Contents
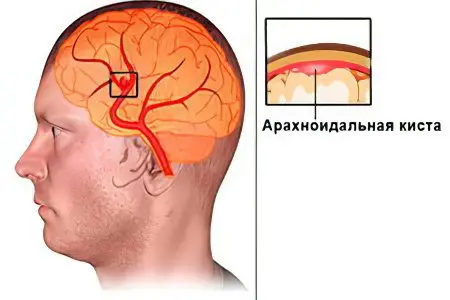
The arachnoid cyst of the brain is a neoplasm of a benign nature, which has the shape of a bubble and is located between the membranes of the brain. These cysts are filled with cerebrospinal fluid.
Typically, a person is not aware of the presence of a cyst until they have an MRI of the brain, since such formations rarely give any symptoms. The first complaints appear in the patient when the cysts reach an impressive size. At the same time, they begin to put pressure on the brain tissue, the person has increased intracranial pressure, which gives characteristic symptoms. Treatment is surgical: the cyst is drained, excised, or shunted.
Arachnoid cyst – what is it?
An arachnoid cyst is a neoplasm bounded by an arachnoid or collagen sheath. Inside it accumulates cerebrospinal fluid, which is called cerebrospinal fluid. The cyst is located between the duplication of the arachnoid membrane. It is due to the place of its localization that this neoplasm received the appropriate name. In the place where the cyst is formed, the arachnoid membrane of the brain is thickened and has a duplication, that is, it is divided into 2 sheets. It is between them that liquor can begin to accumulate.
Cysts are most often small, although they may swell when filled with cerebrospinal fluid. Such bubbles put pressure on the cerebral cortex and cause the corresponding symptoms.
The site of cyst formation may vary. Its favorite localization is the cerebellopontine angle, the Sylvian sulcus, or the area above the Turkish saddle. As practice shows, about 4% of the population are carriers of such cysts, but most people do not know about their existence, since there are simply no symptoms. Most often, arachnoid cysts are diagnosed in men. An explanation for this has not been found, but scientists believe that there is a relationship between the frequency of traumatic brain injuries, which occur much less frequently in women. Arachnoid cysts account for about 1% of all brain tumors.
What are arachnoid cysts?
Depending on the origin of cysts, primary and secondary tumors are distinguished. Primary cysts are pathological neoplasms of the brain that are obtained by a person from birth, for example, Blake’s pouch cyst. Congenital cysts are malformations of intrauterine development, since the nervous tissue is laid in the first weeks after conception.
Secondary cysts develop throughout life, appearing after trauma, inflammation or bleeding in the brain area. Most often, collagen fibers predominate in the composition of such cysts.
Depending on the structure of the cyst, complex and simple neoplasms are distinguished. Simple cysts are represented by a poutine membrane, they can independently produce cerebrospinal fluid. Complex cysts are included in other tissues, for example, glial cells can be found in them.
Depending on the clinical manifestations of the neoplasm, there are frozen and progressive cysts. Progressive formations give neurological symptoms, which only intensify over time. The cysts themselves increase in size. Frozen cysts have a latent course and do not increase in size. It is important to distinguish a progressive cyst from a frozen one, as this allows you to decide on further therapeutic tactics.
In addition to the arachnoid cyst, which is formed within the cranium, there are retrocerebellar cysts. They form in the thickness of the nervous tissue and provoke the appearance of neurological symptoms. Neurons with such cysts die. It is easier to get rid of an arachnoid cyst, as it is located outside the brain. While retrocerebellar cysts are located in its thickness.
Symptoms of an arachnoid cyst

Arachnoid cysts most often do not give themselves away with any symptoms. This is true for small neoplasms. In the vast majority of cases, congenital cysts are discovered by accident, during neurosonography through a fontanel that has not closed in a child. Or they can be diagnosed during an MRI for another pathology. When an infection that affects the brain enters the body, the cyst can make itself felt. Provoke its growth, and hence the symptoms, can be trauma to the brain, as well as damage and vascular disease.
If the volume of cerebrospinal fluid located in the cavity of the cyst begins to increase, this provokes its growth. At the same time, symptoms indicating an increase in intracranial pressure manifest. Depending on the location of the neoplasm, the patient will begin to be disturbed by the corresponding neurological symptoms. Signs of the presence of a cyst will be experienced by one in five of its owners.
These include:
Specific headache in the bones of the skull – carnialgia.
Dizziness.
Noise in ears.
Sensation of pulsation in the head.
Gait disturbance.
A spinal cyst can give symptoms that resemble a clinic for a herniated disc.
An increase in intracranial pressure is accompanied by the following manifestations:
Severe headaches.
Pain in the area of the eyeballs.
Nausea and vomiting. Often vomiting occurs at the peak of the headache and does not bring relief to the person.
Convulsions.
As the cyst grows, headaches become more intense, they begin to disturb the person on an ongoing basis. Nausea manifests itself in the morning hours, at the same time, most patients vomit. If a person ignores the manifestations of a cyst, then problems with hearing and vision may arise, the eyes will begin to double, the sensitivity of the limbs and coordination in space worsens, and speech suffers.
Immobilization of one half of the body, a decrease in muscle strength from paresis are severe manifestations of an arachnoid cyst that occur only in advanced cases. Episodes of loss of consciousness and convulsive seizures are also characteristic of large cysts. Patients may experience hallucinations. In childhood, there is a delay in speech and mental development.
If a person begins to feel worse, then this clearly indicates the growth of the cyst in size. If it becomes very large, then this is associated with a risk of death due to rupture of the cystic cavity.
In addition, a cyst that compresses the brain structures for a long period of time will lead to irreversible changes in its tissues. As a result, a person will develop a persistent neurological deficit against the background of degeneration of nerve cells.
Symptoms of an arachnoid cyst, depending on its location:
Arachnoid cyst, located in the temples, manifests itself as symptoms of increased blood pressure, convulsions, impaired sensitivity and motor activity on the side opposite to the location of the tumor. Temporal arachnoid cyst is manifested by the same symptoms as a stroke. However, they are less pronounced and progress more slowly.
If the cyst is located in the region of the posterior cranial fossa, then this is manifested by clamping the brain stem. As a result, the patient may experience respiratory and cardiac disorders, paralysis and paresis, coordination deteriorates, and nystagmus develops. When the tumor becomes large, the risk of coma and death from compression of the stem structures increases.
When the cerebellum is clamped in a person, coordination disorders are observed first of all, gait suffers. Involuntary movements may appear, bouts of dizziness occur, nausea and noise in the head are disturbing.
Causes of the formation of an arachnoid cyst of the brain
If a cyst is formed during fetal development, then this is due to the influence of pathogenic factors on the fetus.
These include:
Intrauterine infections: toxoplasmosis, herpes, rubella virus, etc.
Intoxication of the body of a pregnant woman. The danger is the intake of alcohol, smoking, drug addiction, the passage of therapy with drugs that have a teratogenic effect.
Impact on the body of the expectant mother of radiation.
Overheating of the body of a pregnant woman. It is recommended to refuse to visit baths and saunas, not to be in the sun for a long time, not to take hot baths.
Marfan’s syndrome and hypokinesia of the corpus callosum are accompanied by the appearance of arachnoid cysts.
Also, an arachnoid cyst can form during life. The provoking factors are:
Received TBI: brain concussion and bruises.
Postponed surgical interventions on the brain.
Infections transferred during life: inflammation of the brain, arachnoiditis and meningoencephalitis.
Postponed intracerebral hemorrhages.
Sometimes these risk factors provide the basis for the growth of a congenital brain cyst.
How to discover?
An examination by a neurologist makes it possible to suspect the presence of a neoplasm in the brain only if the cyst reaches a significant size. Only in this case does it give certain neurological symptoms.
Therefore, if the doctor suspects the presence of a cyst, he will refer the patient to the following studies:
EEG.
REG.
Echo-EG.
MRI or CT scan is the most informative and allows you to clarify the diagnosis. The use of contrast-enhanced MRI is especially important. This method makes it possible to distinguish a cyst from a brain tumor.
How to treat a cyst?
If the arachnoid cyst does not grow and develop, then treatment is not required. A person will need to register with a neurologist and undergo an MRI examination every year. This will make it possible to monitor the growth and development of the cyst, if any.
When the cyst progresses and causes neurological symptoms, it needs to be treated. Drug correction is reduced to taking drugs that normalize cerebral circulation (nootropics, vasotropes, antioxidants). Sometimes the patient is prescribed drugs that allow the adhesions to dissolve (Karipain, Longidase). The help of a surgeon is needed when taking medications does not solve the problem.
Surgery is designed to reduce intracranial pressure, it is implemented in three ways:
Shunting. The result of this procedure is the formation of pathways for the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid from the cyst cavity into the peritoneal cavity.
Fenestration. This method involves aspiration of the contents of the cyst with the further creation of holes. They connect the cystic cavity with the cerebral ventricle or subarachnoid space.
Drainage neoplasms using needle aspiration.
Modern neurosurgeons prefer to use endoscopic interventions, as they have minimal trauma to the brain.
The operation is prescribed only on the condition that other methods of treatment are ineffective. In case of hemorrhage in the area of the cyst, or in case of its rupture, removal of the neoplasm is required. The operation is performed by trepanation, which is associated with a number of complications. The rehabilitation period is quite difficult and time-consuming.
Prognosis and prevention
The prognosis depends on how the brain cyst manifests itself. For many years or even throughout her life, she may not give herself away in any way. If the cyst progresses, then the prognosis worsens. Sometimes such neoplasms cause a person to become disabled, or even die. However, this situation is observed only in advanced cases. If the surgeon’s help was timely, then the person recovers completely. However, it is impossible to exclude the risk of its recurrence.
As for preventive measures, they can be as follows:
Take care of your health during pregnancy.
Careful pregnancy planning.
Timely treatment of injuries, inflammation and vascular pathologies of the brain.
Arachnoid cyst is not a sentence. Often people with such neoplasms live their whole lives and are not even aware of their presence. If the cyst begins to manifest itself, then treatment should not be delayed.










assalomu aleykum mani oʻgʻlim toʻqqiz yosh bosh miyasida kista bor ekan va cherepnoy davleniyasi ham bor ikki marta hushini yoʻqotdi nima qilsam boʻladi yana siyib qoʻyish yozilib qolganini bilmayapti juda asabiy ishtahasizlik bosh oʻgʻrigʻi shu ogʻriq payti zarda qayt qiladi