Contents
What is cerebral atherosclerosis?
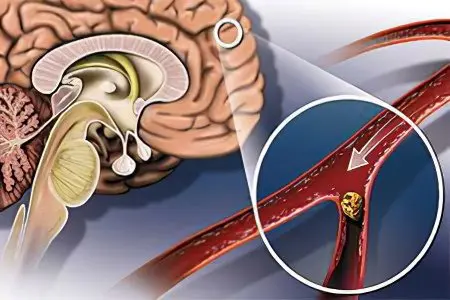
Atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels – this is a steadily progressive systemic lesion of the vessels located in the corresponding organ. In medicine, you can find other definitions of this disease, for example, atherosclerosis of the cerebral type or atherosclerotic lesions of the cerebral vessels, but the essence remains unchanged. The work of the central nervous system is disrupted, which gradually leads to irreversible consequences.
The etiopathogenetic mechanism for the development of cerebral atherosclerosis is associated with metabolic disorders of a protein-lipid nature, with damage to the intima of brain vessels by their decay products and directly by the fatty complexes themselves, with the formation of atherosclerotic plaques.
According to statistics, in the vessels of the brain, atherosclerosis most often affects the arteries of the subcortical nodes, the arteries of the thalamus and the pons. In most cases, formations are formed according to the type of fibrous plaques, lipoidosis is less common.
Men are more affected than women. In them, serious atherosclerotic changes begin to affect the vessels of the brain 10 years earlier. However, at an older age (after 55 years and older), both women and men are approximately equally affected by this pathology of the cerebral vessels. Statistics inexorably indicate that in recent years there has been an increasing number of young people who have barely reached 30 years of age.
In addition, certain atherosclerotic lesions of the cerebral vessels are most often observed in people who suffer from hypertension.
Symptoms of atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels
Among the obvious signs indicating the development of a pathological lesion of the cerebral vessels, one can single out:
Bad memory. A pronounced decrease in memory, which manifests itself in forgetting events that occurred in recent times. At first, memory impairments make themselves felt episodically, they are especially noticeable only after mental and physical fatigue. As atherosclerosis progresses, the dips become more noticeable, but memory for past events is retained for a long time. On the subject: 15 substances that speed up brain function and improve memory.
Decreased mental performance, which manifests itself in the form of rapid fatigue. The patient is not able to focus his attention on a certain object for a long time, to concentrate his own thoughts.
Emotional lability – Another common symptom of atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels. At the same time, the mood of a person is characterized by instability, variability. That is, even minor events lead to the appearance of a brightly colored emotional reaction. Most often, such people are tearful, prone to depression and increased anxiety, they often have fears for their own health, and there is a lack of self-confidence.
Insomnia. Patients often complain of regular insomnia.
Headache. Headaches and frequent dizziness are constant companions of this type of cerebrovascular disease. They differ in that they occur during the period when a person changes his position from horizontal to vertical. That is, in other words, he gets out of bed, and not even with a jerk, but rather slowly.
Epilepsy is another striking symptom of progressive cerebral atherosclerosis of the cerebral vessels, observed in older people. It is expressed in the occurrence of convulsive seizures.
Senestopathyhow the symptoms of atherosclerosis of the vessels of the brain are manifested in the fact that a person complains of tingling in the face, numbness of the legs, the appearance of heat in the occipital region.
Cheyne-Stokes breathing or periodic breathing, which is characterized by certain cycles: shallow breaths are replaced by deep ones, after the seventh breath, breathing becomes rare again, then there is a pause and the cycle repeats. Most often, such breathing is observed when atherosclerosis affects the arteries that feed the medulla oblongata.
Ataxia more often observed with damage to the arteries, feeding the cerebellum or vestibular apparatus. It is expressed in the inconsistency of the movements of various muscles, in the loss of balance when walking and standing, in the inaccuracy and awkwardness of movements, while the strength of the limbs is not lost.
In addition, patients in varying degrees manifest speech, auditory and visual impairments, as well as transient paralysis. Often it is difficult for the patient to endure loud sounds, an irritable reaction to light may occur.
It is advisable to distribute symptoms in atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels over several periods, for a clearer understanding of the progression of the disease:
The first stage characterized by pseudo-neurosthenic manifestations with recurrent headaches, tinnitus, sleep disorders, intolerance to bright light, loud sound, decreased performance and other manifestations of a similar nature.
The second stage The development of the disease is marked by more pronounced clinical manifestations, with the development of depression, anxiety-delusional symptoms, with confusion.
The third stage characterized by the development of dementia with severe memory impairment. Dementia is formed against the background of organic lesions of the brain by atherosclerosis. A person becomes helpless, disorientation in time may occur, however, generally accepted norms of behavior remain intact for a long time.
An important symptom that both the patients themselves and their relatives with cerebral atherosclerosis should be aware of is a cerebral or hypertensive crisis. It is accompanied by headaches, and quite intense, there may be weakness in one upper or lower limb. Often the crisis is accompanied by visual and speech disorders. As a rule, it lasts up to 2 days, and then the patient’s condition stabilizes. If the symptoms do not go away after this time period, then it makes sense to assume that these manifestations are signs of a stroke.
After the crisis, the patient is complacent, may be in a euphoric state, while all interests are reduced to everyday issues, and normal performance is lost.
Causes of atherosclerosis of the brain
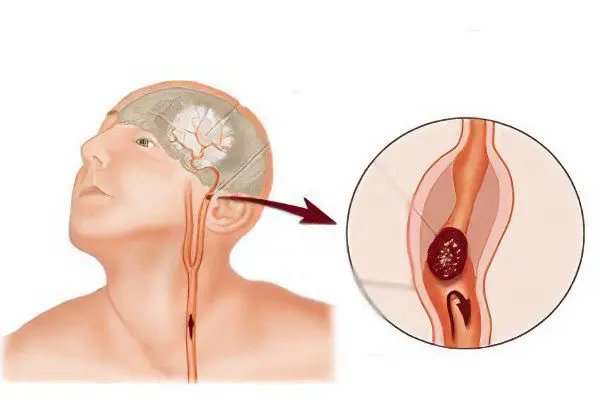
The factors leading to the development of atherosclerosis localized in the vessels of the brain are identical to the risks that form atherosclerosis of any blood tract. It is important to remember that any atherosclerotic plaque can develop over several decades.
Influence on the speedy progression of the pathological process can:
Smoking. The World Health Organization claims that it is the intake of tobacco smoke that becomes a factor that provokes the development of atherosclerosis of the cerebral vessels. Its action is multifactorial, but the most dangerous effect is the narrowing of the arteries of the brain and the gradual loss of their elasticity.
High blood pressure. If arterial hypertension remains without proper therapeutic effect for a long time, then this leads to thickening and narrowing of the blood vessels of the brain, resulting in an increased risk of atherosclerotic plaques and stroke.
Diabetes. With the development of the disease, there is a violation of the processing in the body of not only glucose, but also lipids, which ultimately have a detrimental effect on the vessels of the brain. In addition, diabetes leads to high blood pressure. In combination with pre-existing arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus increases the risk of developing pathological vascular lesions by 4 times.
Obesity. In overweight people, as a result of lipid and carbohydrate metabolism disorders, there is a stable increase in blood cholesterol, which is a powerful factor provoking the development of atherosclerosis. Moreover, the problem of overweight is relevant at this point in time, according to statistics, about 25% of the Russian population suffers from obesity. And these people are of working age.
High blood cholesterol. Regardless of what leads to an increase in its amount, the risk of developing cerebral atherosclerosis increases several times. The danger especially increases against the background of a steadily elevated level of LDL.
Belonging to the male sex or gender reason. It is at the age of 60 that men are more likely to receive a diagnosis of cerebral atherosclerosis. Although after a woman passes menopause, the chances of suffering from atherosclerosis of the brain are equal. This is due to the fact that the level of estrogens, which inhibit the development of atherosclerosis in the female body, decreases significantly after menopause.
Наследственность. If the family had relatives who at an early age suffered from cerebral atherosclerosis, then the risk of a similar pathology increases significantly.
Diet high in saturated fat negatively affects the state of blood vessels, including the brain. This, first of all, leads to an increase in cholesterol levels and the rapid growth of atherosclerotic plaques. In addition, in the presence of a hereditary predisposition, a high-fat diet can provoke an increased action of existing genes responsible for increasing cholesterol levels. As a result, its synthesis will acquire an anomalous character.
Minimal physical activity or physical inactivity – one of the most powerful factors in the progression of atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels. Any load: walking, running, swimming – accelerates the excretion of HDL from the body and contributes to the prevention of the disease.
Age is a factor provoking the development of pathology, which cannot be excluded. The first fatty spots on the vessels are found already at the age of 10 years, and they become most pronounced on average by the age of 50. This is due both to the action of other provocative causes, and to the slowing down of metabolic fat, carbohydrate, vitamin processes in the body. Failures in the work of the immune system, endocrine gland, liver, multiple past infections, etc., also affect.
Stress and bad habits in general, are the cause of many diseases, and cerebral atherosclerosis is no exception.
Diagnosis of atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels
In order to establish the presence of a lesion, it is often necessary to visit several specialists. After all, often in addition to neurological disorders, the patient complains of hearing and vision disorders. In addition, often clinical symptoms are not observed at all, or a person does not attach due importance to them, and the first serious reason for a comprehensive diagnosis is, at best, a brain crisis, and at worst a stroke.
If atherosclerosis of the cerebral vessels is suspected, the patient should be redirected from any specialist to a neurologist. Further clarification of the diagnosis and the necessary research for this are assigned to them. In the diagnosis of cerebrovascular disease at this point in time, methods based on ultrasound predominate.
So that an accurate diagnosis is made, the patient can be referred to:
duplex scanning. First of all, this study provides information about the state of the extracranial arteries that feed the brain. Combined with an ultrasound examination of the cranial arteries, doctors get a fairly complete picture of atherosclerosis. This kind of study allows you to assess the degree of narrowing of the vessel, to determine the nature of the existing atherosclerotic plaque.
Transcranial dopplerography – a study that allows you to assess the state of intracranial vessels.
Angiographic study cerebral vessels. This is one of the varieties of x-ray methods. It is known that the vessels are not visible on the x-ray, so an angiographic study involves the introduction of a contrast agent intravenously. However, due to the high traumatism, this method can only be carried out according to strict indications.
Computed tomography method used primarily in patients with stroke. It is necessary to clarify the affected area and determine the tactics of further treatment of cerebral atherosclerosis.
Additionally, an immunological analysis blood and cholesterol levels.
Magnetic resonance therapy It is also used to study the state of cerebral vessels and provides the most accurate information about existing atherosclerotic plaques. However, not every clinic has a tomograph at its disposal, so this research method is not as popular as research conducted using ultrasound.
If, according to the results of the studies, the neurologist sees that the vasoconstriction exceeds 50%, then the patient is necessarily sent for a consultation and a possible additional examination to a vascular surgeon. He re-evaluates the condition of the admitted patient and then decides on the cost-effectiveness of the surgical intervention.
Treatment of atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels
Therapy of this pathology is a long, and most often, lifelong process. This problem is solved by a neurologist whose duties include identifying people with similar problems, assessing the severity of the disease and implementing conservative therapy. First of all, it is designed to improve the blood supply to the brain, to prevent arterial thrombosis.
Medication
As for therapy with drugs, the modern scheme of exposure is reduced to:
Antiplatelet therapy, which aims to reduce the risk of ischemic stroke. Drugs used for this purpose: acetylsalicylic acid and clopidogrel. However, a hemostasis study is required beforehand.
Lowering cholesterol. In parallel, drugs are used to lower blood cholesterol levels. These can be statins (which prevent the synthesis of cholesterol in the liver, reduce LDL and increase HDL) – lovastatin, atorvastatin, simvastatin, pravastatin, as well as fibrates (reducing cholesterol and triglycerides) – gemfibrozil, fenofibrate, clofibrate. In addition, anion exchange resins or bile acid sequestrants are prescribed, which promote the excretion of cholesterol, examples of these agents: hestyramine, colestipol. Reduce the absorption of cholesterol in the small intestine will help ezetimibe, atromide, miscleron, etc.
In addition, in complex therapy, patients are prescribed drugs aimed at preventing the development of circulatory disorders. These can be coronary lytics, as well as drugs that dilate arteries and anticoagulants in case of a threat of blood clots in the vessels of the brain.
Iodine and diosponin preparations will help reduce cerebral ischemic disorders. In addition, calcium iodine, potassium iodide or iodine solution can be prescribed for the same purpose. Drugs are taken in courses to exclude iodism.
Surgery
When hemodynamically significant stenoses are detected, either complete blockage of the arteries, or unstable plaques, the vascular surgeon decides on the need for surgical intervention. Modern medicine has reached significant heights in the issue of restorative operations on blood vessels, including the brain.
The following types of surgery are currently available:
Endarterectomy. It is based on the fact that fatty growth is eliminated by an open method. To do this, a skin incision is made to gain access to the clogged vessel. After that, the surgeon stops the blood flow in this place, the wall of the blood path is quickly dissected and the fat deposit is removed. After such manipulations, the surgeon can only sew up the damaged area with a vascular suture. In this way, plaques on extracranial vessels can be removed.
Stents and balloons. Stents and balloons are used to eliminate atherosclerotic formation on intracranial vessels. That is, endoscopic removal of atherosclerotic plaque is necessary. To do this, an endoscope with a stent is inserted into the widest vessel, and then, under constant monitoring with an X-ray, it is advanced to the place where there is a narrowing of the artery due to the presence of plaque. It is there that the stent is installed, which, by increasing the lumen of the vessel, restores the flow of blood through it.
It should be understood that cerebral atherosclerosis is classified as a chronic disease, so treatment is most often lifelong. Depending on how timely the diagnosis was made and treatment started, the prognosis will also depend. In the practice of neurologists, extensive forms of cerebral atherosclerosis are known, which, nevertheless, allowed people not only to live for a long time, but also to remain efficient. However, it is not uncommon for the first clinical manifestation of this disease to end with a stroke and death for a person. Therefore, such an important role of the doctor is separated by the timely diagnosis of the disease and its qualified treatment.









