Contents
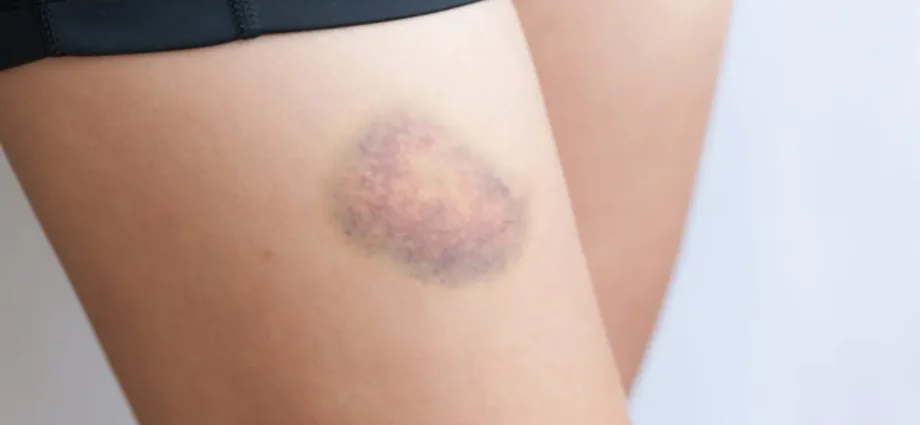
They can signal the onset of a serious disease – deep vein thrombosis, which, if left untreated, leads to death. Spider veins and bruises, because we are talking about them, can be dangerous, but not always. Check if you should start to be afraid or consider your ailments only as a cosmetic defect.
Shutterstock See the gallery 8
- 10 common habits that destroy the human brain Are you doing it too?
The human brain is a complex mechanism and a very sensitive organ. If it functions properly, a person enjoys mental and physical balance. When «center …
- This doctor “reversed” heart disease without medication. Now he wants to do it with Alzheimer’s
Dr. Dean Ornish became famous in the 90s for his unusual approach to coronary artery disease. The doctor managed to withdraw it only through …
- Can I sleep in a bra? Does it keep the breasts from sagging? This is what you need to know before you make up your mind
Sleeping in a bra has always aroused a lot of controversy. A lot of myths have already arisen around this. Some people believe that sleeping in a bra can contribute to the formation of …
1/ 8 What is thrombosis?
Deep vein thrombosis is a very serious disease. In its course, a clot forms in the vein, most often of the lower limb. If it is large, it can travel through the bloodstream to the heart and completely block the circulation, resulting in sudden death. Smaller clots are also dangerous as they can reach the pulmonary vessel and cause an embolism in it.
2/ 8 Causes of thrombosis
We may have a genetic predisposition to this disease, but deep vein thrombosis most often arises when two of the three symptoms, the so-called Virchow’s triad. These include: slowing blood flow (e.g. due to limb immobilization or pressure on the veins), advantage of activating factors over those inhibiting the coagulation system and damage to the vascular wall (e.g. as a result of trauma or microtraumas during leg surgery. If all or at least two of them occur) , there is a high risk of thrombosis.
3/ 8 Symptoms of thrombosis
Reddening of the extremities is a common symptom of thrombosis. They may be slightly visible or even bruise. Tenderness is also common. If you notice a similar symptom on your body and do not associate it with any of the strokes, this is cause for concern.
4/ 8 Fever is an unusual symptom of thrombosis
With deep vein thrombosis, you may also feel an increased warmth in the area where the embolus is located. In extreme cases, there is even a fever.
5/ 8 Thrombosis in pregnancy
One of the most characteristic symptoms of venous thrombosis in the lower limb is swelling around the ankles. It should be especially paid attention to by pregnant women, in whom the probability of thrombosis is high, because they usually underestimate this symptom – swelling seems to be a natural side effect of pregnancy.
6/ 8 Contraception and thrombosis
Unfortunately, the use of hormonal contraception or HRT during the menopause increases the risk of venous thrombosis. When we take pills containing estrogen and progesterone at the same time, it is smaller but still exists. In older women, hormonal contraception can even lead to arterial thrombosis. But twenty-year-olds also get thrombosis. The risk is greatest when an obese and smoking woman is using hormonal contraception. Most often, thrombosis occurs in the first year of using contraception, but it does not prevent us from regular examinations and self-monitoring. There are cases of blockages that occur after many years of using HRT or taking birth control pills.
7/ 8 Complications
Thrombosis is serious mainly because of complications that can happen very quickly once the clot begins to travel through the blood vessels. One form of complication is pulmonary embolism, which is characterized by shortness of breath and chest pain. Failure to dissolve the clots can result in death. Worse still, a clot locates in the heart completely blocking the circulation.
8/ 8 Treatment of thrombosis
There are a few basic tests to check for a blood clot in a vein. One of them is ultrasound. In addition, the doctor may order phlebography or magnetic resonance imaging. The most common treatment of the disease is to administer anticoagulants that dissolve the “plug”. It can be heparin or various types of enzymes. They must be adjusted individually so that the elimination of the risk of embolism does not end with the risk of the so-called stroke.