Contents
Many people are faced with various diseases in which inflammatory processes begin to develop in bone and cartilage tissues. In recent years, the number of patients diagnosed with osteoarthritis of the ankle has increased. Against the background of the development of this disease, patients can lose the mobility of the lower extremities and become permanently disabled.
What is ankle arthrosis?
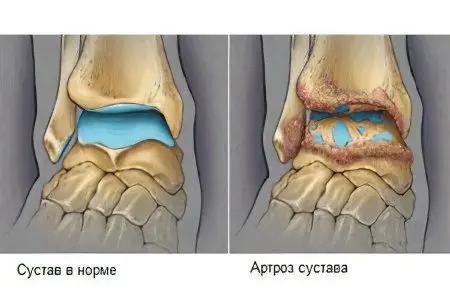
Arthrosis of the ankle joint is a disease in which degenerative processes develop in cartilage tissues. With the progression of arthrosis, irreversible processes begin to occur in the cartilage of the joint, which cause serious consequences.
To date, modern medicine classifies arthrosis of the ankle joint as follows:
Acute arthrosis.
Post-traumatic arthrosis.
Deforming arthrosis.
The study of this disease is carried out by leading experts from around the world who have been conducting research in this area for many years. According to the obtained statistical data published in the specialized mass media, for every 100 examined patients, 6 have arthrosis of the ankle joint.
Most often, this disease affects the elderly, of the total number of patients, 80% are elderly men and women. Such a high figure is explained by the fact that with age, the work of many internal organs, the circulatory system is disturbed, bone and cartilage tissue becomes thinner. Despite this prevalence, osteoarthritis of the ankle joint is highly treatable.
Causes of osteoarthritis of the ankle joint
Arthrosis of the ankle joint is a disease that develops against the background of certain reasons, which include the following:
strong physical loads that are on the musculoskeletal system, in particular on the lower limbs;
any degree of obesity (people who have problems with being overweight often have problems with the joints, since in the process of movement they have an additional physical impact);
doing power and active sports can cause the development of arthrosis of the joint;
uneven distribution of the load on the lower limbs during movement;
any injuries: bruises, falls, blows, etc.;
wearing the wrong shoes often provokes the development of arthrosis;
advanced age (in older people, cartilage tissues begin to thin over time, which lose elasticity and begin to crack);
salt deposits;
harmful working conditions (many people spend the whole working day on their feet, without rest);
various diseases (chronic and inflammatory);
hereditary predisposition, etc.
Symptoms of osteoarthritis of the ankle
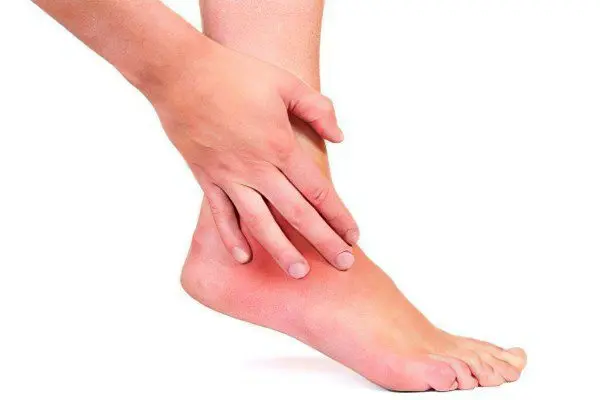
Arthrosis of the ankle joint can be accompanied by various symptoms:
pain, aggravated by any physical load on the musculoskeletal system;
crunch in the joints;
fatigue that appears after moving even for short distances;
atrophy of muscle tissue in the lower extremities;
subluxations that occur against the background of a violation of the functionality of muscles and tendons;
swelling that appears in the ankle joint;
inflammatory processes, accompanied by an increase in temperature;
stiffness and impaired motor functions of the lower extremities;
acquisition of the axis of the lower leg in an x-shape, etc.
Degrees of arthrosis of the ankle joint
Modern medicine defines 3 degrees of arthrosis of the ankle joint, which can be identified during hardware diagnostics. The first two degrees of arthrosis respond well to treatment, after which patients regain their former mobility. With the transition of this disease to the third stage of development in patients, deformation of the joint begins to occur. Many patients who develop arthrosis of the 3rd degree become disabled.
1 degree
The first degree of arthrosis is considered the initial stage of this disease. Individuals may not have severe symptoms. Most often, patients turn to medical institutions for excessive fatigue. Some patients experience pain in the lower extremities, which disappear on their own during sleep or daytime rest.
During the diagnostic measures, arthrosis of the ankle joint of the 1st degree is detected quite rarely, since specialists almost never find pathological changes.
2 degree
Arthrosis of the ankle joint of the 2nd degree is accompanied by certain symptoms that people should pay close attention to. Patients develop severe pain that does not go away during rest. In some cases, inflammatory processes in the ankle joint area may develop, against the background of which reddening of the skin and an increase in temperature occur.
With the progression of inflammation, swelling, loss of activity and mobility of the lower extremities, as well as meteorological dependence appear (the joints of patients begin to hurt more when the weather changes). If medical assistance is not received in a timely manner, this category of patients may develop more serious problems that will require constructive treatment.
3 degree
After the transition to the 3rd stage of development, arthrosis of the ankle joint begins to cause discomfort and excruciating pain to the patient. This is due to the fact that against the background of the progression of this disease, ossification of the cartilage tissue occurs. As a result, the joint loses its depreciation qualities and mobility. The patient begins to hear a crunch in the joint with any movement of the lower limb. If you self-medicate, or do not pay attention to these symptoms at all, you can get disability as a result of foot deformity.
Deforming arthrosis of the ankle joint
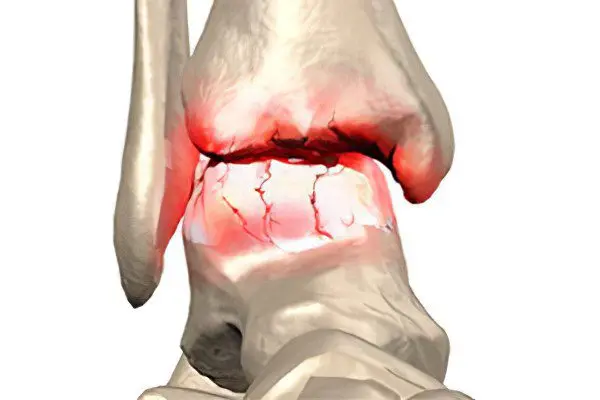
Deforming arthrosis most often develops in people who daily, for several hours, are in a standing position, since they have a strong effect on the ankle joint. This category of patients can also include patients who regularly subject their body to strong physical exertion.
The following factors can cause the development of deforming arthrosis:
excess weight;
inflammatory processes;
cartilage tissue dysplasia;
hereditary predisposition to arthrosis;
diseases of the endocrine system (arthritis most often affects people who are diagnosed with diabetes mellitus at any stage of development), etc.
Deforming arthrosis, which has developed in the ankle joint, is divided into several degrees:
First degree. Deforming arthrosis is accompanied by pain. When conducting hardware diagnostics in such patients, it is possible to detect compaction of the talus, as well as narrowing of the joint gap. Patients may experience discomfort in the joint area at the time of movement.
Second degree. Patients experience joint deformity, a strong pain syndrome, a feeling of fatigue during any physical activity.
Third degree. At this stage of development, the disease is accompanied by pronounced symptoms. In patients, against the background of joint deformity, mobility is limited, pain appears, which can only be removed with special preparations.
Treatment of this form of arthrosis of the ankle joint (grades 1 and 2) is possible with medication. Without fail, patients are prescribed physiotherapy procedures and recommendations are given regarding the choice of special shoes. When this form of arthrosis has passed into the 3rd stage of development, its treatment is possible only with a surgical method.
Treatment of arthrosis of the ankle joint
The key to successful treatment of osteoarthritis is timely diagnosis. Each person who has found symptoms of this disease or just discomfort in the joint area should contact the nearest medical facility. At the appointment with the orthopedic traumatologist, the patient will undergo a personal examination. During palpation of the ankle joint, a specialist will be able to identify serious deviations.
To confirm his diagnosis, the doctor will send the patient for an additional examination:
for radiography;
for computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging.
When choosing a method for treating arthrosis that has developed in the ankle joint, a specialist must use various modern techniques, thanks to which the process of cartilage tissue degeneration stops. First of all, the doctor must prescribe medications to his patient that can save him from a severe pain syndrome. After that, patients begin to take drugs that relieve inflammation in the joints.
The course of treatment includes the following:
physiotherapy exercises (all exercises must be performed under the supervision of an instructor who will ensure that the patient does not get injured during training);
normalization of weight (if the patient is obese, he should urgently go on a diet that limits the intake of fats, salts and other harmful substances);
medical preparations;
ointments that have an analgesic effect;
physiotherapy procedures, including magnetotherapy, etc.
[Video] Dr. Evdokimenko – Ankle Exercises:









