Contents
What is ascariasis?
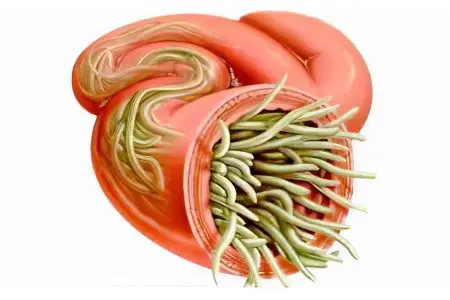
Ascaridosis is a type of helminthiasis caused by roundworms belonging to the class of nematodes, the family Ascarididae (roundworms). They parasitize in the intestines of humans and animals. According to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), 807–1,2 billion people worldwide have ascariasis. [1].
There are several types of these parasites that infect various representatives of vertebrates: cats, dogs, birds, pigs. Basically, they are selective in choosing the main host, preferring only a certain species and not affecting other animals. The species Ascaris lumbricoides (human roundworm) parasitizes only in the human body, where it can live from one to two years.
The main place of life of ascaris is the small intestine. At the same time, the worms do not have any adaptations such as scolex, which allow them to attach to the walls of the intestines. In order to stay in the intestines, an adult roundworm has to constantly make movements in the opposite direction to the movement of the food bolus. This helminth cannot be found alive in the feces. Only dead individuals or eggs laid by roundworm females get there. Reproduction begins only when there are sexually mature females and males in the intestines. Individuals of the same sex are incapable of reproduction, most often they exist in the human body until the natural end of their lives. Such cases are rare, since in mass invasion there is no shortage of both sexes.
In countries with high sanitary and hygienic standards and an excellent level of development of medicine, the incidence of ascariasis is much lower than in developed countries, where even clean water and quality food are not enough. Most often, children from 3 to 7 years old become infected with this parasitic infection. This age category is characterized by insufficiently careful adherence to hygiene requirements, children wash their hands from time to time, often eat poorly washed fruits and vegetables, and play with animals.
Manifestations of ascariasis most often disturb patients during the migration of larvae and adults through the body. The symptoms present depend on the stage of parasitic invasion and the location of the helminths. Most often, invasion manifests itself in the form of violations of the normal functioning of the digestive system (due to the vital activity of adults), and the respiratory system (where larvae migrate).
Ascariasis in most cases does not lead to death, although violations in the human body can result in dangerous complications. Most often, this development threatens children and adults with weakened immune systems.
Who is Ascaris?

Ascaris is the worm Ascaris Lumbricoides, belonging to the group of round helminths. The length of females can reach 40 cm, and the length of males is 25 cm, the width of individuals is from 4 to 6 cm. The tail part of the males has a characteristic bend towards the abdomen. The color of ascaris is white-pink or yellow-pink, the shape is spindle-shaped. Ascaris eggs can be found in soil, in water, on plant products. The mode of transmission of parasites is oral-fecal (through water, soil or food contaminated with worm eggs).
Ascaris larvae enter the human body if personal hygiene rules are not observed. The disease manifests itself in an increase in body temperature to high levels, in general malaise, in a persistent dry cough, in violation of the gastrointestinal tract, in allergic reactions. To detect parasitic infestation, stool sampling for worm eggs is required; auxiliary methods are a general blood test and serological tests. Adult ascaris often can be detected when performing an x-ray of the lungs and intestines.
How long do roundworms live in the human body?
Roundworms live in the human small intestine. They are kept in it due to the constant movement in the direction opposite to the movement of food. Together with feces, roundworm eggs and dead individuals are excreted. The parasite lives in the human body from one to two years, then it dies of old age. In the intestines, when infected, individuals of both sexes most often grow.
What do roundworm eggs look like in stool?
Ascaris eggs in the feces are quite difficult to see with the naked eye, since their size does not exceed 0,05-0,07 mm. They may be round or oval in shape. If the helminth egg is not fertilized, then its shape will be incorrect. The egg has a dense shell of even layers. The eggs can only be seen under a microscope. They will appear in the feces after about 2-3 months from infection with parasites.
How many eggs does roundworm lay daily?
Every day, a sexually mature roundworm in the human intestine lays more than 200 non-invasive eggs. They, together with faeces, are released into the external environment. After entering the soil, under favorable conditions, the eggs acquire the ability to cause disease two weeks later.
Ascariasis symptoms
Ascariasis in an adult who does not have severe chronic pathologies can be asymptomatic for a long time. Such signs of ascariasis as belching, heartburn, indigestion, pain in the intestines [2], patients may attribute to violations of the usual diet or diet. The reason for this carelessness is that ascariasis does not have specific symptoms that are unique to this disease. In most cases, it has to be differentiated from other disorders of the digestive system.
Manifestations of symptoms of ascariasis depend on the stage of the disease and comorbidities. Distinguish between the early stage of helminthiasis (migratory), and late (intestinal). The migratory phase lasts for 2-3 weeks, while the larvae migrate through the bloodstream through the liver and lungs. The intestinal phase lasts a year or more, as long as roundworms are in the patient’s small intestine.
In what organs do symptoms of ascariasis occur?
Most of all, the small intestine suffers from ascariasis, where mature individuals feed and reproduce. However, the complex cycle of development of this parasite forces them to penetrate both the respiratory and circulatory systems. Here, roundworm larvae stay for a short time compared to the intestinal phase of the disease.
Organs into which ascaris can get during a massive invasion:
The intestines throughout its length, including the caecum and appendix;
ducts of the pancreas;
Stomach and esophagus (short term);
Gallbladder and choledochus (bile ducts);
Lungs;
Liver;
A heart.
In other organs, the presence of ascaris is atypical for this type of helminth. In such cases, they form cavities like abscesses. Such formations do not increase and cannot be destroyed on their own. They do not pose a danger, since roundworm larvae cannot develop into adults in them.
Symptoms of ascariasis in the migration phase

Symptoms of ascariasis most often appear in the gastrointestinal tract and respiratory system. Helminths damage the tissues of the lungs and intestines, and also cause allergic manifestations. The time of manifestation of symptoms depends on the concentration of ascaris in the human body. Invasion with a small number of roundworms causes erased, mild symptoms (fatigue, weakness, decreased performance) or does not provoke any manifestations at all.
Symptoms of ascariasis with massive invasion:
Cough – can be dry and wet, have a different intensity, contain mucous sputum in the discharge, sometimes streaks of blood. Appears due to damage to lung tissue when the larvae move from the pulmonary capillaries to the alveoli.
Pain in the chest of moderate intensity – caused by the movement of the larvae, as well as the temporary disconnection of the lobe of the lung from the respiratory process.
Shortness of breath during physical exertion – manifests itself with a severe allergic reaction, as well as with a history of bronchial asthma.
Subfebrile temperature (37-37,9) with the addition of chills, muscle and joint pain, increased sweating, abdominal pain.
Tachycardia is a rapid heartbeat with a frequency of 80 beats per minute or more.
Jumps in blood pressure – more often in the direction of hypotension with a decrease in pressure to 90/60 mm Hg. Art. and less.
Accession of allergy symptoms in adult patients occurs infrequently and is fully manifested only with increased sensitivity of the body. Most often, allergic symptoms appear during the molting period of ascaris larvae and can be expressed by edema, skin itching, and a rash. The factor that triggers biochemical reactions in the body is the circulation of IgE class immunoglobulin. The consequence of this is urticaria, enlarged lymph nodes, allergic hepatitis and myocarditis. The most severe complication of an allergy to ascaris waste products is anaphylactic shock, which can be fatal from suffocation.
At a late stage of development of ascariasis and when it passes into a chronic form, most of the symptoms are associated with the activity of mature ascaris in the small intestine.
Symptoms of ascariasis in the intestinal phase

The field of how roundworms enter the small intestine for the second time, they begin to grow there.
This leads to the following symptoms:
Instability of the stool, in which constipation is replaced by diarrhea.
Flatulence of the intestines, dysentery symptoms.
Abdominal pain, vomiting and nausea. Pain is localized mainly in the right iliac region and in the region of the navel. The nature of the pain is cramping.
Itching in the anus and redness of the skin of the anus.
Loss of appetite, sudden weight loss. The patient looks emaciated and exhausted.
Neurological symptoms are expressed in hysterical seizures, in violations of normal nighttime rest (patients often have nightmares), night cries are characteristic. Seizures are not ruled out. Periodically there are headaches, dizziness. Patients with ascariasis get tired very quickly.
On the part of the organs of vision, violations are observed quite rarely, however, a pathological reaction to bright light, anisocoria and amblyopia is not excluded.
Blood pressure in patients with ascariasis is most often lowered.
Blood tests in the intestinal phase: the level of eosinophils returns to normal, and the level of hemoglobin falls.
Against the background of a decrease in immunity, the skin and mucous membranes begin to suffer first. Suppuration, inflammation are often observed. The patient becomes more vulnerable to various infectious diseases.
If roundworms pierce the intestines, they can enter the caecum and provoke the development of acute appendicitis.
Massive invasions often lead to blockage of the bile ducts with the development of cholecystitis, obstructive jaundice, liver abscess, peritonitis, granulomatous hepatitis. With a massive accumulation of worms in the intestine, symptoms of intestinal obstruction develop.
Clinical medicine describes cases of ascaris suffocation, when the worms crawled into the airways, throat and sinuses. In addition, parasites can be found in the lungs, in the right ventricle of the heart, in the human brain.
Ascariasis is extremely dangerous for pregnant women, since the process of bearing a fetus is complicated by severe toxicosis, which contributes to intrauterine growth retardation and violations of labor.
Complications of ascariasis

This type of helminthiasis does not pose a great danger to human life or health. Part of the infected patients safely exist together with roundworms, unaware of their existence. However, in certain categories of patients (pregnant women, persons with a history of chronic pathologies), roundworms can cause complications. The immunity of such people is significantly weakened, and the parasitic invasion spreads faster.
The most common complications of ascariasis are:
Intestinal obstruction, its cause is blockage of the lumen of the small intestine by a ball of helminths. Another reason for this complication is intestinal spasm due to damage to the neuromuscular regulation of its walls. The nerve endings in this case are irritated by the secretions of ascaris. Symptoms – abdominal pain, prolonged lack of bowel movements, severe swelling of the abdominal wall. Food cannot move through the intestines, rupture of its wall and peritonitis are possible. Untimely medical care increases the risk of intoxication, vomiting appears with the smell of feces.
Acute pancreatitis – provoked by the entry of helminths into the ducts of the pancreas. As a result, the secretion of digestive enzymes, which normally go to the duodenum, is disrupted. As a result, enzymes are retained and activated in the pancreas, which destroys its structure. Symptoms – girdle pain radiating to the back, dagger pain in the upper abdomen, vomiting. The process may end in pancreatic necrosis.
Obstructive jaundice – occurs due to the penetration of helminths from the duodenum 12 into the choledoch (bile ducts). Helminths completely clog the narrow ducts, bile is deprived of the possibility of a natural outflow. Stagnation of bile leads to an increase in the level of bilirubin, the skin and sclera of the eyes acquire a yellow tint. The absorption of fats from food is disturbed, headaches and drowsiness appear, heaviness in the right hypochondrium. The higher the bilirubin level, the more intense the symptoms.
Peritonitis – is not a specific symptom, occurs due to bacterial infection of the peritoneum as a result of intestinal rupture, as a complication of appendicitis, with pancreatic necrosis. Untimely diagnosis of peritonitis and lack of assistance leads to death.
Appendicitis – in patients with ascariasis, this complication often appears, which may be associated with the penetration of ascaris into the caecum. Symptoms – pain in the right lower abdomen, radiating to the navel, hyperthermia, vomiting. The condition is life-threatening, requires immediate medical attention, delay with it is fraught with death.
Hepatic abscess – occurs due to the entry of ascaris into the liver through the portal vein system along with the blood flow, as well as through the bile ducts. Helminths damage the mucous membrane of the organ, pyogenic bacteria enter the liver tissue through damage, and an abscess occurs.
Purulent cholangitis – develops due to helminth damage to the mucous membrane of the biliary tract and the attachment of bacteria to the process, causing tissue inflammation. Symptoms – significant hyperthermia (up to 39 ° C), chills, severe pain in the right hypochondrium.
Pneumonia – appears during the pulmonary stage of development of ascariasis. The bacteria that cause inflammation of the lungs multiply in damaged capillaries and respiratory alveoli. Symptoms of bacterial pneumonia are manifested by rapid breathing, fever, wheezing when listening to the lungs. The short stay of the larvae in the respiratory system does not allow the attending physician to establish a connection between pneumonia and ascariasis.
Atypical localization of ascaris – manifested as a result of the ingress of helminth larvae or adults with blood flow into the sinuses, middle ear, lacrimal canal, into the organs of the genitourinary system. There they do not cause tissue destruction, they die over time and are discovered quite by accident.
Asphyxia as a result of obstruction of the airways – occurs as a result of a reflex spasm of smooth muscles, as a result of which the airways are blocked, breathing stops. The cause of the spasm is irritation of the mucous membrane of the pharynx by parasite larvae. Asphyxia may be preceded by a severe, agonizing cough.

The appearance of complications is most often provoked by excessive motor activity of roundworms. It increases when exposed to drugs, the addition of intestinal infections, hyperthermia. Sexually mature individuals begin active movements in the digestive system, provoking complications. Their risk increases with re-infection, which is explained by the peculiarities of the development of the parasite.
Causes of infection with ascariasis

The source of infection and the owner of ascaris is only man. Together with the faeces of the sick, the eggs of the worms enter the soil. There they can exist for many years, although they turn into larvae ready for invasion after only two weeks. But the larvae cannot develop outside the human body. Favorable conditions for the maturation of eggs is an air temperature of +24 degrees, moisture-saturated air and soil. Ascaris eggs enter the human body with water or soil-contaminated food. First of all, these are unwashed berries and vegetables. Lack of personal hygiene and careless attitude to hand washing are two dangerous factors that increase the risk of infestation.
Ascariasis is very often recorded in preschool children. After all, they are unable to fully comply with the rules of personal hygiene and very often come into contact with the soil (with sand). The risk group also includes rural residents, gardeners, summer residents, people living in adverse conditions. The peak of infection with ascariasis occurs in the autumn and summer months, when contact with soil and water occurs much more often. In addition, the risk of eating contaminated vegetables and fruits, as well as unboiled water, increases.
Infection occurs through the fecal-oral mechanism, through the alimentary route. That is, the eggs released into the external environment must again enter the intestines. They are brought there through the mouth through the gastrointestinal tract. In the future, the larvae migrate through the body with final settling in the intestine.
Often there are cases of self-infection with ascaris eggs produced by adults in the patient’s own intestine. This route of infection occurs in children. They do not wash their hands, which contain helminth eggs, spreading them on food and toys, household items. Repeated ingestion of eggs leads to the beginning of a new cycle of reproduction of the parasite.
Even if the larvae got into the circulatory system for some time, it is impossible to become infected with roundworms through the blood. The parasite migrates through the pulmonary circulation: from the digestive tract to the liver and lungs of a person. From there, the roundworm enters the pharynx and into the oral cavity. When kissing, coughing and sneezing, when in contact with saliva, it is impossible to become infected with roundworms, since such migration occurs only during sleep.
To protect yourself from possible infection as much as possible, you must adhere to the following rules:
Gloves must be worn during any work with the ground.
All herbal products should be thoroughly washed.
Nails should be cut short, especially for farmers, gardeners, gardeners.
Before preparing food or eating, wash your hands with soap and water.
Children should learn from an early age to keep their hands clean.
Diagnosis of ascariasis

Detection of ascariasis can be difficult because each stage of helminth development has characteristic changes. For an accurate assessment, the doctor may need several weeks (at least 2-3), during which you can verify the presence of ascaris in the body. This time is usually enough to detect complications caused by helminth invasion.
Ascariasis diagnostic methods used in adults at various stages of the disease:
General and biochemical blood test;
Blood test for antibodies;
Sputum analysis;
Fecal analysis for roundworm eggs;
Analysis of urine;
X-ray of the lungs;
Ultrasound.
Blood test for ascariasis
In most cases, these methods do not show specific changes that occur in the body with ascariasis. An increase in the level of leukocytes is noted during the movement of the larvae into the lungs from the digestive tract. Thus, the immune system responds to the body’s contact with the helminth. A high level of leukocytes is due to an increase in the fraction of eosinophils – blood cells that react to parasite invasions earlier than others. This reaction is short-lived, it manifests itself within a few days. The same symptom can be observed with allergies of a completely different origin.
Analysis for antibodies to roundworms

The serological diagnostic method accurately determines the presence of invasion. It is based on the determination of antibodies to ascaris in the patient’s blood serum. They form immediately after the helminth larvae enter the body. A kind of defense cannot resist the parasite protected by the cuticle. The formation of antibodies briefly delays its development in the initial stage.
Serological methods of research on antibodies to roundworms

Ring precipitation reaction;
The reaction of indirect hemagglutination;
Agglutination reaction with carmine;
Accelerated erythrocyte sedimentation in the presence of ascaris antigen in the sample;
Immunofluorescent analysis;
Reaction precipitations;
Complement fixation reaction;
Bentonite-flocculation reaction.
The method for determining antibodies to roundworms is informative at the larval stage of helminth development. The intestinal phase of the disease is most accurately diagnosed by analyzing feces for worm eggs.
Sputum analysis for ascariasis

The method is informative in the pulmonary phase of development of ascariasis. Microscopic examination of sputum secreted when the patient coughs reveals ascaris larvae in it. This symptom is accompanied by an increased content of eosinophils in the blood.
In the absence of discharge, lavage is examined – a washout of bronchial secretions obtained during bronchoscopy. Such a study is rarely carried out, since it is quite laborious and associated with unpleasant sensations for the patient. It is performed as the only means of diagnosing ascariasis in a seriously ill patient.
Stool analysis for ascariasis

The most common method for diagnosing this disease. It is based on such a feature of the development of roundworms as the laying of a large number of fertilized eggs by a sexually mature female. A yellow-brown elliptical helminth egg with a diameter of 30 to 60 microns is perfectly differentiated when analyzing feces under a microscope.
Methods of research:
According to Krasilnikova;
By Kalantarian;
On Fullenborn.
The absence of helminth eggs in the patient’s stool cannot be a guarantee that the disease is absent. At the larval stage, the parasite does not lay eggs; it will be able to produce them only a few months after entering the body. Therefore, fecal analysis should be repeated. If several individuals of only the female gender enter the body, the presence of unfertilized eggs in the feces is permissible. They are small in size, differ in color and are difficult to distinguish under microscopic examination. Male helminths do not lay eggs at all, although they cause significant damage to the body.
Urine analysis for ascariasis

A specific biochemical analysis of urine for the presence of volatile fatty acids will help confirm the presence of ascariasis. Such acids are secreted by both adults and helminth larvae in the process of carbohydrate metabolism. The method allows to determine the presence of the parasite at the earliest stage of the disease, before the onset of puberty and the period of oviposition. The method can lead to erroneous conclusions, since the same violation occurs in other pathologies.
Radiography in ascariasis
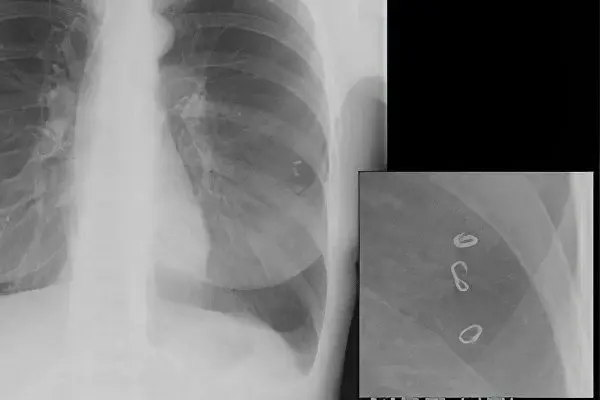
The method is used to determine changes in the lungs and intestines. It is an affordable and inexpensive diagnostic method, it is used immediately at the first suspicion of ascariasis.
Changes revealed on the x-ray:
X-ray of the abdominal cavity – the accumulation of feces and air is diagnosed with intestinal obstruction, it can be carried out in order to distinguish ascariasis from other pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract. Directly ascaris on the x-ray is not determined.
Chest x-ray – characteristic changes in tissues are detected during the pulmonary stage of ascariasis (within 10 days). A volatile Leffler infiltrate is diagnosed, which changes its location after a few days. Differences between ascariasis and pneumonia, as well as neoplasms in the lungs, become apparent when the image is repeated, when accumulations of parasites move to another area. Pneumonia can be diagnosed in immunocompromised patients as a secondary complication of the disease.
Ultrasound examination for ascariasis
A feature of this method is the different reflection of sound waves from body tissues. Ultrasound is not able to detect the localization of ascaris, but this study effectively diagnoses diseases of the digestive system that are similar in symptoms (gastric and intestinal ulcers, colitis, Crohn’s disease). In case of complications, ultrasound reveals organ damage caused by ascaris (cholangitis, pancreatitis, intestinal obstruction).
The most accurate method for diagnosing ascariasis of all of the above is considered to be a serological test for antibodies. The remaining research methods are used only for differentiation, since the results obtained with their help may indicate pathologies that are completely far from helminthiasis.
Treatment
For the treatment of ascariasis, the doctor selects the drug, taking into account the age of the patient and the characteristics of the organism, the severity and massiveness of the invasion. Modern antiparasitic agents guarantee a cure of the disease by 80-100%.
Anthelmintic therapy for ascariasis is not difficult, but must be carried out under the guidance of the attending physician. In its arsenal there is a large number of modern highly effective means that can completely destroy the parasite in a single dose. Unlike bacteria, helminths are not able to develop resistance to certain drugs. However, most of these drugs are highly toxic, and an overdose can harm the human body. Correctly calculated dose and its division into several doses help to reduce the risk of toxic effects.
Directions of complex treatment of ascariasis:
The destruction of ascaris – is carried out with the help of highly effective means that allow you to completely remove parasites from the body.
Treatment of symptoms of ascariasis – carried out after the destruction of parasites, symptoms such as coughing, stool disorders, abdominal pain, etc. are stopped.
Prevention of reinvasion – the destruction of sources of re-infection that remained in the domestic environment of patients. To eliminate the outbreaks, a complex of sanitary measures is being carried out.
Complete nutrition – is used to restore the health of children who are lagging behind in growth. A special diet in the treatment of ascariasis is not required.
A course of vitamin preparations is used to replenish the stock depleted by helminths during the invasion.
Treatment of complications of ascariasis – the use of additional methods, the use of surgery for appendicitis or intussusception of the small intestine.
Additional supportive therapy – is used as prescribed by the attending physician, prescribing enzymes and probiotics to restore full digestion, other medicines.
Treatment of concomitant chronic diseases – is carried out with the aggravation of the course of intestinal infections and exacerbation of other pathologies.
Treatment of ascariasis begins immediately after the diagnosis is clarified. In regions with a high level of invasion, preventive treatment of all residents with a single dose of the drug is carried out.
Be sure to treat ascariasis before surgery on the intestines or lungs. The addition of complications caused by ascariasis can cause death during surgery or in the postoperative period.
Drug treatment of ascariasis
To eliminate ascariasis, antiparasitic drugs are used, which are used taking into account the localization of ascaris and the form of the disease. Ascariasis can be diagnosed in both acute and chronic stages of the development of invasion. The doctor takes into account the individual characteristics of the patient and possible contraindications to the use of highly toxic drugs.
Name of the drug | Receive mode | Противопоказания |
Decaris (Levamisole) | It is used for massive invasions. Adults once 120 – 150 mg, children – 2,5 mg per 1 kg of weight. | Not intended for pregnant and lactating women and children under 14 years of age. |
Mebendazole (Vermox) | It is the drug of choice for simultaneous ascariasis and trichuriasis. It is taken 100 mg 2 times a day for 3 to 4 days. | Contraindicated in ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease, liver failure. Not intended for children under 2 years of age, pregnant and lactating women. |
Mintezol (thiabendazole) | 50 mg/kg body weight twice a day for a week. The drug is effective in the early stages of the disease. | Contraindicated in children under 2 years of age, pregnant women, nursing mothers. |
Albendazole | For adults, the dose of 100 mg is divided into 2 times a day. Take three days. For children, the dose is 25 – 50 mg / day (age from 2 to 10 years). | Contraindicated in children under 2 years of age, pregnant women, nursing mothers. |
Piperazine Citrate | A highly effective remedy for the treatment of ascariasis and enterobiasis, used in the form of tablets or solution. The chemical compound (Piperazine Adipate) is non-hygroscopic and takes on a crystalline form. Dosage – 3 times a day an hour after meals, the course of treatment – 3 days. | Parallel administration of chlorpromazine is prohibited. |
Pirantel | 10 mg/kg once orally after meals. | Can be used during pregnancy under the strict supervision of doctors. Prohibited in renal failure and children under the age of six months. |
When ascariasis is in the migratory phase, drugs for nematodes of universal action are used to treat invasion in children and adults:
Mebendazole – Wormin, Mebex, Vermox (from 90 to 130 rubles), Thermox, Vero-Mebendazole, Vermakar;
Levamisole – Decaris (from 70 to 90 rubles);
Thiabendazole – Mintezol, Mertekt, Arbotekt, Tresaderm, Mintezol, Tekto.
Additionally, bronchodilators are prescribed for obstructive bronchitis and pneumonia, as well as corticosteroids.
The intestinal stage of ascariasis is stopped by the following drugs:
Pyrantel pamoat – Helmintox (from 90 to 120 rubles), Pyrantel (from 30 to 50 rubles), Kombantrin, Nemocid, all drugs are designed for a single use;
Decaris – take in accordance with the instructions, focusing on the age and weight of the patient.
Mebendazole – Wormin, Mebex, Vermox, Termox, Vero-Mebendazole, Vermakar.
Universal preparations for specific therapy of ascariasis:
Santonin – taken for 2 days, the dosage of the drug is adjusted depending on age. Preparation for treatment with Santonin in adults – bowel cleansing with a laxative. The dosage of the drug is 3 rubles / day, one hour before meals. At night, a laxative is necessarily taken, easily digestible food is used. Repeated course of treatment – a month later. Contraindications for use – gastroenteritis, nephronephritis.
Sankafen is a highly effective drug that acts similarly to Nemozol. Before treatment with Sankafen, the patient is given a cleansing enema the day before, he takes a laxative. Dosage – 2 times a day, course of treatment – 2 days. The drug is taken the next day after a light breakfast, in 2 doses with an hourly interval, the entire daily dose. After 2-2,5 hours, food is allowed, in the evening a mild laxative is prescribed. The second day of treatment of ascariasis is similar, with the difference that in the evening they take a saline laxative. The diet during treatment is prescribed with the restriction of fats and spicy foods.
Self-treatment of ascariasis is prohibited, since an incorrectly calculated dose can result in serious intoxication of the body. Short-term side effects from the use of drugs are so diverse that they can lead to negative consequences for the patient.
In addition to the oral method of taking drugs, oral methods can also be used. With massive invasion, it is allowed to administer the drug using a nasogastric tube – directly from the nose to the stomach, bypassing the oral cavity and contact with saliva.
Laxatives are not used in the treatment of acute ascariasis, especially in case of constipation. It can be caused by intestinal obstruction, and additional stimulation of the intestinal muscles will lead to rupture of its wall and the development of peritonitis. It is possible to use laxatives after deworming for the speedy removal of dead or paralyzed roundworms from the body.
If a bacterial infection is suspected, a course of antibiotic treatment may be required. In general, the treatment of ascariasis, not complicated by concomitant pathologies, is quite short-term.
Other treatments for ascariasis
Use of oxygen

A modern method for the treatment of ascariasis, developed by N. Kravets.
The method consists in introducing oxygen into the stomach under low pressure using a thin probe or catheter (in the treatment of children from one to three years old). The probe is inserted through the nose, the device is connected to an oxygen bag, a pneumothorax apparatus, or a Richardson balloon. No bowel cleansing required. The procedure is performed in the supine position, on an empty stomach, with minimal doses. The course of treatment is 2 days for 2 hours. A couple of hours after the procedure, you can eat as usual, limiting only fatty and spicy foods.
Lack of stool throughout the day is a reason to take a laxative. Contraindications to the use of the method are exacerbation of gastric and duodenal ulcers, the risk of peritonitis, inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Heptylresorcinol
Heptylresorcinol – the drug is produced in the form of tablets. They should not be chewed to avoid irritation of the mucous membrane of the mouth, pharynx and esophagus. Before treatment, you need to check whether the patient is able to swallow the drug without chewing it. Preliminary preparation – 12-hour fasting, taking a laxative before bedtime (salt preparation). In the morning, the patient takes the full dose of the drug with an interval of 5 minutes between tablets, washed down with water.
During the day, the patient observes bed rest, at night or the next morning, a saline laxative is taken. Possible side effects (abdominal pain, vomiting) are stopped with a warm heating pad or enema. The diet throughout the treatment is similar to that of Santonin treatment.
Contraindications for use – peptic ulcer, inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, general weakness of the body. Repeated course – within 20 days.
henopodium oil

It has a sharp taste, has a light yellow color.
The dose of the drug is measured using a graduated pipette, mixed with a laxative (castor oil), taken at the same time. Preparation for treatment – bowel cleansing with an enema the night before. The next day in the morning, 2 hours after a light breakfast, a solution of the drug is taken. The next meal is in 3 hours. For constipation, a laxative is prescribed or an enema is given. Contraindications to the use of chenopodium oil are kidney pathologies, infancy, acute gastrointestinal diseases, central nervous system pathologies, general weakness. A second course of treatment is carried out after 2 months under the control of laboratory tests.
Enterosorbents to restore bowel function (Polifepan, Polysorb, activated charcoal) complete the treatment of ascariasis. Monitoring the effectiveness of anthelmintic therapy is carried out a month after the course.
Which doctor treats ascariasis?

Diagnosis and treatment of ascariasis is carried out by a parasitologist. Such a doctor of narrow specialization is not available in all medical institutions; more often, an infectious disease doctor deals with parasitic infestations. It performs the same functions of diagnosing and treating ascariasis as a parasitologist. Since the first symptoms to which the patient pays attention are disorders of the digestive or respiratory system, it is possible to contact a general practitioner or family doctor. To clarify the diagnosis or to stop the consequences and complications of ascariasis, narrow specialists of related profiles are involved.
Consulting doctors in the treatment of ascariasis:
Immunologist – with manifestations of allergies;
Surgeon – for examination and surgical treatment of complications;
Gastroenterologist – in the presence of chronic pathologies of the digestive system;
Microbiologist – for conducting an in-depth examination and making an accurate diagnosis.
Do I need to go to the hospital with ascariasis? After the diagnosis and initial examination, the doctor prescribes treatment. Since in most cases it is a single dose of antihelminthic medicine, treatment at home is sufficient. Hospitalization is not required to comply with the recommendations of the infectious disease specialist, it is possible to issue a sick leave.
You can confirm recovery after laboratory tests (fecal analysis, etc.). Only a repeated negative result can be a guarantee that the patient has got rid of helminths.
Treatment in a hospital is carried out only in the presence of serious complications. Such life-threatening conditions as appendicitis, intestinal obstruction, and pancreatitis require special attention. Accession to ascariasis processes provoked by pathogenic bacteria can significantly worsen the patient’s condition. Medical supervision is required for patients with diabetes mellitus, heart or respiratory failure, as ascariasis can provoke a sharp deterioration in their well-being.
Treatment of ascariasis during pregnancy

If ascariasis in the average patient is considered a dangerous disease, then during pregnancy this risk increases several times. The placental barrier cannot serve as a barrier to the penetration of the larvae of this helminth into the body of the fetus. Toxins released during the life of ascaris have a negative effect on the body of a woman who is expecting the birth of a child. There are pains in the abdomen, nausea increases, vomiting may occur.
If roundworm larvae have entered the lungs of an unborn child, he will most likely suffer from chronic bronchitis or pneumonia, inflammation of the respiratory tract, and manifestations of allergies after birth. These diseases are extremely difficult to treat. Roundworms that penetrate the liver of a newborn child cause inflammation (hepatitis) and chronic jaundice.
When choosing an anthelmintic agent for the treatment of ascariasis in a pregnant woman, the doctor prefers the least toxic drug. Piperazine and Heptylresorcinol are most commonly used.
Prevention of ascariasis

Prevention of ascariasis is of great importance for a complete cure for this disease. Even after the expulsion of parasites from the body, ascaris eggs could remain in the environment surrounding the patient. This factor can lead to reinvasion. Preventive measures will help to avoid a new infection as a result of ingestion of eggs and larvae of the parasite. Ignoring preventive measures increases the incidence of ascariasis again.
Measures for the prevention of ascariasis:
Early screening of the disease. If you suspect infection with roundworms, you should undergo the necessary diagnostic test: a fecal test for helminth eggs, a blood test to detect antibodies to roundworms, and other studies. With a positive result, treatment is carried out, and an explanatory conversation on the observance of hygiene rules. Infection of at least 10% of the population prescribes in some countries a mandatory check once a year for all residents of the region. At 40% infection, general prophylactic treatment with anthelmintic drugs is recommended.
Thorough hygienic hand washing. Since the earth is the most likely environment for the spread of roundworms, the development of their larvae from eggs, everyone who has contact with the soil should pay special attention to thorough hand washing.
Washing products that do not undergo heat treatment before eating. Fruits, vegetables, bird eggs may be in contact with soil containing roundworm larvae. Since these products can be used for food without heat treatment, they should be washed with special care. Short-term heating at a temperature of about +50°C will completely eliminate the risk of contamination from products.
Conducting briefings by SES employees. Categories of the population at increased risk of contracting ascariasis should have full information about this disease and precautions. These are employees of public catering, preschool institutions, agricultural workers and sewers. Such briefing is required to be carried out by the sanitary and epidemiological services of the region. Particular attention should be paid to educating children in the skills to comply with hygiene standards by their parents and kindergarten teachers.
Soil protection from faecal contamination. Sanitary protection of the soil includes the following activities: analysis of the composition of the soil before the start of construction of facilities and the allocation of agricultural land, mandatory cementing of cesspools, and the creation of an appropriate legislative framework.
Monitoring of the state of water and sewer networks. A worn-out sewerage system, due to its defects, pollutes the soil with feces. Through damage to water pipes, roundworm eggs enter the water for drinking and cooking.
Disease vector control. Ascaris eggs can be transferred to food by flies and cockroaches through contact with faeces and contaminated soil. That is why the fight against them in catering enterprises is of such great importance.
High-quality protection against infection with ascariasis is created by the joint efforts of SES doctors, epidemiologists and infectious disease specialists, as well as the regional administration. But their efforts will be in vain if the patient is exposed to infection due to non-observance of elementary hygiene rules.









