Contents
Ascospherosis is a disease that affects the larvae of bees. It is caused by the fungus Ascosphera apis. The popular name of ascospherosis is “calcareous brood”. The title is apt. The larvae affected by the fungus after death are very similar to small chalk balls.
What is dangerous ascospherosis
The fungus that has grown to a visible state looks like white mold. It is what he is. Ascospherosis affects mainly drone larvae at the age of 3-4 days. Like any mold, the fungus grows on weakened organisms. Varroa-infected bees are more likely to be affected by ascospherosis.
This type of fungus is bisexual. It has sex differences in vegetative filaments (mycelium). When two threads fuse, a spore is formed, which has a very sticky surface. Due to this property, spores can spread not only within the same hive.
The most frequent cases of ascospherosis are in summer. Mold thrives in damp places and high humidity. Favorable conditions for the development of ascospherosis arise:
- rainy summer with high humidity;
- when keeping an apiary in a humid area;
- after prolonged cold snaps;
- with excessive use of oxalic and lactic acid.
Organic acids are often used by beekeepers to combat another bee problem, varroatosis.

In these places, the conditions for reproduction of the ascosphere apis are the most favorable, since the walls of the hive can become damp due to insufficient or improper insulation. Air circulation is also worse than in the center, where the bees work hard with their wings.
Symptoms of bee disease
The appearance of ascospherosis in the hive can be seen by the dead larvae lying in front of the hive, on the landing site or on the bottom under the combs. When checking the hive, you can notice a white coating on the bee larvae. If the cell is not sealed, the head end of the larva is covered with mold. If the cells are already sealed, the fungus will grow through the lid and infect the larva inside. In this case, the honeycombs look covered with a white coating. In the opened cells, one can find hard lumps attached to the walls of the combs or lying freely on the bottom of the cells. These are larvae that died from ascospherosis. These “lumps” occupy about ⅔ of the volume of the cell. They are easy to remove from the cell.
Infection methods
The spores of the fungus infect the larvae in two ways: from the inside and through the walls of the combs. When it enters the intestine, the spore germinates from the inside and then spreads through the walls of the honeycombs to other cells. The mold grows through the lids and wraps around the honeycombs completely.
When spores get on the skin of the larva from the outside, the mycelium grows inside. In this case, ascospherosis is more difficult to detect, but there is a chance that it will not take on catastrophic proportions.
Ways of transmission of ascospherosis:
- bringing spores together with pollen into the hive by bees who have returned home;
- rearrangement of frames with bee bread, honey or brood from an infected hive to a healthy one;
- when a bee feeds infected food to a healthy larva;
- spread by bees cleaning infected cells;
- when using inventory common to the entire apiary;
- with insufficient disinfection of hives.
Initially, the bees bring the fungus from greenhouses, where it is always warm, humid and has poor air circulation. Mold thrives in greenhouses, and, once on a bee, it begins to grow in a living organism. Due to the fact that the mycelium grows into the body of a bee or larva, it is very difficult to treat ascospherosis.
Stage of the disease
Ascospherosis has 3 stages:
- light;
- medium;
- heavy.
The light stage is also called the latent stage, since the number of dead larvae is not more than 5 pieces. Such a number is easy to overlook or write off for other reasons. But the mold tends to grow and move to the next step. The average degree is characterized by the loss of larvae from 5 to 10.
Losses in severe form are 100-150 larvae. It is believed that mild and moderate forms can be left untreated, since losses are low. But ascospherosis is a bee disease caused by a fast-growing living organism. Mold is easier to eliminate immediately, as soon as its focus has been noticed, than to wait until the fungus grows and matures into spores.
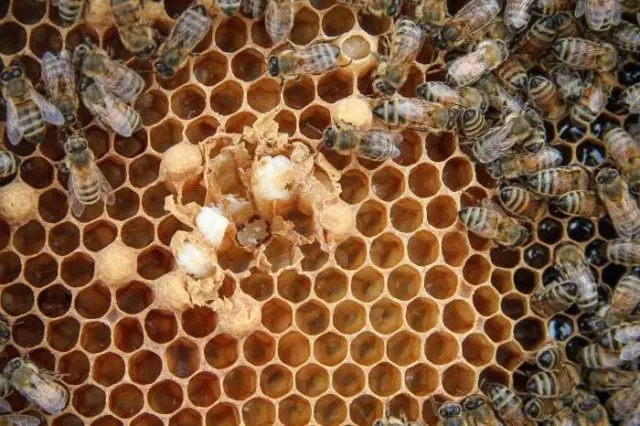

How to treat calcareous brood in bees
Ascosfera apis is sensitive to fungicidal preparations in the same way as any other mold. The main thing is not to overdo it with the dosage and not poison the bees at the same time. Garden fungicides should not be used, however. Their concentration for plants should be higher, and it would be too expensive to select a dosage for bees by an experimental method. For the treatment of ascospherosis in bees, separate fungicides have been developed:
- levorin;
- ascozol;
- ascovite;
- mycosan;
- Larvae;
- clotrimazole.
Nystatin is also recommended as an antifungal drug, but beekeepers have sharply opposed opinions about it. In addition to industrial antifungal drugs, beekeepers are trying to treat ascospherosis with folk remedies:
- garlic
- field horsetail;
- onions;
- celandine;
- yarrow;
- iodine.
Of folk remedies, iodine is the most effective. In fact, all other methods are based on the presence of free iodine ions in garlic and onions. The concentration of these ions is low and it is required to make extracts.
Antifungal drugs only stop the growth of the ascosphere. There is only one guaranteed way to get rid of ascospherosis: the complete burning out of infected bees. If the colony of bees is weak, it is better to do so.
How to treat ascospherosis of bees
Since any mold is difficult to destroy, in the treatment of ascospherosis it is necessary to carry out a whole range of measures aimed at stopping the development of the fungus:
- carry out the processing of all hives in the apiary;
- bees are moved to a new disinfected hive;
- bees are treated with fungicidal preparations.
To destroy the fungus inside the bees, it is convenient to use a fungicide diluted in sugar syrup. Such treatment of bees from ascospherosis is best done in the fall after honey is pumped out. After taking honey, the colony of bees is still fed with sugar in order to restore food supplies for wintering. The sale of such honey is prohibited, and it is undesirable to apply such treatment in the spring. But the bees will provide the “medicine” and the larvae in the cells.
Driving bees
Treatment of ascospherosis begins with the placement of a colony of bees in a new disinfected hive. Honeycombs taken from a healthy family and new dry land are placed in it. The old infected uterus is replaced with a young healthy one.
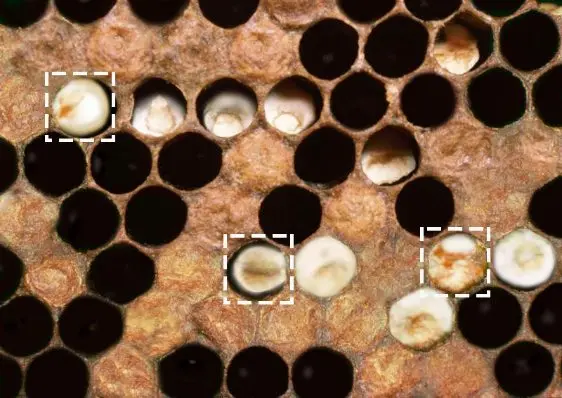
Heavily infected brood is removed and the wax is melted. If the combs are not heavily infested, they can be placed in the hive, isolating the queen from the brood. But if possible, it is better to get rid of diseased larvae, even if there are several of them. Mold grows quickly. Podmor is burned, and they do not insist on vodka or alcohol as a panacea for all diseases.
Since the bees themselves can also be infected with mycelium or ascosphere spores, they are treated with medication or folk remedies.
Treatment of bees from ascospherosis with a medical method
The method of application of preparations for ascospherosis of bees depends on the form of the preparation and the time of year. In spring, early summer and autumn, fungicides can be fed with sugar syrup. In summer it is better to use spraying. Doses and methods of administration can usually be found in the instructions for the drug.
Syrup for feeding is prepared in the proportion of 1 part water to 1 part sugar. For spraying, take a less concentrated solution: 1 part sugar to 4 parts water.
Askozol
To feed 1 ml of ascosol, it is diluted in 1 liter of sugar syrup at a temperature of 35-40 ° C. Feed 250-300 ml per day per family for 1-2 weeks. You have to feed every other day.
In summer, bees, walls and frames in the hive are sprayed with the drug. For spraying, 1 ml is diluted in 0,5 l of a less concentrated solution. Spraying is carried out with a fine spray. The consumption of the composition is 10-12 ml per one honeycomb frame. Spraying is repeated every 2-3 days until the family recovers. This usually takes 3 to 5 treatments.
Levorin
This fungicide acts on the redox enzymes of the ascosphere. It is usually used as a top dressing. For 1 liter of syrup, 500 thousand units are taken. Levorina. Give twice with a break of 5 days.
Nitrofungin
It is preferable to use for the treatment of beehives. Spray walls and frames with an aerosol. Consumption of half a bottle per hive. When feeding, make an 8-10% solution.
Clotrimazole
One of the most effective fungicidal preparations. Used for spraying beehives. In autumn, they are added to sugar syrup for feeding.

Iodine
Iodine is difficult to attribute both to folk methods of dealing with ascospherosis, and to industrial ones. It is “in the middle”. Levorin is an industrial preparation based on iodine. But iodine fungicide can be made by hand.
Treatment of ascospherosis in bees with iodine monochloride is very effective, according to beekeepers. In this case, it is not even fed or sprayed on the frame and wall. 5-10% iodine monochloride is poured into polyethylene lids, covered with cardboard and placed on the bottom of the hive. Evaporating, the drug stops the development of the fungus.
A solution of iodine in sugar syrup for processing the hive is made independently. Iodine tincture is added to the syrup until a light brown liquid is obtained. This composition is sprayed every 1-2 days. You can also feed the bees with the solution.
Treatment of ascospherosis in bees by folk methods
Really popular methods include attempts to cure ascospherosis with the help of herbs. Even for prevention, this is not good enough. Bunches of yarrow, horsetail or celandine are wrapped in gauze and placed on frames. Remove when grass is completely dry.
Garlic is kneaded into gruel, wrapped in polyethylene and laid out on frames. Of all the folk remedies for combating mold on bees, garlic is the most effective.
Dried herbs are also used. They are crushed into dust and sprinkled with bee streets. A handful of powder is consumed per hive. A decoction is made from horsetail: put, without ramming, into a saucepan, pour water and boil for 10 minutes. Infuse for 2 hours, filter and make syrup for feeding. Give the syrup to the bees for 5 days.
Sometimes a strong solution of potassium permanganate is used. But this tool can only be used to disinfect the wooden parts of the hive.
Decontamination of hives and inventory
There are many ways to disinfect hives, but treatment by any of the methods must be carried out as quickly as possible, since the mycelium of the fungus will grow into the wood. If this happens, there will be only one way to cure ascospherosis: burn the hive.
The hive is burned with a blowtorch or “drowned” for 6 hours in an alkaline solution. Small inventory items are disinfected twice. If possible, they can also be soaked in alkali. The honey extractor is smeared with a strong solution of lye or laundry soap and left for 6 hours. Then rinse thoroughly with water. All fabric items are boiled.
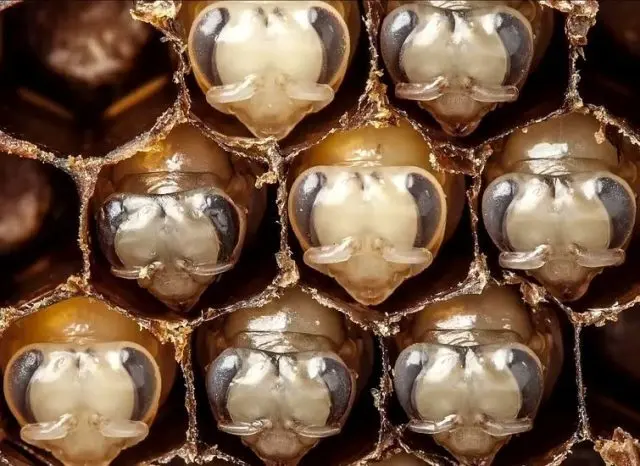

The combs are removed from the infected hives and the wax is melted. If there are more than 50 affected larvae, the wax is only suitable for technical purposes. Merva is destroyed from him.
It is undesirable, but you can use combs from a family slightly infected with ascospherosis. In this case, the cells are thoroughly disinfected. Based on 100 liters of disinfectant, take 63,7 liters of water, 33,3 liters of perhydrol, 3 liters of acetic acid. In this quantity, 35-50 frames with honeycombs can be processed. Honeycombs are kept in solution for 4 hours, then dried thoroughly.
A set of preventive measures
The main prevention of any mold is its prevention. The most favorable conditions for the development of ascospherosis are dampness, lack of ventilation and relatively low temperatures. In this case, no immunity will save. For prevention, it is necessary to provide bee colonies with acceptable conditions. If the hives remain to winter outside, then make external insulation and good ventilation.
It is for this reason that it is necessary to insulate the hive from the outside, and not from the inside.
It will not be possible to completely avoid dampness, especially if the winter is warm and slushy or there have been thaws. Therefore, in the spring, the bees are first transplanted into a clean hive free from ascospheres, and all frames are checked and those affected by ascospherosis are thrown away.
Another way to avoid ascospherosis is to feed the bees with pure honey, not sugar syrup. The syrup weakens the bees, and is only acceptable for medicinal purposes. Collected pollen is also left to the bees. A strong colony of bees is less susceptible to ascospherosis than one weakened by hunger.
Do not use inventory from someone else’s apiary. It can be infected with ascospherosis. Periodically it is necessary to take samples from the hive and take tests for the presence of pathogenic microorganisms. Podmor and other debris from the bottom of the hive will do.

Conclusion
Askosferoz is able to leave the beekeeper without the main means of production. But with a careful attitude to bee colonies, the growth of the fungus can be noticed even at the initial stage and measures can be taken in time.









