Contents
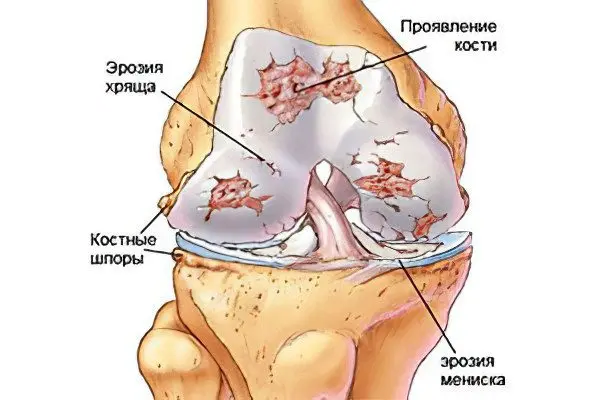
Arthralgia of the knee joint is a symptom of joint pain in the knee area. Arthralgia develops due to irritation of the nerve endings, which are concentrated in the synovial joint bag.
It is the knee joints that are often exposed to strong overloads, as they are responsible for flexion and extension of the leg in different planes. A significant functional load on the joints, inflammatory diseases, salt deposits, endocrine pathologies, neurological problems, excess weight – all this can lead to arthralgia.
Not surprisingly, hundreds of patients turn to doctors with complaints of knee pain every day. Such patients should be carefully examined, which will determine the causes of arthralgia and prescribe the correct treatment. The fact is that sometimes even an X-ray examination of the joint does not allow visualizing any pathology. However, arthralgia often becomes the first symptom of serious organic lesions of the knee and other joints. In addition, knee pain can be a sign of a formidable extra-articular pathology.
Symptoms of knee arthralgia
Symptoms of arthralgia of the knee joint primarily depend on what exactly provoked the pain.
Therefore, depending on the pathology, the following features of knee pain can be distinguished:
With deforming arthrosis, cartilage tissue suffers, which provokes pain in the knee during exercise. The pain intensifies at night, and the joint itself turns red and swells during the period of exacerbation.
With inflammation of the veins and arteries, pain in the knee bothers a person from time to time. Most often they proceed by the type of seizures. Other signs of thrombosis and phlebitis are described above.
With inflammation of the lymph nodes, the pain will increase when pressure is applied to the knee joint, as well as when wearing tight clothing.
Arthralgia provoked by trauma depends on the nature of the injury. In this case, the pain can be pulling or sharp. Sometimes the load on the joint leads to increased pain, and sometimes to its weakening.
Skin diseases are accompanied by swelling and redness of the tissues. The pain is most often burning. Sometimes it is so intense that it is even difficult for a person to move a limb.
With bursitis, the mobility of the knee joint is significantly limited, since painful sensations do not give it normal movement.
In arthritis, there is intoxication of the whole organism.
Thus, several signs can be distinguished, more often than others developing with arthralgia: pain of a different nature, which increases with palpation, swelling in the joint area, redness of the skin, local fever, impaired knee mobility. Sometimes arthralgia is accompanied by crunching or knocking in the knees.
Causes of knee arthralgia
Arthralgia often accompanies the course of various acute infectious diseases. Moreover, pain in the knee joint can develop even before the first symptoms of the underlying disease appear in a person. If arthralgia is provoked by an infection, then the person will complain of bursting pains in the knees and elbows. In parallel, the patient experiences discomfort in the muscles. In this case, the mobility of the joints is not limited. After a few days, the joint pains disappear, as the intoxication of the body is weakened.
Sometimes pain in the knee joint develops after an infection. Moreover, at first glance, such diseases are in no way connected with the joints. It can be urogenital or intestinal infections, tuberculosis, secondary syphilis, endocarditis. Chronic foci of infections that have been present in the body for a long time are capable of provoking arthralgia of the knee joint. These include cholangitis, pyelonephritis, paratonsillar abscess, and even parasitic infestation.
Often the knee joints hurt with rheumatic diseases. Manifests rheumatoid arthritis with damage to the joints of the lower and upper extremities. In this case, the person will experience stiffness in the legs and arms in the morning. The pains are intense, migrating, covering both knees. Getting rid of them is difficult.
Gouty arthritis is manifested by arthralgia as an attack. Moreover, pain occurs only in an isolated joint. It debuts suddenly for a person, quickly gains intensity and lasts for several days.
Deforming osteoarthritis and other degenerative-dystrophic lesions of bone tissue are manifested by arthralgia of the knee joints. Pain often occurs with changes in the weather, is dull, aching in nature, the joints crackle during movement. When a person is at rest, pain does not bother him. When taking painkillers, the pain quickly disappears.
Endocrine diseases such as hypothyroidism and hyperparathyroidism can cause knee arthralgia. In addition, pain will occur in the pelvic bones and in the region of the spinal column.
Bursitis of the knee joint, accompanied by damage to the intra-articular bag, is another cause of arthralgia. At the same time, the tissues surrounding the knee swell, become hot to the touch, and turn red. Joint movements are limited, a general increase in body temperature is possible.
Other risk factors that can provoke arthralgia of the knee joint include:
Poisoning the body with heavy metals, such as thallium and beryllium.
overload of the knee joint.
Regional inflammation of the lymph nodes.
Injuries of the knee joint.
Long-term use of drugs.
Postallegic reactions of the body.
Hypothermia of the joint.
Deterioration of the nutrition of the tissues of the joint due to age-related characteristics.
Osgood-Schlatter disease, which is accompanied by the destruction of the tuberous tissues of the tibia. Pathological changes occur during puberty. Pain occurs during squats, climbing stairs and other stresses on the joint. In addition, it can proceed according to the type of pain, which is localized in the lower part of the knee. Local tissue swelling is possible.
Dermatological diseases such as erysipelas or dermatitis.
Some people develop patellar ligament tendinitis. In this case, the pain will be concentrated in its lower part. At first, they disturb a person only after physical exertion, and then they are present on an ongoing basis.
Baker’s cyst is another cause of knee arthralgia. Pain occurs when the cyst begins to put pressure on the nerve endings. They spread to the entire knee, aggravated by prolonged standing, as well as by bending the knee. If the cyst compresses the vessels, then the patient will experience numbness of the limbs.
A meniscus cyst can form in the inner and outer meniscus. Arthralgia worries after a load on the knee.
Perthes disease affects children. Pain in this case is localized in the region of the hip joint, and in the knee occurs while walking. As the pathology progresses, necrosis of the femoral head occurs.
atherosclerotic disease. Sometimes the accumulation of cholesterol and plaque calcification can occur in the vessels located in the area of the knee joint. This will lead to the fact that the pain is localized in the knee. Other symptoms of vascular lesions include numbness and heaviness in the legs, muscle fatigue. If atherosclerosis of the vessels is not treated, then the development of tissue necrosis with the formation of gangrene of the leg is possible in the future.
Flat feet. In this case, arthralgia of the knee joint will be pronounced, it will be difficult for the patient to squat. Pain is also localized in the foot, thigh, back. Flat feet are indicated by the disproportion of the calf muscle. The arch of the foot will be flattened.
Phlebitis of the vessels in the area of the knee joint can provoke characteristic pains. In this case, the skin in the area of inflammation will be red, possibly local and general fever and swelling. When a person lifts his leg up, the pain syndrome recedes a little (if the veins are affected). When the phlebitis is concentrated in the arteries, the pain will decrease when the leg is lowered.
Arthralgia of the knee in pregnant women

Often, women bearing a child complain of arthralgia of the knee joints.
There are several reasons for this, including:
Increase in body weight and swelling of tissues. Especially often these causes lead to joint pain during the third trimester of pregnancy.
The shift in the center of gravity increases the load on the knee joints.
Hormonal fluctuations in the body can affect the muscles and ligaments of the knee joints.
Calcium deficiency, which is spent on the needs of the child, will affect the condition of the woman’s musculoskeletal system.
Arthralgia of the knee joint in childhood
In childhood, arthralgia of the knee joint often has a passing character. During the so-called periods of growth, muscle tissue is stretched. At the same time, the vessels do not have time to stretch after it, which leads to a deterioration in their throughput and severe pain.
Most often, arthralgia has a aching character, focuses in the area of u19buXNUMXbtwo joints. In this case, the mobility of the knee does not suffer. This problem is relevant for children of preschool and school age. As a rule, by the age of XNUMX, arthralgia ceases to bother a person.
In addition, children are more likely than adults to receive various injuries that are hushed up. In particular, sprains and bruises. This can be another cause of knee pain. Also, one should not lose sight of the likelihood of a child developing flat feet.
Diagnosis of arthralgia of the knee joint

If the first signs of arthralgia of the knee joint occur, it is necessary to contact a therapist. In the future, it may be necessary to consult narrow specialists, such as an orthopedist, rheumatologist, vascular surgeon.
After the initial examination and listening to complaints, the patient will be assigned the following tests and instrumental examinations:
Donating blood for a general analysis. It is important to assess the level of leukocytes, the ESR index. With their increase, it will be clear that there is inflammation in the body.
Blood chemistry. The doctor will be interested in rheumatoid factor, ASL-O, liver tests, the presence of C-reactive protein in the blood, etc.
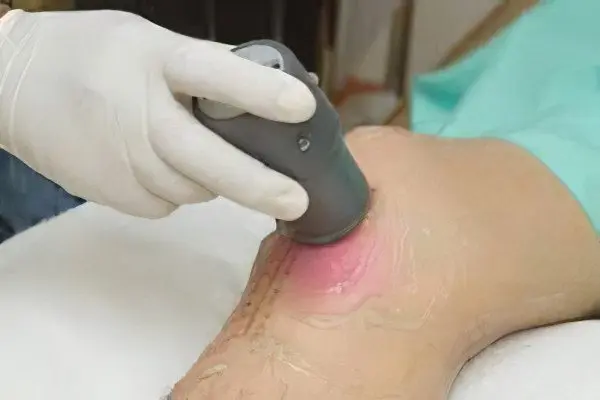
X-ray examination of the knee joint. If the study is uninformative, for example, at an early stage of osteoporosis, then it is supplemented by MRI or CT.
If a cyst is suspected or if the vessels are damaged, the patient may be prescribed an ultrasound scan.
The collection of joint fluid allows you to detect atypical cells or bacteria in it.
A serological blood test allows you to diagnose allergic and immune pathologies.
If all of the above methods do not make it possible to establish the cause of arthralgia of the knee joint, then it makes sense to send a person for examination to a psychotherapist.
Treatment of knee arthralgia
Depending on the cause of knee arthralgia, the patient may need emergency or delayed medical attention.
You should immediately consult a doctor in the following situations:
Pearl, dislocation, subluxation or other serious injury to the limb.
Hemorrhage in the joint.
Purulent processes in the area of the knee joint with intoxication of the body, fever and throbbing pains. A similar situation is most often observed with a knee injury with the addition of an infection.
The inability to move the knee for no explainable reason.
Any of these situations requires a doctor’s house call. The leg, before the arrival of the ambulance, must be given a position that allows you to relieve pain as much as possible. If there is no open wound, then you can apply a cold compress to the knee, or a heating pad with cool water. It is forbidden to massage the affected area, or apply an elastic bandage to it.
[Video] Dr. Evdokimenko – KNEES HURRY, causes and treatment:









