may be accompanied by an increase in daily diuresis up to 3 liters. The person himself suffers from intense thirst, his mouth dries up.
Mental disorder. The patient’s irritability increases, he becomes anxious, he is haunted by fears that he is unable to explain. Many people begin to experience the fear of death, from which it is impossible to get rid of.
Complications of atrial fibrillation

Atrial fibrillation in 35% of cases turns into ventricular fibrillation, which increases the likelihood of developing a heart attack and stroke, as well as acute cardiac ischemia.
More than 70% of patients with atrial fibrillation suffer from heart failure. In 20-30% of patients, dysfunction of the left ventricle of the heart develops.
Atrial fibrillation is associated with risks of cognitive impairment and vascular dementia.
the disease requires treatment, otherwise the consequences can be the most serious, up to death. It is important to direct efforts to eliminate those factors that led to heart rhythm failures. To make a diagnosis, you need to contact a cardiologist.
Association of atrial fibrillation and stroke
Against the background of atrial fibrillation, the likelihood of developing a stroke increases. In women, the risks increase by 2 times, and in men by 1,5 times. Some experts believe that a stroke necessarily occurs in all patients with atrial fibrillation. Other scientists are of the opinion that the risk increases, but is not 100%.
If a person receives blood-thinning drugs, the likelihood of developing a stroke is reduced. However, fibrillation negatively affects the blood supply to the brain. The patient may experience blood stasis in the heart, which leads to the formation of blood clots in it. They are able to migrate through the vessels with the blood flow. If these clots reach the brain, then a person has a stroke.
Taking anticoagulants helps prevent a stroke, so these drugs are prescribed to all patients suffering from atrial fibrillation. It must be remembered that blood thinning drugs can cause bleeding if taken for a long time. However, the risk of blood loss is significantly lower than the risks that a stroke carries.
Warfarin is the most commonly prescribed drug used to treat patients with atrial fibrillation. Therapy with this drug should be under the control of blood counts. To do this, the patient will need to regularly visit a specialist and take tests. Based on their results, dose adjustments are made.
Treatment of atrial fibrillation

Restoration of sinus rhythm is required for patients in the following cases:
Developing paroxysmal atrial fibrillation.
A drop in blood pressure, heart failure, shortness of breath and other negative manifestations of atrial fibrillation.
There is a high probability that the restored sinus rhythm can be maintained. This is possible in cases where atrial fibrillation developed less than a year ago.
Depending on the type of atrial fibrillation, the patient must undergo certain preparatory measures:
Provided that the attack of atrial fibrillation lasts no more than 2 days, preliminary preparation for the restoration of sinus rhythm is not required. Non-fractional heparin is used before and after cardioversion. In Europe, treatment may be with Heparin or Apixaban. Sometimes cardioversion is performed without the use of blood thinners at all. This is possible if the likelihood of developing blood clots is minimal. Heparin is used without fail if the patient has disturbances in the movement of blood through the vessels.
If atrial fibrillation continues in a patient for more than 48 hours and its causes are not established, then the patient is shown taking anticoagulants before cardioversion.
Alternatively, the patient may have a transesophageal echocardioscopy prior to cardioversion. This procedure allows you to detect already formed blood clots. If they are not available, then cardioversion is carried out under the guise of heparin therapy.
Both Warfarin and Aspirin increase the risk of bleeding, but the effectiveness of the first drug is higher.
Also, patients are prescribed therapy with new anticoagulants, but it would not be entirely correct to call them “new”. Rather, they refer to direct oral anticoagulants.
Electrical cardioversion
Treatment of atrial fibrillation with current discharges is one of the most effective methods of therapy. A high-voltage electric current pulse is passed through the patient’s heart once. This procedure allows you to restart the myocardium and stabilize the heart rhythm.
The effect of such therapy is equal to 95%. The charge power is 100-200 kJ. Sometimes the procedure is performed with access to the heart through the esophagus. However, such a procedure is associated with a high risk of severe complications and even complete cardiac arrest.
RF catheter ablation
Radiofrequency catheter ablation is one of the optimal methods for the treatment of atrial fibrillation. During the procedure, the doctor destroys the source that provokes the appearance of unnecessary impulses in the heart. In this case, the operation is carried out with closed access.
To begin with, the specialist determines the altered area of uXNUMXbuXNUMXbthe heart. Then a catheter is passed through the femoral artery to it, which is a source of electrical impulses. They destroy the pathological focus.
Maintaining a stable heart rate
It is not enough just to eliminate disturbances in the work of the heart, it is important to make these results fixed. If the patient does not receive treatment, then in 45-85% of cases, atrial fibrillation recurs no later than one year after the cardioversion.
Antiarrhythmic drugs and beta-blockers are prescribed by the doctor at the time of discharge.
Heart rate control
In order to control the heart rate in patients, they are shown a daily ECG. For young people, the norm is a heart rate of 60-80 beats per minute at rest and 90-115 beats per minute with moderate exercise.
Types of surgery for atrial fibrillation
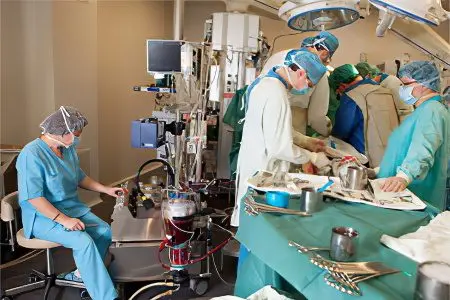
Isolation of the left atrium from the conduction system of the heart. During the procedure, doctors are forced to turn off the heart chamber, which increases the likelihood of blood clots.
Pacemaker installation. This device is aimed at blocking pathological impulses, which allows you to maintain a normal heart rhythm.
Insertion of a pacemaker. This device independently resets the heart when its rhythm is disturbed.
Operation Maze. During the procedure, the doctor performs multiple incisions on the heart, creating an artificial labyrinth in its left sections. It prevents the conduction of pathological impulses to the ventricles. Such a surgical intervention is not often performed, since it requires the patient to be connected to a heart-lung machine.
Operation Corridor. It boils down to the fact that the atria are isolated from the conduction system, forming a passage to the ventricles.
Radiofrequency ablation. In this case, the pulmonary veins are isolated from the paths that are responsible for conducting electrical impulses. This method of treatment is used when medical correction does not achieve the desired success, or if the patient has had cases of thromboembolism before. Ablation is also performed in the presence of contraindications to the implementation of endovascular catheter techniques.
Emergency care for patients with an acute attack of atrial fibrillation
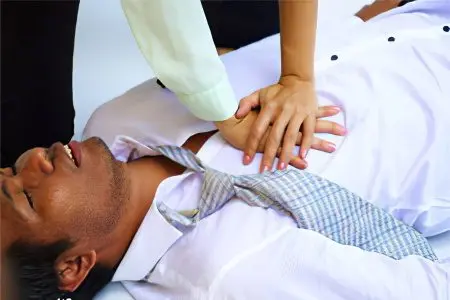
If a person knows that he may have an attack of atrial fibrillation, then he should be able to give himself first aid. These events are carried out until the moment when the medical team arrives.
They are called vagal tests:
Sinus massage. The patient lies on his back, finds the carotid artery on the neck and gently massages it clockwise.
Pressure on the eyeballs.
Stimulation of the cough reflex.
Valsalva maneuver: you need to take a deep breath and tighten the abdominal muscles.
Pressure on the root of the tongue to induce vomiting.
Forecast for life
The prognosis of atrial fibrillation largely depends on the form of the disease. Most often, violations occur according to the type of seizures that recur over many years. As a result, the disease becomes chronic. If the heart rate during attacks rises to 300-600 beats per minute, then the prognosis worsens.
The prognosis can be considered more favorable in the case when, against the background of arrhythmia, no disturbances are observed in the work of the myocardium. For many years, the patient may not notice attacks of atrial fibrillation at all. The more regular attacks occur, the lower the quality of life of a person.
Prevention of atrial fibrillation

Atrial fibrillation is a serious disease that threatens the life of the patient. Therefore, it is necessary to direct efforts to prevent its development. To do this, it is necessary to treat all heart diseases in time, monitor blood pressure.
It is important to give up bad habits, avoid stressful situations, and prevent physical and mental overstrain.
The main measures for the prevention of atrial fibrillation can be identified as follows:
HLS. Leading a healthy lifestyle.
Compliance with a diet. The menu should contain food of plant origin. You need to give up fatty foods. Be sure to include dried apricots, pumpkin and walnuts in the diet.
Physical culture lessons. If a person has already developed atrial fibrillation, then morning exercises are a prerequisite that must be fulfilled. Exercise should be feasible, skiing and swimming are useful.
Rejection of bad habits. Smoking and alcohol abuse increase the likelihood of developing heart disease.
Emotional overstrain is unacceptable. To support the work of the nervous system, you need to perform auto-training. If a person is under stress, it is necessary to take sedatives.
High-quality and high-grade rest. Sleep should be at least 8 hours a day. During this time, the body has time to recover and accumulate sludge.
Weight control. Obesity is one of the main factors in the development of arrhythmia. If a person gets rid of extra pounds, he will significantly unload the cardiovascular system.
Blood glucose control. This measure is especially relevant for patients with diabetes.
Control of blood cholesterol levels.
To improve the prognosis, you need to contact the doctor when the first signs of atrial fibrillation appear. The doctor will select adequate therapy that will prevent the development of a heart attack or stroke.









