Contents
- Where does asparagus grow?
- Can you grow asparagus
- How does asparagus grow in the garden?
- How to grow asparagus outdoors
- How to plant asparagus seedlings
- How to plant asparagus outdoors
- How to care for asparagus outdoors
- Growing asparagus in a greenhouse
- Features of growing asparagus in different regions
- Growing asparagus at home on a windowsill
- Harvesting and storage of crops
- How Asparagus Reproduces
- Diseases and pests
- Conclusion
- Reviews about growing asparagus
Growing and caring for asparagus outdoors requires some knowledge. The plant is considered a vegetable. Dense shoots are used for food, which, depending on the variety, are green, white, purple. For treatment, folk healers use the roots. Beautiful bright orange berries are usually used for decorative purposes.
Where does asparagus grow?

Asparagus grows in almost all countries. The plant tolerates heat and cold well. Large vegetable plantations are found in European countries, Asia, Africa and in the Federation. The plant is considered perennial. In one place, without a transplant, asparagus can grow up to 20 years. The vegetable is not afraid of frost, but it can be destroyed by sudden frosts.
Can you grow asparagus

If desired, any gardener is able to grow a garden crop. The vegetable grows well in the greenhouse, in the garden and on the windowsill. However, when grown indoors, most likely, an ornamental plant is obtained. Asparagus has a very long root. It is difficult to provide conditions in the house for a full-fledged vegetable suitable for food to grow.
How does asparagus grow in the garden?
Garden culture loves a sunny area, nutritious soil that is not overgrown with weeds. The vegetable grows well on sandy soil. Asparagus needs a lot of free space. The site for landing is chosen on the south side, closed from blowing by the wind. The soil is acceptable non-acidic with a lot of humus. Externally, growing asparagus resembles bushes with pods. Shoots or stems may grow.
According to external signs, the vegetable is of three types:

- white asparagus grows underground. According to taste values, it is put on the same place with truffles or artichokes. The technology of growing garden crops requires constant hilling. The complexity of the process affects the high price of the finished product. However, white pods have many useful substances, for which they are valued by vegetarians.

- green asparagus more common in England, as it is better suited to the local climate. The pods have a pronounced taste, are rich in vitamins B and C. The harvest time for garden crops lasts from spring to mid-summer.

- purple asparagus acquires its unusual shade from exposure to sunlight. During cooking, the pods regain their natural green color. The vegetable grows on any bed, a little bitter in taste. If you do not collect the shoots in time, they become rough.
Each type of asparagus requires certain growing conditions, likes different soil, weather conditions.
How to grow asparagus outdoors
The whole process of planting asparagus in the open field and caring for it does not require complex technologies. Garden crops are grown like a regular garden vegetable. Propagated by seedlings or dividing the bush. Briefly, the process can be described in several steps:
- Seeds are sown in the garden in early spring. The holes are made 3 cm deep, indented from each other by about 30 cm. If a garden crop is planted with seedlings, then it is ensured that the upper buds are at ground level.
- With any method, before planting the crop, the land in the garden is abundantly fertilized with compost.
- Plant care consists of standard actions. The bed is loosened, kept clean from weeds. As the soil dries, watering is carried out. Three top dressings are made per season.
If the right place and soil are initially chosen for the garden crop, it will grow up to 20 years. Yields will maximize from the sixth year.
How to plant asparagus seedlings
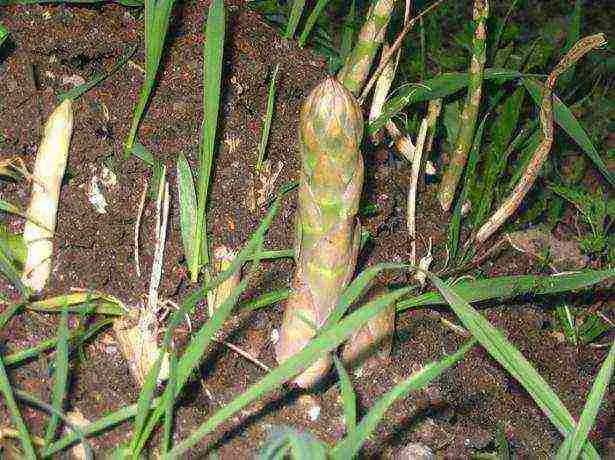

Most often, for the successful cultivation of crops, gardeners sow asparagus for seedlings. The technology is more in demand in cold regions, where frosts still persist in spring.
When to sow asparagus for seedlings
The exact time of sowing seeds of garden crops depends on the climatic conditions of the area. Usually this period falls on March-April. The gardener individually determines the timing, analyzing the weather of past years.
Preparation of planting containers and soil
Containers for seedlings are boxes, cups, flower pots. They must be disinfected with a solution of manganese or other store preparations.
The soil is prepared light. Seedlings like to get plenty of air to the roots. If you use shop soil, then 5 part sand and 1 part vermiculite or coconut substrate are added to 1 parts of it.
Seed preparation
A feature of garden crop seeds is difficult germination. They need a lot of time to hatch. Optimally, before sowing, place the seeds in a solution of any biostimulator, for example, Epin and keep them there for 2 days.
You can use ordinary warm water for soaking, but the duration of the process is increased to 4 days. Moreover, 2 times a day, the water in the soaked seeds is changed. It is important to maintain one temperature for 4 days. Such parameters can be achieved if the seed container is kept in a warm place.
Soaked seeds are spread on a damp cotton cloth, left in a warm place until sprouts appear. Hatching will begin in about a week.
Planting asparagus for seedlings
Usually growing asparagus from seeds in the country is carried out in containers. The process consists of the following steps:
- the container is filled with soil, lightly compacted by hand;
- without making grooves, the seeds are simply laid out on the soil surface in 3-4 cm increments;
- on top of the grain sprinkled with loose soil 1 cm thick;
- crops are moistened from a sprayer;
- the container is covered with glass or a transparent film, placed in the light in a warm place.
In order for germination to go faster, it is necessary to constantly maintain heat and moisture. On the shelter from the inside, condensation will accumulate in drops. Once a day, the film or glass is lifted for ventilation. Maintaining a temperature of + 25 ° C around the clock, sprouts will appear in 1,5 months.
On the video sowing for seedlings:
Seed care
After mass shoots, garden crop sprouts are not completely sprinkled with dry peat. In the interval between 10-15 days, top dressing is carried out with complex fertilizer. Seedlings are watered, the soil is carefully loosened, and the container is turned daily in different directions to the light. In about a month, the stems will grow 15 cm high. The crops are thinned out. The strongest plants should remain at a distance of 10 cm from each other.
Asparagus seedlings are hardened at the end of May. First, she is kept outside for 1 hour. Every day the time is increased until they reach 12 hours.
How to plant asparagus outdoors
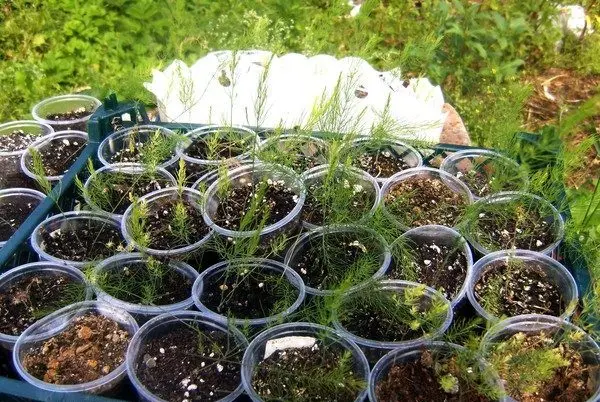

The process of growing asparagus in the garden begins with planting seedlings. At this point, the culture has passed the stage of hardening, ready to meet with open ground.
Planting dates for asparagus in the garden
Planting asparagus, like most garden crops, is best done in warm soil. At this point, the time for return frosts should have passed. In most regions of the Federation, the beginning of June is considered the optimal time for planting seedlings. In the south, you can plant earlier.
Site preparation
A garden bed is being prepared in a sunny area. If the soil is poor, during digging, 1 bucket of humus is added per 2 m1, mineral complexes are added according to the instructions. Clay soil is considered heavy for the plant. During the digging of such a site, sand is introduced.
Seedlings can be planted not only in spring, but also in autumn. In the second case, during soil enrichment, mineral complexes are replaced with fertilizer containing phosphorus and potassium. Nitrogen fertilizers should not be applied in autumn. Rapid growth of shoots before winter is not needed.
How to plant asparagus outdoors
There are two ways to plant a garden crop: seeds or seedlings.
Planting asparagus seeds in open ground
If the sowing method is chosen, then on the prepared bed, grooves 5 cm deep are cut with a stick or the tip of a chopper. The seeds that have been soaked are sown densely. Many of them will not germinate. It is better to break through the extra shoots later. The sown grooves are covered with a thin layer of loose soil, lightly clapped with the palm of your hand. Garden crops are watered with warm water. After soaking up the liquid, the bed is mulched. Seeds germinate for a long time. They need warmth and moisture. Covering the beds with white agrofiber helps to ensure a good microclimate for crops.
Planting asparagus seedlings

For planting seedlings, the depth of the grooves in the garden bed is increased to 30 cm. It is important to consider that over 20 years of life in one place, garden crop bushes will grow strongly. If the vegetable is not supposed to be transplanted in the future, then the seedlings in the row are arranged in increments of 40 cm. The aisles are left at least 1 m wide.
After cutting grooves at the bottom, mounds are formed from the fertile soil. Seedlings are placed on them with roots, sprinkled with loose soil, pressed with a hand. If the roots are long, they are shortened with scissors. The optimal length of the rhizome branches is 5 cm. After planting the seedlings, the groove is abundantly filled with water, covered with peat or sawdust mulch.
How to care for asparagus outdoors
A simple agricultural technique for growing asparagus requires the usual work for a gardener. The culture requires timely watering, top dressing, weeding from weeds.
Watering and top dressing
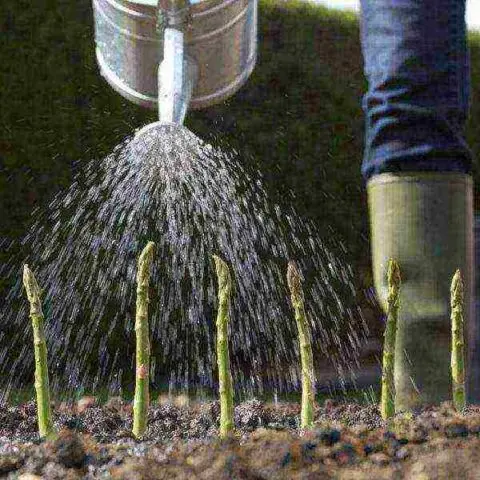

Garden crops do not tolerate excess moisture in the ground, but seedlings need to be watered frequently. The first two weeks after planting, the plants are watered abundantly to speed up the formation of roots. Immediately after soaking up the water, loosen the soil. If this is not done, the resulting film will block the access of oxygen to the roots. Seedlings need to constantly keep the soil moist, and adult plants are watered less frequently. However, the drying of the soil should not be allowed, otherwise the shoots will become bitter.
Fertilizing the culture is definitely needed, since the yield depends on it. The plant practically does not need nitrogen. Copper and potassium are needed, as these substances affect the succulence of the shoots. The best fertilizer is organic and herbaceous infusions.
During the season, asparagus requires three dressings:
- The first top dressing of garden crops in the spring is done with organic matter. Dry granules of potassium, phosphorus and calcium are poured from mineral fertilizers, after which they are watered abundantly.
- The second top dressing falls on July. Asparagus is poured with a solution of chicken manure at a high concentration of 1/10. Top dressing gives strength to the plant after harvest.
- The final third top dressing of the culture is done in the fall at the end of October. 1 g of superphosphate and potassium salt are added per 2 m30.
Organics makes asparagus shoots tender, tasty, and gives them a white color. Experienced vegetable growers used in spring or autumn, with the advent of sprouts, each plant was covered with a bucket of humus.
Trimming
After planting the seedlings, shoots will appear in the garden. You cannot cut them. Asparagus should grow into openwork bushes. In the second year, pruning is undesirable. In extreme cases, you can cut 1-2 shoots. Full pruning of the crop is carried out in the third year. Shoots about 12 cm high are subject to cutting. Sanitary pruning of the plant is carried out in the fall. All yellowed shoots are cut off, leaving stumps 2,5-5 cm high above the ground.
Asparagus transplant
Transplantation of asparagus to a permanent place is carried out in May. Do it in the second year of life. You can transplant a garden crop in September so that the plant gets even stronger over the summer. Dig up a garden bed for planting. 1 buckets of compost are added per 2 m4. The depth of the trenches during spring planting is made in half the bayonet of a shovel. If the crop is transplanted in the fall, the grooves are dug deep into the bayonet.
Under each plant contribute 25 g of mineral complexes. You can sprinkle 1 g of fertilizer on 70 m of trench. At the bottom of the grooves, mounds are formed from the soil, asparagus is planted with roots, covered with earth. After transplanting, the plants are watered abundantly.
Preparation for winter
In order for the asparagus to overwinter well, in the fall, before the onset of frost, the shoots are cut short. Hemp protruding from the ground is covered with soil, forming a hill. Peat or compost is additionally poured on top.
Growing asparagus in a greenhouse
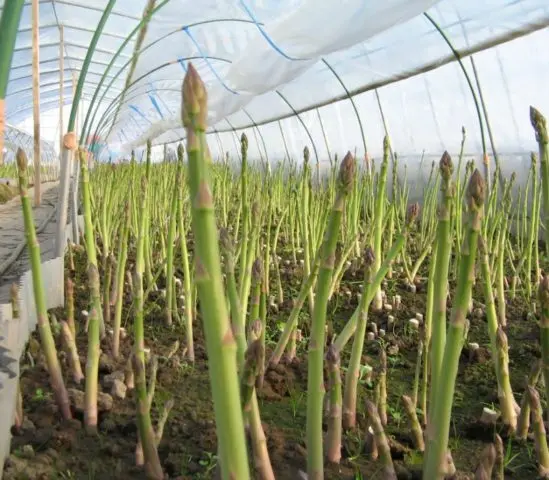

Greenhouses can be used to grow asparagus from seeds at home. However, not all varieties can be sown. Early ripe hybrids are most suitable, for example: Connovers Colossal, Franklin, Arzhentelskaya and others. The advantage of greenhouse crop cultivation is early harvests. Asparagus does not require artificial lighting. The plant gets enough natural light. The temperature is maintained in the range from + 15 to + 20 °C. Watering is carried out less frequently, since moisture evaporates less in the greenhouse. Top dressing and other procedures are performed in the same way as when growing a vegetable in open ground.
Features of growing asparagus in different regions
Asparagus grows in all regions except the far north. For cold areas in the garden, it is optimal to leave male plants. They are characterized by increased frost resistance. Female plants are more thermophilic.
Growing asparagus in the Moscow region
Especially for the climatic conditions of the Moscow region, varieties of asparagus were bred. The most popular are Early Yellow, Harvest 6, and Danish White. Varieties are well suited to the climate of Belarus. To get a good harvest, the culture is grown in seedlings.
Growing asparagus in Siberia
Cold-resistant varieties of asparagus withstand frosts down to -30 ° C with little snow cover. They can be grown in Siberia. For the winter, the plants are covered with mounds of earth and a thick layer of manure. Overheating, organic matter releases heat, from which the asparagus rhizomes are heated. In the spring, until a positive air temperature is established, a greenhouse is stretched over the bed, protecting the young shoots of the vegetable from frost.
Growing asparagus in the Urals
Agrotechnics for growing crops in the Urals is similar to that for Siberia. More mulch in the fall, a greenhouse in the spring.
Growing asparagus in the Leningrad region
For the entire middle lane, including the Leningrad region, the cultivation technology and varieties are the same as for the Moscow region. The climate is about the same.
Growing asparagus at home on a windowsill
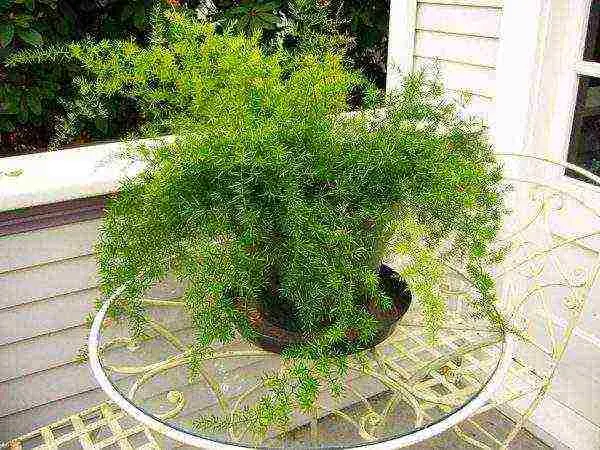

The culture is intended for planting in a greenhouse or garden. It will not be possible to grow full-fledged asparagus at home on the windowsill. A long rhizome requires a great depth of the earth, and branches grow strongly on the sides. In a flower pot, asparagus will grow simply as an openwork ornamental plant.
Harvesting and storage of crops
If the gardener took good care of the asparagus, followed agricultural practices, the culture will thank the harvest.
Asparagus yield
The disadvantage is the low yield of vegetables. Only young shoots are eaten. Depending on the variety and time of growth in one place, 1-2 kg of shoots are collected from 2 m5 of the plot. The first harvest from a plot of 6 acres will bring about 1200 kg of vegetables. With each year of growing a crop in one place, the yield will increase.
When to Harvest Asparagus
The first vegetable crop is harvested only in the third year after planting. However, if the plants are weak, the asparagus harvest is postponed to the fourth year. The maturity of the shoots will be signaled by thick bushes in the garden. The size of the shoot ready for harvest is approximately 2 cm thick and up to 20 cm long.
How to harvest asparagus
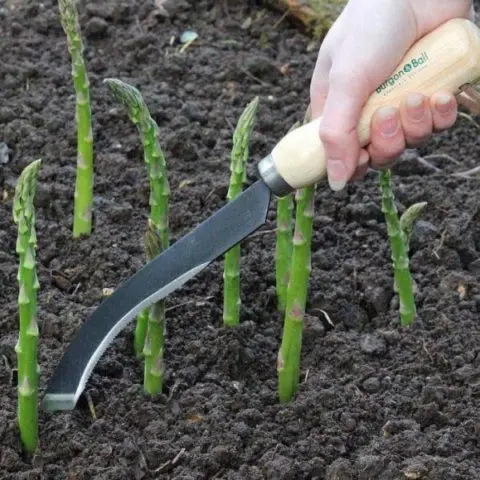

It is optimal to cut 3 shoots from one bush, a maximum of 5 pieces. A special sharpened knife is used to harvest the vegetable. First, the ground is raked around the escape. The cut is made 3 cm above the rhizome. The remaining stump is covered with peat or compost. In cold regions, shoots are cut every two days. In the southern regions, asparagus grows faster. Shoots are cut 1-2 times a day.
How to save asparagus
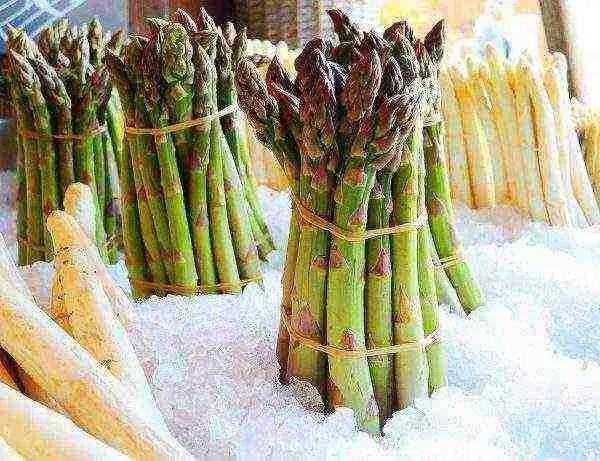

Asparagus shoots are not subject to long-term storage. On the third day, the vegetable begins to coarsen, loses its juiciness. To keep the harvest up to 4 weeks, the shoots require a minimum humidity of 90% and an air temperature of 0 ° C. Usually they are wrapped in a wet cloth, sent to the refrigerator. Freezing helps to keep vegetables longer. The shoots are wrapped with a film or cloth, put in the freezer.
How Asparagus Reproduces
There are three ways to propagate culture. Each gardener chooses the most suitable option for himself.
Reproduction of asparagus by dividing the bush
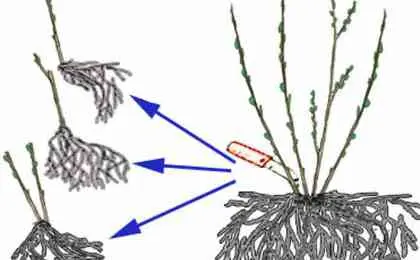
The easiest way allows you to propagate the culture in spring and autumn. If the summer is not hot, then you can try to perform the procedure at this time of the year. First, dig out an adult bush. With a knife or hands, sprouts with full-fledged roots are separated. Each seedling is planted in the garden in the same way as seedlings.

Similarly, a garden crop bush can be propagated by rhizomes, dividing it in the spring before the appearance of young shoots. Each root should have 1 bud.
Reproduction by cuttings

The method of propagation of culture is complex, does not always give a positive result. Cuttings are carried out from spring to June. Cuttings are cut from last year’s green shoots, dipped in a solution of a root growth stimulator, and planted in containers with wet sand. Each seedling is covered with a glass jar or cut PET bottle. Asparagus cuttings are periodically ventilated, sprayed with water. Rooting should occur after 1,5 months.
Reproduction by seeds
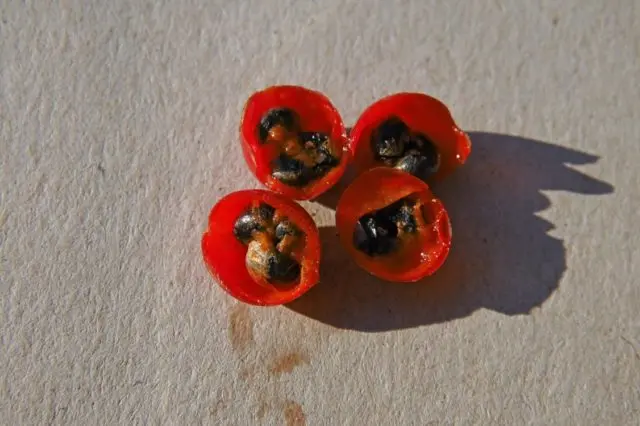

Garden crops are planted with seeds on seedlings or immediately in open ground. The propagation method is not very popular, since asparagus seeds do not germinate well. In addition, the gardener experiences additional difficulty in caring for seedlings.
Diseases and pests

Asparagus is resistant to diseases, rarely affected by pests, but sometimes unpleasant situations occur:
- The beginning of the root rot of a garden crop is signaled by crumbling twigs. The plant is treated with Fundazol or the entire bush is removed.
- In June, shoots of garden crops can be affected by rust. They become dark in color, wounds appear. The fungus is treated by spraying with a fungicide.
- The asparagus fly, which lays eggs inside the shoots, is considered a dangerous pest of garden crops. The emerging larvae eat the plant. Insecticides help fight the fly. The most popular drug is Aktellik.
- The asparagus ratchet loves to feed on succulent stems, foliage, and even seeds. Adult beetles are harvested by hand. The larvae are destroyed in the soil by introducing the Actellik preparation.
To prevent the death of plantings, preventive treatments are carried out. Plants are inspected weekly.
Conclusion
Growing and caring for asparagus in the open field is difficult at the initial stage. In the future, the culture requires minimal labor and timely harvesting.











