Contents
At what age do the molars of a child change: teething and symptoms
Permanent molars in a child “come out” each in its own time. Their appearance stretches from 5-7 years to full maturation. Changing teeth can be painful and are accompanied by an increase in body temperature.
How baby teeth can change
Formally, milk teeth also have roots, they practically do not differ from permanent ones. However, when the time is right for the change, the roots of the deciduous teeth simply dissolve, allowing the permanent teeth to grow. There is one more difference: there are only 20 milk teeth, while 32 “adult” teeth should be formed.
A child’s molars can be deciduous or permanent.
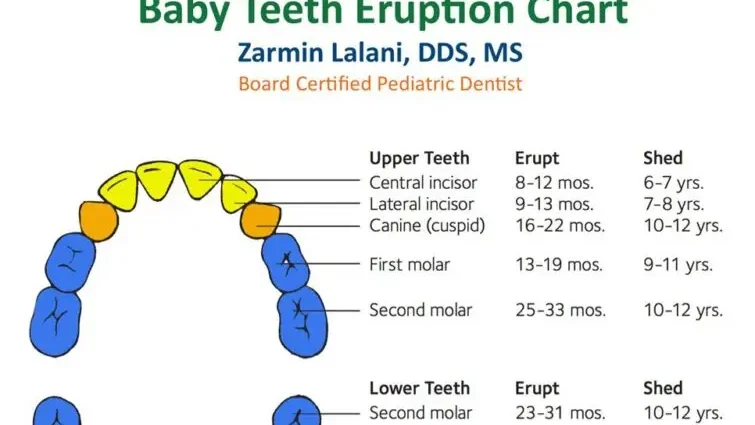
Milk teeth are formed in the mother’s womb, and begin to grow after birth. The first temporary molars – molars can appear as early as 6 months. The growth of deciduous teeth should be completed by the age of 3 years.
At the age of 3, permanent teeth begin to form in the gums, and milk teeth gradually loosen. The change from dairy to permanent ones begins at about 5 years old, and ends by the age of 14. A wisdom tooth can bring surprises. The date of its appearance may be very delayed.
At what age do permanent teeth appear
Permanent teeth grow under milk teeth. Their appearance is individual. In some children, they can begin to “crawl out” from 5-6 years old, in others it is necessary to wait for their appearance up to 7 years. This is also not a pathology, most likely, the teeth are simply not ready to appear yet.
The first molars do not push out the milk teeth. They stand in the place where there were no teeth yet. Teeth grow in pairs. Behind the first molars, 2 incisors appear, later – 2 more. After the incisors, premolars appear, the teeth located in front of the molars. They will be followed by 2 pair of premolars. Then the canines are cut, and behind them are 2 pair of molars. The growth of teeth ends with the appearance of 3 pairs of painters – wisdom teeth. They come out later than everyone else and take up empty spaces at the end of the jaw. These teeth can appear as early as 21 years of age.
Milk teeth gradually change to permanent
First, these teeth appear on the lower jaw, and then on the upper. The appearance of each tooth can be considered, the interval is given for the teeth of both jaws:
- 6-8 years old – 1 molar;
- 6-8 years old – central incisor;
- 7-9 years old – lateral incisor;
- 9-12 years old – canine;
- 10-12 years old – 1 premolar;
- 10-12 years old – 2 premolar;
- 11-13 – 2 molars;
- 17-21 – 3 molars.
The duration of a tooth replacement depends on the child’s health.
The main symptoms of teething
The appearance of milk teeth in an infant is quite painful. He begins to whimper for no apparent reason, his temperature may rise. The signs of the appearance of teeth are as follows:
- The kid is naughty and stops eating.
- The gums are swollen, and white bumps can be seen on them.
- Saliva flows profusely.
- The temperature rises.
- Upset stomach may appear.
Mom should follow the recommendations of the pediatrician to relieve pain.
Permanent teeth can appear in some painlessly and imperceptibly, while others suffer from unpleasant symptoms. There may be fever and salivation. At this time, the child’s immunity may decrease and a runny nose may appear. Gum inflammation can be reduced with dental gels by applying them with a disinfected finger. Gum massage will help a little.
If the high temperature persists for several days, you need to see a doctor.
If permanent teeth grow in the second row behind milk teeth, you need to visit a dentist. In order not to spoil the bite, milk must be removed. It is not difficult to remove them, since nothing was left of the roots at the time of the appearance of permanent teeth.
Rooted teeth appear in infants from 6 months of age. But their roots disappear when the permanent ones are ready to form. The intervals for changing teeth are standard, but there may be deviations that depend on the state of the baby’s health.