Contents
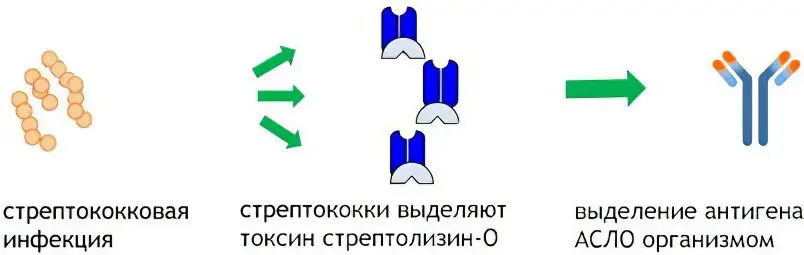
Antistreptolysin-O (ASLO, ASO) are antibodies that are produced against streptolysin, which is an antigen of group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus (GABHS). This streptococcus inhabits the dermis and mucous membranes of the body.
The determination of ASL-O is a very important analysis that is carried out in a laboratory setting. It allows you to identify a harmful bacterium that has pyogenic abilities. This microorganism belongs to the genus Streptococcus pyogenes. Scientists discovered the bacterium back in the 19th century. It has been established that this smallest spherical organism is capable of causing serious damage to human health.
ASL-O in the blood: norm and pathology

In order for beta-hemolytic streptococcus not to harm the body of its carrier, it must be detected and destroyed in time. To do this, scientists have developed a research method that allows you to determine ASL-O in the human body. It makes it possible to detect antibodies to beta-hemolytic streptococcus in the blood, which confirms its presence in the body.
Normal antibody titer values may vary slightly depending on the individual laboratory, but the average values will be as follows:
If the child is under 14 years old, then the values u150buXNUMXbshould not exceed XNUMX U / l.
For people over 14 years old and for an adult, this figure should not exceed 200 U / l.
The most common way to detect a pathogenic microorganism is using a litmus test, which is easy to use. It is carried out quickly and does not require financial costs. This method makes it possible not only to determine the presence of antibodies to bacteria, but to establish their titer. To do this, the kit includes special reagents. However, some scientists still prefer turbodimetric research, although it is more expensive and requires special instruments.
What could be the result?
The litmus test allows you to observe how a disease develops in a person. At the same time, it must be carried out several times, with an interval of a week. This will allow you to make the most accurate forecast.
Possible options:
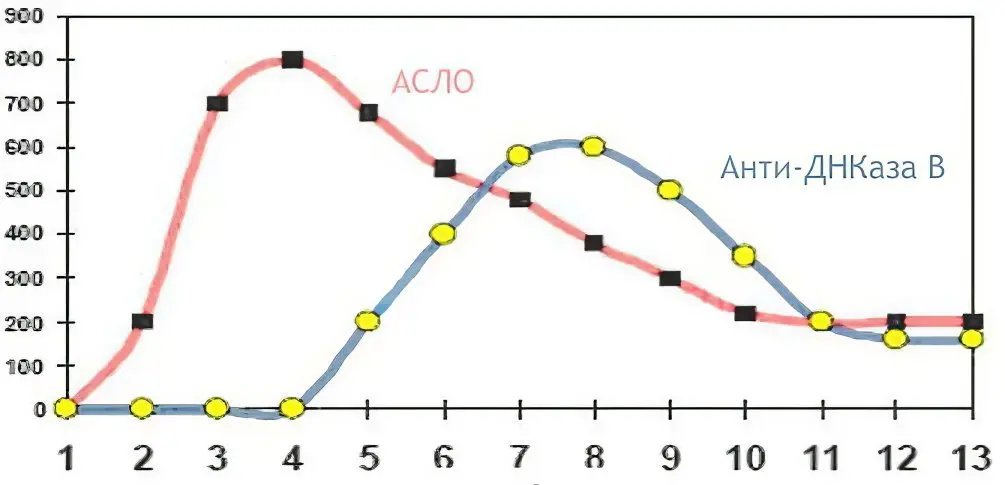
The amount of antibodies increases in the blood a week after the infection has occurred. After about 3-5 weeks, the test results will be maximum. If the body successfully fights bacteria, then their level will begin to decrease, and after 6 months – 1 year it will return to normal.
If there is a persistent increase in antibodies, then this most often indicates that the disease has a complicated course. A person develops a rheumatic process. This can happen after suffering a sore throat. At the same time, antistreptolysin-O will remain at a high level for a long time.
If the ASLO titer begins to decline or returns to normal after 30-60 days from the onset of the disease, then you can count on its favorable outcome. This means that there is no risk of developing rheumatism, and the prognosis for a full recovery is favorable. If a person receives high-quality and adequate treatment, then recovery will come quickly.
If the ASLO titer does not decrease even after 6 months from the onset of the disease, then the likelihood of its recurrence is high. At the same time, the forecast cannot be called favorable.
Also, when conducting a test for ASL-O, it must be taken into account that in approximately 15% of all patients, the antibody titer may remain within the normal range. In this case, streptococcus in their body will continue to exist. In addition, a radically different situation may develop, when the level of antibodies remains high, but there are no signs of the disease. High values of ASL-O can be observed in patients suffering from chronic inflammation of the tonsils, rheumatoid arthritis. Carriers of the infection are people who believe they are healthy, but at the same time beta-hemolytic streptococcus is present in their body. It does not manifest itself until the immune system is able to restrain it.
The growth of ASL-O leads to the body’s response to the penetration of streptococcus bacteria into it, namely GABHS. A person who has had a streptococcal infection should not expect that he will develop immunity to this bacterium. Such immunity does not differ either in the degree of its severity or in stability over time. In this case, the likelihood of developing complications of infection is extremely high. Infection with coccal flora threatens the development of rheumatic lesions that lead to heart defects in previously healthy children. Moreover, even a single transferred angina can provoke a serious illness. Therefore, it is so important to identify the causative agent of the disease and completely destroy it.
Sometimes doctors suggest testing for ASL-O for adults who have not had a sore throat. The fact is that this technique makes it possible to detect rheumatoid arthritis. However, the level of antibodies will not be as high as with a streptococcal infection. In parallel, the patient is offered to take an analysis for rheumatoid factor and CRP-protein of the acute phase, which will clarify the diagnosis.
Why can ASL-O rise?
Beta-hemolytic streptococcus can cause serious harm to the human body that it infects. Infection occurs quickly, food and contact transmission is possible, the infection can also be spread by airborne droplets. The danger is both an infected person suffering from symptoms of the disease, and a carrier of the bacterium.
When this pathogen enters the human body, it develops diseases such as:
Angina.
Pharyngitis.
Erysipelas.
Myositis.
Pneumonia.
Glomerulonephritis.
Scarlet fever.
Beta-hemolytic streptococcus is dangerous in terms of the development of serious complications, including:
Purulent inflammation of the middle ear and sinuses.
Inflammation of the brain.
Pyoderma.
Osteomyelitis.
Glomerulonephritis.
Inflammation of the heart muscle.
Rheumatism with further development of heart disease.
Toxic shock.
Sepsis.
Neurological disorders in a child.
If the patient develops complications of the disease, then the test shows high values of antibodies in the human blood. At this time, streptococcus is able to affect almost any organs and organ systems. It actively creates bacteria similar to itself, which produce a huge amount of toxins. At the same time, human immunity fights with all its might against foreign microorganisms, which determines the severity of the course of the disease.
After a single episode of tonsillitis, pharyngitis, cellulitis, or erysipelas, some people may become more susceptible to streptococcal infections. This contributes to the occurrence of relapses of the disease. At the same time, in the blood of such patients, the test for ASL-O will always give high levels of antibodies.
Dealing with disease complications
Immediately after infection, the bacterium is quite difficult to identify. In the blood, antibodies will not be detected at all. In order for a pathogen to settle in and begin to multiply, and for the immune system to recognize it and begin to resist, time must pass. After a few days, the immune system will begin to produce antibodies aimed at fighting the microbe. It is on them that the test for ASL-O will give a reaction.
If there is a suspicion of an infection that has occurred, a smear of mucus from the throat should be taken. Then the laboratory will perform a bacterial culture, which after 3 days will allow you to evaluate the results.
It is very important to determine the source of inflammation if a child suffers from tonsillopharyngitis. After all, treatment is built on the use of antibiotics, which must be selected correctly. The ASL-O test allows not only to detect streptococcus, but also to prevent possible complications, which is achieved through timely antibiotic therapy.
To date, scientists are developing a vaccine that is designed to stop the process of GABHS reproduction in the human body. This drug is called StrepAvax. It contains particles of M-proteins taken from 26 strains of beta-hemolytic streptococcus, which are more common than others. Of course, this vaccine will not solve all the problems associated with this pathogenic flora, but will significantly reduce the incidence among the human population, and will also make it possible to avoid serious health complications. Until this vaccine is developed, the existing achievements of modern medicine should be used and, if necessary, a test for ASL-O should be carried out.
Streptococcus – the school of Dr. Komarovsky:










Men Remaprobaga analiz topshirgandim shu analizim normada 200 bolsa menda 1600 chiqdi
Assalomu alaykum bu kassalikni davolashni ham òrgatsangiz òglimda 800 analizida
500 chiqdi menda davolasa boladimi
Salom o’g’lim 5 yow uning analizida ALSO 198 chiqqan buni davolasa boladimi
Assalomu alaykum bugun kizimni analizida 1000chikdi 7yosh davolash usulini xam yozilar iltimos