Contents
Inflammation can occur at any age, but more often the diagnosis is made in children and adolescents 10-19 years old. And among acute surgical pathologies, appendicitis accounts for 89,1% of cases.
Statistics for the last 10-15 years show that in the group of adolescents and young people the prevalence of the disease decreased by 5%, but at the same time in the group of patients aged 30-69 increased by more than 6%. And if there are more girls among adolescents, then in the group of adults, the diagnosis is more often made to men.
What is appendicitis
The appendix is the appendix of the large intestine, also called the blind appendix. Until recently, the appendix was considered a rudiment. However, recent research has shown that it is an important part of the immune system and an organ that helps the body fight infection.
It is believed that the appendix is a place where representatives of a beneficial microbiome accumulate, which maintains the balance and proper functioning of the intestines.
Inflammation of the appendix is called appendicitis.
Causes of appendicitis in adults
Appendicitis can be attributed to a polyetiological disease, that is, several factors act at once, which lead to inflammation. In clinical practice, there are several reasons for its development, namely, the closure of the intestinal lumen and the penetration of pathogenic microflora, its active reproduction.
Fecal masses, foreign bodies, neoplasms, parasites can close the lumen of the process. At the site of closure, mucus accumulates, where the microbiome begins to multiply. The narrowing and squeezing of the process disrupts the processes of blood circulation, lymph flow, which leads to a rapid progression of inflammation and necrosis of the tissues of the appendix.
According to some reports, the risk of appendicitis is higher in those who suffer from constipation, which predisposes the formation of fecal stones and occlusion of the blind process. Also at risk are people who abuse protein foods and neglect foods with fiber. After all, it is she who regulates intestinal motility.
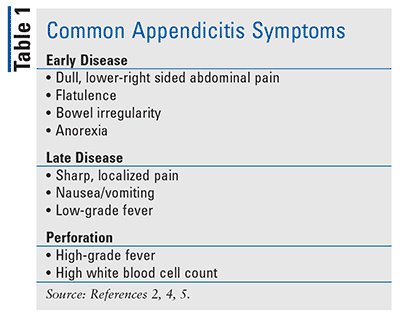
Symptoms of appendicitis in adults
| Pain | sudden |
| Where does it hurt | in the region of the navel, lower abdomen on the right |
| Nausea, vomiting | more often single |
| Temperature | normal, or within 37-38 degrees |
The appendix itself is located on the right side of the lower abdomen. The formation of acute pain is one of the classic symptoms. The pain is concentrated in the navel, and as the process develops, it moves to the lower right side of the abdomen. Characterized by increased pain for a short time, with movement, deep inspiration, coughing or sneezing.
Other typical signs of appendicitis include:
- nausea, up to vomiting;
- decreased or complete lack of appetite;
- constipation or, conversely, diarrhea;
- flatulence, painful bloating;
- fever, chills, symptoms of intoxication;
- urge to defecate.
However, such symptoms are formed only in 50% of cases. In some patients, the symptoms may be less pronounced or there may be no pain at all. In addition, the symptoms in men and women may be different.
Women symptoms of appendicitis are reduced to the formation of a sharp pain in the abdomen, nausea, vomiting and fever appear. At the beginning of the development of the disease, the pain is pressing, pulling, and even not necessarily on the right side, which can be mistakenly recognized as gynecological problems. But over time, it spreads throughout the abdomen and becomes cramping. And such symptoms most often occur in the evening or at night against the background of normal health.
Appendicitis during pregnancy has an even more specific picture. In the first trimester, the pain can move up and radiate to the back and sides, which is accompanied by excruciating nausea and the urge to vomit.
In men The clinical picture of appendicitis depends on the age, form and stage of the disease. But still more often with acute inflammation there is severe pain in the abdomen. Typically “male” symptoms are spontaneous pulling up of the right testicle. When pulling the scrotum, there is discomfort and pain in the anus and a pronounced urge to empty the intestines.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of appendicitis is carried out according to the algorithm. The first thing to start with is a review of the symptoms. Doctors are asked to tell in more detail about when and what symptoms appeared, how they developed and how long they persist, what preceded them. This indicator is extremely important in terms of differential diagnosis, that is, it allows you to distinguish one disease from another.
It is important to take into account other health problems, factors that can lead to serious complications or cause the development of appendicitis:
- medical manipulations and operations in the abdomen, transferred in the recent past;
- taking medications or supplements;
- bad habits, alcohol abuse, drugs, etc.
Only after that they proceed to the examination and determination of specific symptoms that indicate appendicitis. Palpation, in other words, feeling the abdomen, will help determine the location and intensity of pain and its characteristics. A pelvic and rectal examination may be needed.
Depending on the clinical situation, imaging methods may be required – abdominal ultrasound, CT or MRI. Based on these data, comorbidities or complications can be seen:
- determine the condition of the appendix and assess its integrity;
- detect signs of inflammation;
- assess blockage within the appendix;
- identify an abscess or other complications.
Treatment of appendicitis in adults
Appendicitis is an acute surgical pathology that requires immediate treatment. Otherwise, the process may burst, and its contents will spill into the abdominal cavity, and a dangerous complication begins – peritonitis. Timely removal of appendicitis is the only measure to prevent serious complications that pose a threat to life.
Surgical treatment is the most common, although in some cases it is possible to cure the pathology with conservative methods – taking medications. However, a 2011 study shows that the most reliable method of treatment, excluding complications in the future, is surgery.
Removal of appendicitis is called appendectomy, which can be performed in 2 ways: classical – abdominal surgery, and laparoscopic, when there are no large incisions. Each of these methods has its own characteristics, indications and contraindications.
For example, abdominal surgery is performed in the case of:
- rupture of the appendix and if its contents spilled into the abdominal cavity;
- the rupture caused an abscess;
- neoplastic processes became the cause of appendicitis;
- in the past there were a large number of operations on the abdominal organs.
Modern treatments
Laparoscopic surgeries are considered the most modern methods of treatment. And this is a priority treatment method for various reasons: less invasiveness, faster recovery, and fewer complications.
The operation itself is performed under anesthesia and includes the following steps:
- the surgeon makes small incisions through which the appendix is accessed;
- the introduction of a camera with illumination to enable the operation;
- other tools remove the process;
- treatment of the site for disinfection of infectious material;
- examination of the operated area and suturing of the operation site.
Prevention of appendicitis in adults at home
No one is immune from the occurrence of appendicitis, however, following the principles of a healthy diet will help reduce the likelihood of its development.
A diet with sufficient fiber, fresh vegetables and fruits, dairy products, maintains normal bowel function, prevents constipation, and the likelihood of closing the lumen of the appendix with feces decreases.
Popular questions and answers
Appendicitis is a common surgical pathology associated with serious complications, a special period of rehabilitation. We were answered the most exciting questions about complications, nutrition and the rehabilitation period after the operation pathophysiologist, immunologist Alena Paretskaya и surgeon, endoscopist Taras Shchedlovsky.
Why is appendicitis dangerous?
“Another problem is the difficulty of diagnosis,” explains doctor-endoscopist Taras Shchedlovsky. – Symptoms depend on many factors: gender, age, body condition, anatomical features, position of internal organs, location of the process, concomitant diseases. There are over 20 symptoms that may or may not be present in appendicitis.
Can appendicitis go away on its own?
What are the complications of appendicitis?
– Purulent peritonitis occurs in 1% of patients, but with perforated appendicitis, it occurs in 8-10% of patients. Peritonitis is the leading cause of death in acute appendicitis. doctor Taras Shchedlovsky. In addition, there may be other complications:
• appendicular infiltrate;
• abscesses (local accumulations of pus) in the abdominal cavity (pelvic, interintestinal, subdiaphragmatic);
• pylephlebitis (septic thrombophlebitis of the portal vein and its branches) is the rarest and most severe complication.
With the transition of the inflammatory process to the hepatic veins, jaundice, hepatomegaly occur, hepato-renal failure progresses, which leads to death.
When to call a doctor at home for appendicitis?
And more important points:
“While waiting for the doctor, in no case should you apply heating pads to the abdomen, take painkillers, laxatives and enemas,” warns surgeon Taras Shchedlovsky. – All this can relieve the symptoms, and it will be impossible to establish the correct diagnosis in time.
Do I need to follow a diet after appendicitis?
“After the operation, you need to follow certain principles of nutrition,” explains doctor-pathophysiologist Alena Paretskaya. – In the first few days after the operation, you don’t want to eat, because the body spends energy on recovery. During this period, it is allowed to drink water in small sips, and with severe hunger – a small amount of clear broth or rice water.
3 – 4 days after the operation, the menu expands due to the introduction of low-fat chicken broths, rice on the water, vegetable puree, but without butter, milk, natural fermented milk products are allowed.
Recommended 5 – 6 meals a day, but in small portions, so as not to overload the digestive tract. In the future, depending on the speed and characteristics of the recovery of the body, recommendations are given for further nutrition.