Contents
Aqueous humor: definition, role, link with glaucoma
A physiological fluid essential to good eye health, aqueous humor is constantly secreted by the ciliary processes. How is aqueous humor formed? What is it made of? What is the link with glaucoma?
Anatomy of the aqueous humor
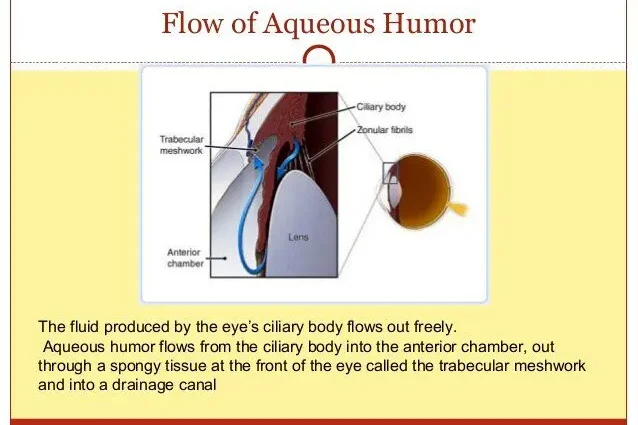
Aqueous humor is a constantly renewed clear and colorless liquid which is located in the space between the lens and the cornea, it plays an indispensable role in the regulation of intraocular pressure. Aqueous humor is formed at the level of the ciliary processes (glands located just behind the circumference of the iris), from plasma.
It is secreted by the ciliary body (located around the perimeter of the iris, behind), circulates in the posterior chamber and goes to the anterior chamber through the pupil. It is then eliminated through a filter, the trabeculum (in the iridocorneal angle) where it passes into Schlemm’s canal to reach the bloodstream.
Its dysfunctions are explained when the trabeculum becomes blocked (iris debris, excess protein), there is then an increase in pressure, hence the appearance of glaucoma.
What is the role of the aqueous humor?
The aqueous humor is produced very regularly, this secretion and this circulation need to be regulated in order to maintain a certain intraocular pressure in the eye.
The aqueous humor also ensures a nutritional metabolic function vis-à-vis the lens, the cornea and the trabeculum by providing the nutrients necessary for their metabolism. Aqueous humor is 99% water. Low in protein, rich in vitamin C, glucose, lactic acid, hyaluronic acid as well as sodium, potassium and chlorine.
Glaucoma and watery humor: what’s the connection?
Glaucoma is an eye disease associated with the progressive destruction of the optic nerve causing irreparable reduction in vision. More generally, glaucoma is linked to the increase in pressure (ocular hypertonia) formed by the aqueous humor inside the eye.
In subjects over 40 years of age, an increase in the secretion of aqueous humor or an obstruction to its excretion may cause an increase in intraocular pressure which may cause compression of the vessels supplying the papilla causing anoxia and optic nerve atrophy which may be more or less rapid, leading to the development of glaucoma.
Glaucoma is the second leading cause of blindness (loss of sight) worldwide. This disease first affects peripheral vision before gradually impacting its center.
There are two types of glaucoma associated with aqueous humor:
- Open angle glaucoma: it is the most well-known form of the disease, having a slow mutation. In most cases, genetic deterioration of the trabeculum impedes the flow of aqueous humor. The intraocular fluid is retained by the filter, the pressure rises and spreads throughout the eye sphere. It affects the optic nerve by gradually destroying the nerve cells that compose it;
- Closed-angle glaucoma: less often, it is the anatomy of the eye that is altered. The passage of aqueous humor to the trabeculum can then be difficult, if not impossible. The same phenomenon of ocular hypertension occurs. Hypertonia manifests itself violently during nocturnal, painful and very devastating attacks requiring urgent treatment. However, the other seizures are often less violent, causing little or no pain. The optic nerve is destroyed in a sneaky, rapid and irreversible way. These glaucomas are particularly aggressive.
How is the diagnosis made?
The screening test is based on measuring eye pressure using a tonometer.
Tonometry is carried out in particular in case of suspicion of glaucoma with the analysis of the optic disc during an eye fundus. When nerve fibers are destroyed, the optic papilla tends to widen and atrophy.
What treatment in the event of a problem with the aqueous humor?
There are two solutions to lower intraocular pressure: either we act by reducing secretion with the help of beta-blocker eye drops, or we promote the flow through surgery or laser.
For glaucoma: the whole stake rests on the early detection of the disease because the functional impairment can be avoided by a long-term drug treatment and well followed, only if it is started before the destruction of the nerve cells.