Contents
What is an arrhythmia?

Arrhythmia – This is a failure in the work of successive contractions of the heart muscle. In humans, the heart beats in a certain rhythm. This rhythm is formed by a certain conducting system of the heart. By itself, it represents nodes, bundles of nervous tissue, the accumulation of these nerve cells and fibers is located in the myocardial region and there it generates all the impulses of the heart and conducts them. The rhythm and frequency of contractions of the heart depends on all this. When there is a failure in the activity of even one formation, then arrhythmia occurs.
With different types of arrhythmias, there is a failure in the frequency of heart contraction, this can lead to an increase in contractions (tachycardia) or, conversely, a decrease in contractions (bradycardia), at the same time, contractions can remain normal. In a healthy person, the heart rate is approximately 60-70 beats per minute.
Symptoms of arrhythmia
Sometimes the arrhythmia proceeds hidden. For a long time, a person can live a normal life and not notice that his heart is working intermittently. However, at a doctor’s appointment, for example, during the annual medical examination, heart rhythm disturbances cannot go unnoticed. Timely detection of arrhythmia will allow timely start of treatment to prevent the development of complications.
However, in most cases, arrhythmia still makes itself felt, worsening the quality of life. Its main symptoms are:
Sensation of a heartbeat (normally a person does not feel it).
Rapid heartbeat against the background of absolute physical and emotional rest.
Sensation of slow heartbeat.
Chest pain.
Dyspnea.
Dizziness.
Fainting or fainting.
Causes of arrhythmia
The cause of arrhythmia can be a disease of the cardiovascular system, as well as arterial hypertension, traumatic brain injury, menopausal changes in the body, diseases of the adrenal glands and the thyroid gland.
Also, the causes of arrhythmia can be frequent stress, overload – both nervous and physical, smoking and alcohol abuse, as well as toxic and medicinal substances. A failure in the rhythm of the heart may not manifest itself for quite a long time, or it may sharply worsen one’s health, it often happens that it is very life-threatening.
Risk Factors
It is wrong to think that the diagnosis of “arrhythmia” is made exclusively for age-related patients. The disease can be detected in young people and even in children. To find out the cause that provoked the development of arrhythmias, doctors use various diagnostic techniques and screening tests.
Knowing the risk factors for arrhythmia will allow you to take preventive measures in time, thanks to which it will be possible to prevent its development. These include:
Genetics. Some types of arrhythmia are inherited, for example, those that proceed according to the type of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. This also includes congenital malformations.
Thyroid dysfunction. It is responsible for the synthesis of hormones that affect the metabolic rate, slow down or accelerate it. Tachycardia develops with thyrotoxicosis, and bradycardia with hypothyroidism.
Hypertension. This disease provokes the development of coronary artery disease with cardiac arrhythmias.
Intermittent hypoglycemia. Arrhythmia often develops in people with low blood glucose levels. Decompensated diabetes provokes the development of arterial hypertension and coronary heart disease, which is accompanied by heart rhythm disturbances.
Obesity. Excess weight is one of the leading risk factors for the development of cardiopathologies accompanied by arrhythmia, for example, coronary artery disease. Moreover, even without disease, the load on the heart with obesity increases significantly, contributing to a rapid heart rate.
High cholesterol. Its indicators can go beyond the norm even in young people, but elderly patients over 55 years of age should be especially vigilant. At this age, there are many additional risk factors that, in combination with high cholesterol, can provoke heart and vascular diseases.
Low level of iron in the blood. Against the background of anemia, organs and tissues suffer from a lack of oxygen. The heart muscle is no exception. The longer a person has anemia, the higher their risk of developing an arrhythmia.
Violations of the hormonal background. Arrhythmia in women most often manifests during the entry into menopause.
Osteochondrosis. Clamping of the nerve roots provokes a disorder of autonomic regulation, which affects the functioning of the vagus nerve and the sympathetic nervous system. Such violations directly affect the work of the heart and blood vessels.
Types of arrhythmia
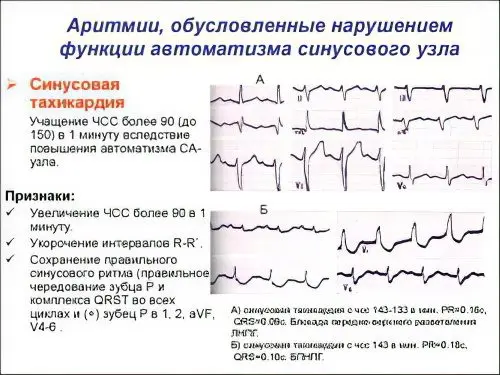
Sinus tachycardia. The main in the field of the myocardium – the formation of electrical impulses – is the sinus node. When a person is sick with sinus tachycardia, the frequency of contraction of the heart muscle sometimes exceeds 90 beats per minute. A person feels such a deviation as a strong heartbeat. The origin of sinus tachycardia is explained by heavy stress, emotional overstrain, fever with colds, not often, but still it can occur from heart disease and all of the above causes of arrhythmia.
sinus bradycardia. It manifests itself in the form of a decrease in the heart rate, often up to 55 beats per minute or even less. Bradycardia can also occur in physically healthy, trained people during rest or sleep. Bradycardia may be accompanied by hypotension, heart disease. As a rule, bradycardia occurs with a decrease in thyroid function. Bradycardia is felt as discomfort in the region of the heart, there may be general weakness and dizziness.
sinus arrhythmia. It is characterized as an irregular alternation of heart beats. This type of arrhythmia is most often observed in children and adolescents. Sinus arrhythmia may be functionally related to respiration. During inhalation, heart rate increases, and during exhalation, it decreases. This respiratory arrhythmia does not affect well-being and, as a rule, does not require treatment. When diagnosing this type of arrhythmia, breath holding is used, during which the arrhythmia disappears.
Extrasystole. This is an extraordinary contraction of the heart muscle. In healthy people, rare extrasystoles can be observed, they can be caused by various diseases, as well as bad habits. Arrhythmia can be felt in this form as strong shocks in the region of the heart muscle or in the form of fading.
Paroxysmal tachycardia. Paroxysmal tachycardia is the correct work of the heart, but with a frequent beat rhythm. Thus, the heart rate can reach 140-240 beats per minute. This type of tachycardia occurs and disappears suddenly. Symptoms: palpitations, increased sweating, and weakness.
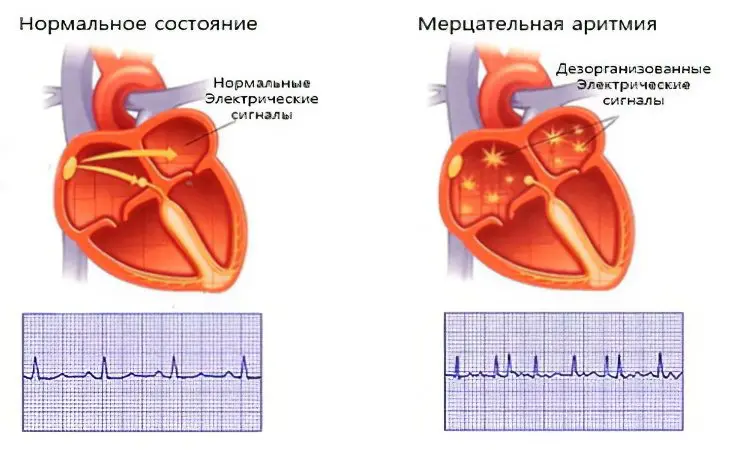
Atrial fibrillation. This disease is characterized as random contraction of individual muscle fibers, while the atrium does not contract completely, the ventricles begin to contract irregularly at a rate of about 100 to 150 beats per minute. With “flutter” of the atria, they begin to contract faster and faster, the frequency of contractions is from 250 to 300 beats per minute. This condition is often observed in people with diseases and heart disease, as well as thyroid diseases and alcoholism.
Symptoms may be absent, the patient may not feel a change in well-being. They most often complain of a fluttering sensation in the chest area, sometimes pain in the heart, and complain of shortness of breath. The main symptom of flickering arrhythmia is a lack of pulse, i.e., the determined heart rate when listening exceeds the pulse rate.
Fluttering and flickering of the ventricles is considered the most severe violation of the rhythm, this can occur from any serious heart disease, due to an injury from electricity, with an overdose of certain drugs.
Symptoms: sudden cardiac arrest, pulse is not palpable, loss of consciousness, hoarse breathing, convulsions, dilated pupils are possible. The first and emergency aid to a person in this condition consists in immediate external indirect heart massage and artificial respiration.
Heart block. With this type of arrhythmia, the conduction of impulses through all structures of the myocardium slows down and stops. The characteristic feature of the blockade is the periodic loss of the pulse, the blockade can be either complete or incomplete. Complete blockades are often accompanied by a decrease in heart rate. They often cause fainting and convulsions. A complete transverse blockade can cause heart failure and even sudden death.
Diagnosis of arrhythmias
Diagnosis of arrhythmia consists in the indicators of the examination of the patient, these indicators include: appearance, skin color, palpation of the pulse, determination of the boundaries of the heart, heart rate, breathing are measured.
Be sure to do an electrocardiogram, with which you can quite accurately determine the type of arrhythmia and choose the right method of treatment.
Complications
The latent course of arrhythmia does not make it harmless. It can cause serious complications, harm health and even cause death.
Of particular danger is arrhythmia, which occurs in combination with heart disease. Complications to which it can lead:
Heart failure. The longer a person has tachycardia or bradycardia, the higher the risk of blood stagnation in the heart cavities. If you control your heart rate, these problems can be avoided.
Stroke. Atrial flutter can lead to it, which in this state are unable to fill the ventricles with the necessary amount of blood. Blood flow disorders provoke the formation of blood clots, which can reach the brain through the vessels, clog one of the collaterals there and become an impetus for the development of a stroke.
Heart failure, against which atrial fibrillation is often observed. If a person is not provided with emergency medical care, he will die.
Arrhythmia treatment

Treatment of arrhythmia involves the provision of medical care, which should be aimed at eliminating the underlying disease that provoked a heart rhythm disorder. In addition, the patient will have to receive medications to stop the symptoms of the arrhythmia itself. With bradycardia, which occurs against the background of organic heart damage, angioprotectors and acetylsalicylic acid are often prescribed in small doses. These drugs allow you to normalize blood flow, improve myocardial nutrition, and reduce the risk of complications of atherosclerosis.
Sometimes arrhythmia is a consequence of taking medications. In this case, their use is completely refused, or the dose is reduced. If the body gives a similar reaction to drugs to reduce blood pressure, then an alternative is required.
Antiarrhythmic drugs
Direct antiarrhythmic drugs – affect the permeability of ion channels, which in turn reduces the heart rate:
Amiodarone. This drug is used to stabilize the work of all parts of the heart. The effect of its use persists for a long time after discontinuation of the drug. It will act for several more months, but only on condition that the person received it for a long time. It is forbidden to prescribe the drug for the treatment of pregnant women, nursing mothers, people with low blood pressure, patients with thyroid pathologies. Do not use amiodarone in patients with potassium deficiency in the body.
Allape’s – an antiarrhythmic drug of class I C. has a moderate antispasmodic, coronary dilating, anticholinergic, local anesthetic and sedative effect.
Ritmonorm – blocker of sodium channels, highly effective in ventricular arrhythmias; with supraventricular arrhythmias, the effectiveness is somewhat lower. Propafenone has a mild beta-adrenergic blocking effect.
Drugs that affect the conduction system of the heart, they slow down the heart rate, so they are more often used for tachycardia and atrial fibrillation:

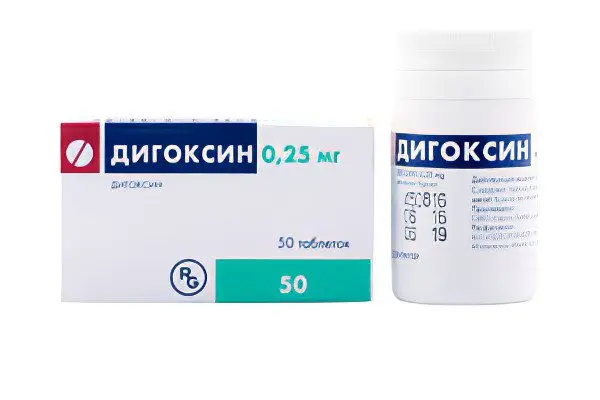
Digoxin – is a cardiac glycoside of plant origin. It is used to treat atrial fibrillation and heart failure. Patients are prescribed 0,25 mg several times a day. If the patient develops extrasystole, then treatment should be abandoned. The drug inhibits sodium and potassium channels, which must be taken into account when prescribing antiarrhythmic drugs. It is forbidden to use Digoxin for the treatment of patients with ventricular fibrillation, with myocardial infarction and against the background of tachycardia.
Propranolol. This drug is not prescribed to patients with hypotension, bradycardia, and against the background of cardiogenic shock. Its use allows you to reduce the heart rate, but can provoke symptoms of atrial flutter. Patients complain of a feeling of stopping or even turning over the heart. It should not be used for therapy in persons with depression. Analogues of Propranolol are drugs such as: Obzidan and Anaprilin.
Metoprolol. This drug has the same effects and contraindications as propranolol. It can be used to treat pregnant women, people with low blood pressure, as well as patients who have had a myocardial infarction but have passed the acute stage of the disease. The doctor determines the dose on an individual basis, depending on the specific clinical case. Take the drug 1 time per day with water. There is no dependence on food. Metoprolol’s analogue is Atenolol.
Bisoprolol. This drug is prescribed to patients with high blood pressure, as it allows you to reduce it. Most people tolerate therapy well, they do not experience severe edema, they do not complain of dizziness. Bisoprolol does not give complications on the heart. The price of the drug is not high.
Others: Timolol, Nadolol, Esmolol, Carvedilol
Sodium channel blockers
Sodium channel blockers are medicines that help bring the heart rate back to normal. Thanks to them, the conduction of impulses is normalized. The blockade will be the more intense, the more the patient’s pulse quickens. Medicines vary in their effect on repolarization time.
If one drug from this group is not suitable for a particular patient, then it can be replaced with an analogue, but with a different mechanism of action on the repolarization process.
There are drugs that increase repolarization time and moderately block sodium channels. They are used to treat sinus node tachycardia, used for atrial fibrillation. These drugs include:
Quinidine. It is used to prevent ventricular fibrillation. The drug helps to lower blood pressure, relieves stress from the heart muscle. Quinidine is not prescribed for quinine intolerance. From its use is refused in the case when during therapy the patient develops thrombocytopenia. The maximum daily dose is equal to 3-4 g. It is divided into several times. It is forbidden to prescribe Quinidine to patients who are undergoing therapy with Verapamil and anticoagulants.
Procainamide. This drug is in the form of a solution for injection. The starting dose is 250-500 mg, and the daily dose is 4 g. It is forbidden to use the drug for the treatment of patients with myasthenia gravis, bronchial asthma, atherosclerosis, severe damage to the kidneys and liver. Do not use it to treat people who have had a myocardial infarction.
Disopyramide. This drug has the same effect on the patient’s body as Quinidine. It helps to increase the tone of arterioles. During therapy, side effects such as: allergies, dyspepsia, headache may develop.
Analogues of the listed medicines are such drugs as: Novocainamide and Aymalin.
The next type of drugs in this group are drugs that reduce the repolarization time and weakly block sodium channels. They are used to treat arrhythmias of the cardiac ventricles, they are prescribed for extrasystole, with arrhythmia that develops after a myocardial infarction. Also, these drugs can be used to stop attacks of atrial fibrillation. These include:
Lidocaine. It is prescribed to patients with bradycardia, as well as to patients who have a high risk of developing blockades. You can use the drug for the treatment of hypotension. However, during treatment, patients may experience fainting, and sometimes even worsen respiratory function. The drug is not used for oral administration. It works for a short time.
Phenytoin or Diphenin. These drugs are prescribed at a dosage of 4 mg / kg of body weight. They are able to slow down psychomotor reactions, they are used with caution in the treatment of people with epilepsy and seizures. It is forbidden to use Phenytoin and Difenin for the treatment of women in position, as they have a negative effect on the fetus.
Mexiletine. This drug has a good effect in terms of the treatment of ventricular extrasystole. It does not irritate the organs of the digestive system. All side effects are limited to the effect of the drug on the central nervous system. If the patient does not tolerate injections of Lidocaine, then it can be replaced by oral administration of Mexiletine, which has a prolonged effect. An analogue of the listed drugs is the drug Diphenylhydantoin.
The third type of drugs in this group are drugs that do not affect the time of repolarization, but at the same time they strongly block sodium channels. They are used to treat tachycardia. These include:
Propafenone or Propanorm. These drugs not only block sodium channels, but also affect the work of calcium and beta-adrenergic receptors. They must be administered slowly, as at high speed the risk of cardiac arrest or the development of bronchospasm increases. For the same reason, you need to carefully calculate the dose. Drugs affect the composition of the blood.
Etatsizin. Its reception allows you to relieve tension from the heart muscle, increase the time of contractions, eliminate the effects of ischemia. The effect develops after 2 doses, but a significant decrease in heart rate is not observed. The drug is taken 3 times a day, gradually increasing the daily dose to 200-300 mg. The drug is used to treat tachycardia, but it can provoke the development of another type of arrhythmia.
Potassium channel blockers

Potassium channel blockers are prescribed for patients who are at high risk of developing ventricular fibrillation. If drugs from the group of sodium channel blockers can be replaced one by one, since the mechanism of their action is the same, then it will not be possible to do this with drugs from the group of potassium channels.
Ibutilide. The drug acts gently, but it has a pronounced effect on the liver. It is prescribed for the treatment of paroxysmal arrhythmias, as well as for atrial fibrillation. The drug can only be used in a hospital, under ECG control.
Sotalol. The drug is prescribed for various types of arrhythmias. It does not accumulate in the liver and kidneys, so it can be used to treat patients with pathologies of these organs. Sotalol blocks the susceptibility of beta-adrenergic receptors. The daily dose should not exceed 80 mg. Mandatory control of the level of creatinine and the amount of fluid consumed.
Nibentan. This is one of the most effective drugs for the treatment of arrhythmia. Its therapeutic effect is similar to that of taking Ibutilide. The drug is prescribed to patients with atrial flutter and ventricular fibrillation. Therapy can only be done in a hospital.
Calcium channel blockers
Verapamil. Verapamil is one of the most commonly prescribed drugs for the treatment of atrial fibrillation. It is forbidden to use it for the treatment of patients with hypotension, as well as in severe heart failure. The drug is well absorbed by the body. It is recommended to take it with meals. The starting dose of the drug is 48 mg. If necessary, the dose can be gradually increased. Take Verapamil several times a day. Experts do not recommend using it in combination therapy with other antiarrhythmic drugs. The drug Diltiazem has a similar effect.
Adenosine. The preferred form of this drug is a drug called adenosine triphosphate. It normalizes the heart rhythm, relieves excitation from the myocardium. The drug begins to work 10 seconds after taking it. During treatment, it is required to control the heart rate so that its rate does not decrease below 55 beats per minute. You also need to monitor the level of blood pressure. The drug is prescribed with dipyridamole. This allows you to increase the level of Adenosine in the blood. If the patient is diagnosed with ventricular tachycardia, then the drug is prohibited from taking.
Additional drugs
This includes drugs that help improve the functioning of metabolism, as well as nutrition of the myocardium and protect it from the effects of ischemia.
Panangin – (or its analogue Asparkam) is used to treat arrhythmias, as an electrolyte that compensates for the loss of trace elements in the myocardium. If a patient is diagnosed with a severe lack of potassium and magnesium in the body, then he is placed in a hospital and the drug is administered intravenously. In the future, the patient is transferred to oral administration of Panangin. It is prescribed 3 times a day. The analogue of the drug is Asparkam.
Mildronate – restores the balance between the delivery and the need for cells in oxygen, eliminates the accumulation of toxic metabolic products in cells, protecting them from damage. As a result of its use, the body acquires the ability to withstand the load and quickly restore energy reserves.
Riboxin – improves myocardial metabolism, has antihypoxic and antiarrhythmic effects. Increases the energy balance of the myocardium. It has a protective effect on the kidneys in conditions of ischemia during surgery.
And other drugs such as: ATP (adenosine triphosphoric acid), Potassium normin, Calypso, Cocarboxylase, Thiotriazoline, Mexicor, Preductal MR.
Diet

Only with the help of one diet to cope with arrhythmia will not succeed. However, compliance with certain nutritional rules can reduce the risk of complications, and is also one of the ways to prevent its development.
The diet should be built in such a way that the heart muscle does not experience a deficiency in trace elements. Inaccuracies in nutrition are a direct path to malfunctions in the endocrine system, which will certainly lead to cardiac dysfunction.
Products that should be present in the diet of a person suffering from arrhythmia:
Buckwheat, nuts, legumes, yeast, spinach, avocados and cucumbers. All of them saturate the body with magnesium.
Bananas, parsley, dried apricots and raisins, potatoes and cabbage. These foods are a source of potassium.
Corn, seafood, fish, beets, seeds, cabbage. They are high in calcium.
People involved in arrhythmia therapy should include seaweed, beet and carrot tops, lean meat in their diet.
What to exclude from the diet?
Products that should not be on the menu:
Canned food, smoked meats, marinades.
Pickles.
Fatty meats.
Sauces and spicy dishes.
Patients with atrial fibrillation should drink enough water. Certain drinks should be avoided.
Basic recommendations for water and drinks:
Under the ban coffee, black and green tea of strong tea leaves, energy drinks with guarana extract.
The daily volume of fluid consumed is 1,5 liters. When these norms are exceeded, the load on the heart muscle increases.
Preferred drinks: teas with mint, linden, chamomile, lemon balm, weak green tea, still mineral water.
Adequate physical activity will help increase the effectiveness of the diet. Exercise should not be too intense, so as not to overload the heart.
Periodically, you can spend fasting days, during which they drink rosehip broth or still water.
Prevention of arrhythmias

Measures aimed at the prevention of arrhythmia and its complications:
Timely treat infectious diseases, do not try to transfer the disease on your feet.
Quit smoking, reduce alcohol intake.
Do not ignore the symptoms that signal diseases of the heart, endocrine gland and arterial hypertension.
Avoid stress.
Control blood glucose and cholesterol levels, monitor weight.
Which doctor to contact
Detection, prevention and treatment of arrhythmia is the responsibility of an arrhythmologist. However, in most polyclinics there is no such narrow specialist in the state, therefore, a cardiologist is engaged in the treatment of heart rhythm abnormalities.
Diagnosis is reduced to performing ultrasound, ECG or Holter monitoring. This is done by the doctor of functional diagnostics.
The detection of concomitant diseases requires consultation with narrow specialists. The endocrinologist is engaged in the treatment of the endocrine glands, the pathological course of menopause requires regular visits to the gynecologist.
If complex conservative therapy did not achieve the desired effect, consultation with a cardiological surgeon is necessary. According to the indications, the patient can undergo radiofrequency ablation or implantation of a pacemaker. The question of the need for an operation is decided on an individual basis.