Contents
Atheroma is not a tumor, as it might seem at first glance, but a special benign formation – a sebaceous gland cyst. Most often, it occurs in seborrheic zones: on the face (wings of the nose, cheeks, forehead, nasolabial triangle, chin), behind the ears. Naturally, this causes discomfort and forms a serious cosmetic defect. Depending on the size and condition of the atheroma, the method of its removal is selected. However, in the conditions of modern medicine, such an operation is not difficult and almost never leads to the formation of a noticeable scar.
Origin of atheroma
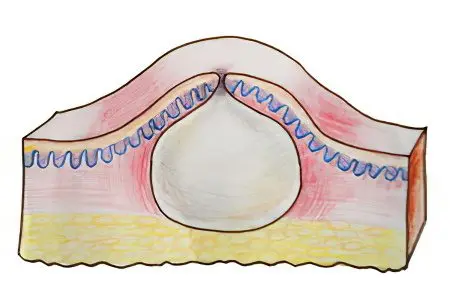
Accumulation of detritus (sebum secretion) in combination with blockage of the excretory duct is the main reason for the formation of atheroma. Most often, a retention cyst is diagnosed in patients of both sexes from 16 to 60 years old. In rare cases, it is a congenital anomaly of intrauterine development of the fetus and is found in young children.
The skin of the human body is protected by about 90 thousand sebaceous glands. This allows it to retain moisture, maintain a constant body temperature and bactericidal properties. All these functions are carried out due to the fact that the sebaceous gland produces a specific secret, while dividing its cells and partially destroying them. This cycle lasts 3-4 weeks, during which the contents of the gland are completely renewed.
Detritus is produced by three types of sebaceous glands:
Large glands on the nose, cheeks, chin, on the scalp;
Middle glands in the zone of vellus hair;
Small glands in the follicles of long hairs of the upper layer of the skin.
The excretory duct can open both into the hair follicle and onto the surface of the skin.
Reasons for the development of atheroma on the face

Factors that provoke the accumulation of secretion and blockage of the sebaceous gland:
Hormonal imbalance during adolescence or during menopause (menopause);
The effect on the fetus of the hormones of the mother’s body in the case of congenital atheroma;
Diseases of the central nervous system and the autonomic nervous system that disrupt the regulation of lipid metabolism;
Metabolic failures;
Pathology of the adrenal glands;
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
Seborrheic dermatitis.
The older a woman gets, the less oily her skin becomes compared to adolescence. In this regard, the skin of men retains elasticity longer due to the influence of testosterone. Under the condition of the development of pathology against the background of autoimmune and hereditary diseases, age-related features of the skin do not matter.
Symptoms of the disease

For a long time, atheroma on the face does not manifest itself in any way, the filling of the cyst occurs within 6-10 months. Detritus consists of particles of mucus and fat, epithelial cells, cholesterol molecules. The size of atheroma on the face varies from a few millimeters to 5-7 cm in diameter. Most often, a person notices atheroma by accident, finding an unusual dense neoplasm on the skin of the face.
Symptoms:
Dense consistency;
Correct rounded shape;
Absence of pain;
The skin above the cyst is mobile, does not fold, its structure and color are not changed;
With inflammation of the cyst and the formation of an abscess, the skin turns red, tissue edema appears, purulent contents shine through the top of the cyst;
With the formation of phlegmon, the purulent discharge spreads in the subcutaneous tissue, the tissues become necrotic, and the body temperature rises.
If you do not take measures to treat festering atheroma on the face, sepsis and death are possible.
Features of atheroma in different parts of the face
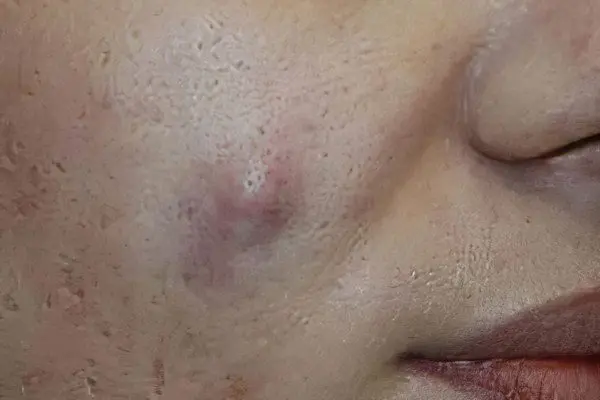
Symptoms of atheroma on the face depend on where exactly it is localized. Most often, a sebaceous gland cyst occurs on the cheeks, on the forehead, on the wings of the nose, on the eyelid, less often on the nose.
Atheroma on the cheek. A large number of sebaceous glands in this area of uXNUMXbuXNUMXbthe face provokes the appearance of atheroma on the cheek. A cyst occurs due to a violation of the rules of skin care, hormonal failure, as a complication of seborrhea. The operation to remove the formation on the cheek ends with the formation of a scar, because you have to cut out the cyst along with the capsule in which it formed. Therefore, it is desirable to get rid of atheroma as early as possible.
Atheroma on the nose. Most often, a sebaceous gland cyst is formed on the wings of the nose as a complication of acne, seborrhea, hormonal imbalance. It should be distinguished from lipoma, papilloma, internal furuncle, phlegmon and dermoid cyst. If the atheroma on the nose becomes inflamed, this process cannot be completely stopped before the capsule is removed. The cyst cannot dissolve on its own, because it consists of sebum, horny substance and cholesterol. To remove a cyst on the nose, a laser or radio wave method is used, as well as total enucleation.
Atheroma on the forehead. A sebaceous gland cyst on the forehead most often forms at the border of the scalp, where there are many hair follicles. This formation requires differentiation from lipoma, fibroma, syphilitic gum. Removal of atheroma on the forehead is carried out by a laser or radio wave method, in which not only the contents of the cyst are husked, but also the capsule in which the atheroma has formed.
Atheroma on the eyebrows. Education occurs in the hair follicle of the eyebrow, usually reaches a small size. Often it opens on its own, which leads to recurrence of atheroma. Removal of the cyst is carried out on an outpatient basis, proceeds without complications. The scar is hidden behind the bristly hairs of the eyebrow, so it is invisible.
Atheroma on the upper and lower eyelids. Since there are more sebaceous glands on the upper eyelid than on the lower one, atheroma is diagnosed in this part of the face 2 times more often. But it rarely reaches a large size, it looks like a small knot. This formation sometimes suppurates and spontaneously opens. It must be distinguished from papilloma, chalazion, keratosis, adenoma and nevus of the eyelid, senile wart. Especially dangerous is the error in differentiating atheroma from lipoma, which can be transformed into lymphosarcoma.
Removal of atheroma on the eye is carried out without waiting for suppuration, and the resulting tissues are subjected to histological examination to exclude a malignant process.
Diagnostics
The specialist is able to make the correct diagnosis by visual examination and palpation of the formation. To clarify the morphology of the removed tissues, their histological examination is performed. Diagnosis of atheroma in the area of the nose and eyes requires a CT, ultrasound or X-ray examination in several projections. Atheroma on the face is treated by a maxillofacial surgeon, a dermatologist-oncologist.
Treatment and removal of atheroma on the face
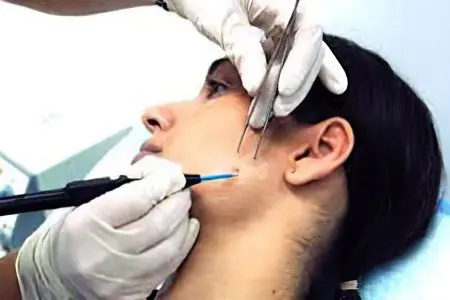
Due to the peculiarities of its structure, the cyst of the sebaceous gland on the face cannot resolve itself. Folk recipes and conservative medicine are ineffective, their use is useless. The only reliable way is the complete and radical removal of atheroma along with the capsule in which it is located.
If spontaneous opening of the cyst occurs, this condition is dangerous because the purulent secret penetrates the subcutaneous tissue and can cause an abscess, phlegmon, or even sepsis (blood poisoning).
Atheroma in the “cold” stage can be removed without complications and the formation of a noticeable scar. For its enucleation, the achievements of laser or radio wave surgery are used. After the laser knife, no scars and scars remain. The operation is performed in 20-30 minutes using local anesthesia.
Removal of inflamed atheroma is carried out in several stages. First, the abscess is opened, removing its contents with the installation of drainage. For 5-7 days, the patient takes antibacterial drugs to relieve the symptoms of inflammation. After 2-3 weeks, the atheroma is completely removed along with the capsule.
Postoperative complications are very rare, so manipulation to remove the sebaceous cyst is considered a simple procedure. Radio wave vaporization (evaporation) of atheroma is a modern non-contact method in which tissues are not damaged, but, as it were, move apart without significant damage. It is used to remove sebaceous gland cysts on the cheeks, on the eyelids, in the area of the nasolabial triangle.
Prevention

To prevent the appearance of atheroma on the face, you need to carefully care for the skin, carry out professional cleaning.
Effective measures to prevent atheroma:
Removing excess fat from the skin with steam baths;
Diet correction – limited consumption of spicy, fatty, carbohydrate foods, the introduction of foods rich in vitamins and fiber into the menu;
Daily removal of decorative cosmetics from the face before going to bed;
Implementation of the recommendations of a cosmetologist for skin care;
Reception of vitamin and mineral complexes to maintain the elasticity of the skin of the face;
Limiting exposure to the skin of the face and body of ultraviolet rays, the use of sunscreen cosmetics;
Protection of the skin in winter from dehydration and dryness;
Enhanced skin care during transitional periods (puberty, menopause) – the use of cleansers, rational menu construction;
Refusal to independently remove blackheads and comedones, from squeezing them out.
You should not be afraid that atheroma is malignant, that is, it will become a malignant tumor. To avoid negative experiences due to psychological discomfort associated with a cosmetic defect, you should immediately consult a doctor if an atypical formation occurs on the skin.









