Contents
Aortic aneurysm of the heart – what is it?
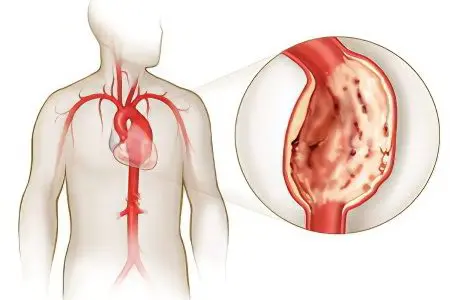
Aortic aneurysm of the heart is a pathological expansion of one of the sections of the largest artery in the human body. The cause of the development of pathology is the weakness of the arterial wall. The process of formation of an aortic aneurysm is irreversible, so this disease requires surgical intervention.
The thoracic aorta is most commonly affected by an aneurysm. It accounts for about 2/3 of all cases. According to post-mortem autopsies, aortic aneurysm is found in 0,6-6,5% of patients. At the same time, any expansion of the lumen of the vessel, exceeding its normal diameter by 2 times, can be considered an aortic aneurysm. As for the age of patients with aortic aneurysm, it mainly develops in the elderly against the background of hypertension and atherosclerosis.
Aortic aneurysm is a deadly disease. A person with such a diagnosis is risking his life every minute. An aneurysm rupture can happen at any time, causing severe internal bleeding. Against the background of such a serious complication, up to 40% of patients die, despite the fact that they are taken to the hospital in a timely manner.
Varieties of aneurysm of the aorta of the heart
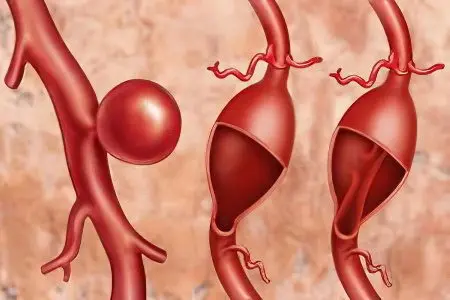
There are several classifications of aortic aneurysm of the heart. Each of them is based on one or another sign.
Types of aneurysm of the aorta of the heart, depending on its segmental localization.
Aortic arch aneurysm – according to various sources, this pathology occurs 3-7 times more often in the male population (mortality in 5 years after its discovery reaches 65%);
Aneurysm of the descending (men suffer more often than women by 3-5 times) and ascending thoracic aorta;
Aneurysm of the sinus of valsalva;
Abdominal aortic aneurysm (this aneurysm is prone to rapid progression and in just a year increases in diameter by 10%, which most often ends with its rupture);
Aneurysm of the thoracoabdominal aorta.
Types of aneurysm of the aorta of the heart, depending on its structure. In this case, false and true aneurysms are distinguished.
A true defect is characterized by bulging of the aortic wall in different directions. Allocate syphilitic and atherosclerotic true aneurysms.
The false aneurysm is limited by a hematoma connective tissue wall. The aortic tissue itself is not directly involved in the formation of a false aneurysm. However, this does not reduce the danger of a false aneurysm.
Types of aneurysm of the aorta of the heart, depending on its shape.
A saccular aneurysm of the aorta, in which the wall of the vessel stretches and forms a container filled with blood. This aneurysm most commonly affects the ascending aorta and is more prone to rupture.
Fusiform aortic aneurysm. This defect is characterized by diffuse protrusion of the aorta over its entire diameter. Such aneurysms can reach an impressive size and provoke the appearance of compression symptoms.
Why does an aortic aneurysm form?
Aortic aneurysm of the heart can be congenital or acquired. Congenital aneurysms occur due to the presence of a hereditary disease in the fetus – Mafan’s Syndrome, fibrous dysplasia, connective tissue disease, etc. Also, various diseases of a woman suffered during pregnancy can lead to the formation of an aortic aneurysm in a child. The prognosis is not favorable, since immediately after birth, the child will need a complex heart operation.
As for acquired aneurysms of the aorta of the heart, the causes of their occurrence can be multiple:
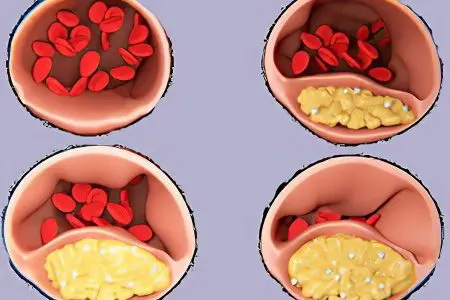
Atherosclerotic lesion of the vascular wall (up to 80% of all cases of aortic aneurysm are provoked by atherosclerosis). Under the cholesterol plaque that forms on the aorta, degenerative processes begin to occur. They weaken the wall of the vessel, which loses its elasticity and gradually begins to protrude. Thus, an aneurysm is formed.
Syphilis at a late stage of its development. In this case, pathogenic bacteria enter the aortic wall with blood flow and begin to destroy it. This cause at this point in time does not often provoke the formation of an aneurysm, since syphilis is successfully diagnosed and treated.
Injuries. They can be obtained as a result of surgical intervention on the heart, during coronography, coronary angioplasty and other medical manipulations.
Specific and nonspecific aortitis, postoperative infections, fungal diseases of the aorta are inflammatory causes of the formation of an aneurysm of the main vessel of the heart. Sometimes atypical localization of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Salmonella and other pathogenic microorganisms leads to its formation.
In addition, it is possible to identify factors that can provoke the formation of an aneurysm of the aorta of the heart. They, in most cases, are associated with a person’s lifestyle.
Among these factors are:
Abuse of alcohol, smoking.
Errors in nutrition (eating foods high in cholesterol).
old age.
Obesity.
The presence of chronic diseases. First of all, we are talking about hypertension. It is diagnosed in 75% of patients with aortic aneurysm of the heart.
Thus, we can conclude that aneurysm is not an independent disease. This or that pathological processes occurring in the body always lead to it. An aneurysm, in fact, acts as a formidable complication of atherosclerosis, hypertension, trauma, etc.
How does an aortic aneurysm manifest itself?
Aortic aneurysm of the heart is very dangerous because it can not manifest itself for a long period of time. The first symptoms often appear when the dilated vessel begins to put pressure on adjacent organs. In this case, the symptoms will depend on where exactly the aneurysm formed.
If the vessel is expanded in the chest, then a person may experience hemoptysis against the background of a dry, hysterical cough, the voice often becomes hoarse, shortness of breath joins, and pronounced pain in the sternum region appears.
An aneurysm of the abdominal aorta is asymptomatic in 40% of cases. Therefore, it is most often discovered by chance, during the examination of the patient for other diseases. Of the symptoms characteristic of an aneurysm located in the abdominal cavity, one can distinguish: pain in the abdomen and back, a feeling of pulsation in the abdominal cavity. With compression of the cardial part of the stomach and duodenum, the patient will begin to lose weight, he will be disturbed by nausea and vomiting, belching and heaviness in the epigastric region.
If a person’s aneurysm reaches an impressive size, then the symptoms intensify. There may be severe headaches and swelling of the upper body.
When an aneurysm forms in the aortic arch, the leading symptoms are increased salivation and bradycardia.
Why is an aortic aneurysm dangerous?

Rupture of an aneurysm of the aorta of the heart is the most dangerous complication of the disease. It will be discussed below.
Also, an aneurysm threatens a person with the following health problems:
The formation of blood clots, which occurs against the background of a violation of the normal blood flow. A thrombus can break away from the aorta and clog other vessels that have a smaller diameter (cerebral artery, arteries of the liver, kidneys, arms, legs, etc.). All this leads to the death of the corresponding tissues.
The development of pneumonia due to compression of the bronchi or trachea by an aneurysm of the thoracic aorta.
Compression of the biliary tract with deterioration of the digestive processes, the development of cholecystitis, pancreatitis, diarrhea, constipation, bloating, etc.
Violation of the heart with the formation of bradycardia, or tachycardia. Sometimes an aortic aneurysm causes permanent changes in the heart valve that are irreversible, even after it is removed.
Ischemic disease of the legs with the further formation of trophic ulcers and other soft tissue injuries.
Rupture of an aneurysm of the aorta of the heart – what does it threaten?
If a person has a rupture of the aorta of the heart, the consequences can be more than sad. Patients develop massive bleeding, against which shock, coma, collapse, and development of acute heart failure are possible.
Blood can begin to flow from a ruptured aneurysm into the esophagus, into the peritoneal cavity, into the pleural region, into the system of the superior vena cava, into the pericardial region. Death most often ends with cardiac tamponade, hemopericarditis, hemothorax, as well as massive internal bleeding.
The following factors can contribute to the rupture of the aneurysm: increased physical activity, injury, especially during a fall, a strong psycho-emotional shock, taking medications that increase blood pressure.
Aortic rupture is accompanied by the following symptoms: increased weakness, lack of consciousness, the appearance of tinnitus, severe sharp pain, pallor of the skin, the formation of a dark spot in the abdomen.
To save the life of a person with a ruptured aortic aneurysm of the heart, it is necessary to call an ambulance as soon as possible.
How can an aortic aneurysm be detected?

Diagnosis of this deadly aortic wall defect is quite difficult. Therefore, if there is a risk of aneurysm formation (revealed atherosclerosis, hypertension, old age, etc.), it is necessary to undergo regular examinations.
Ultrasound can detect an aneurysm in the early stages of its formation, and even when it is not there yet, but it should appear soon.
Abdominal aortic aneurysm lends itself well to visualization on x-ray. The fact is that calcium settles on the aneurysm, which gives a shadow during the study.
If an aneurysm is detected during an ultrasound scan, then an MRI or CT scan is prescribed for him. These techniques allow you to collect maximum information about the existing defect.
Therapies
If the aneurysm does not progress and does not give any symptoms, then the patient is registered with a vascular surgeon. To reduce the risk of complications, the patient is prescribed anticoagulants (Aspirin, Warfarin, Clopidogrel), regulates the level of his blood pressure (Amlodipine, Enalapril, Ramipril, etc.) and cholesterol (Simvastatin, Atoris, Fenofibrate, etc.) in the blood with the help of drugs funds.
The only way to get rid of an aneurysm is through surgery. The indication for its implementation is an increase in bulging by 4 cm or more for an abdominal aneurysm, by 5,5 cm for a thoracic aneurysm. Also, surgical removal of the defect is required when its growth per year exceeds 0,5 cm.
If the patient has a ruptured aneurysm, then the operation will be performed on an emergency basis. Only in this case there is a chance to save the life of the patient.
As for surgery, it can be of two types:
Carrying out an open type operation, when an artificial vessel is installed in the patient, replacing the damaged area with it.
stent operation. In this case, a puncture of the femoral artery is performed along which a metal stent is led to the site of the aneurysm. Having reached the right place, the stent opens and strengthens the aorta from the inside. This is a low-traumatic procedure, but it requires the clinic to have specialized equipment and a properly qualified vascular surgeon.
Prognosis of the disease
As for the prognosis of the disease, it largely depends on the size of the aneurysm, on the presence of atherosclerosis, on the location and type of defect. If we consider the prognosis as a whole, then it remains unfavorable, which is associated with a high risk of death of the patient from aneurysm rupture. If the formation reaches 6 or more centimeters, then the probability that it will rupture during the year is 50%, and with an aneurysm of a smaller diameter, the percentage of its breakthrough decreases to 20%.
The earlier an aortic aneurysm of the heart is detected, the more favorable the prognosis that the operation will be successful and the lower the mortality rate of patients during the operation.









