Contents
- The pathogenesis of the development of antiphospholipid syndrome
- Features of the diagnosis of APS
- Reasons for the development of APS
- Types of API
- The danger of antiphospholipid syndrome
- Complications of APS
- Antiphospholipid syndrome during pregnancy
- How to detect APS during pregnancy
- What body systems suffer from APS, symptoms of disorders
- APS treatment
- Antiphospholipid antibodies in the blood – normal or pathological?
Only forty years ago, doctors did not even suspect the existence of antiphospholipid syndrome. The discovery belongs to the doctor Graham Hughes, who practiced in London. He described in detail its symptoms and causes, which is why sometimes APS is also called Hughes syndrome.
With the development of antiphospholipid syndrome, antiphospholipid antibodies (AFLA) appear in the blood, contributing to increased formation of blood clots in the lumen of blood vessels. They can cause pregnancy complications and even cause its termination. Most often, APS is diagnosed in women aged 20-40 years.
The pathogenesis of the development of antiphospholipid syndrome
Against the background of antiphospholipid syndrome, antibodies begin to circulate in human blood, which destroy phospholipids located in the membranes of body tissue cells. Phospholipids are present in platelets, in nerve cells, and in endothelial cells.
Phospholipids can be neutral or negatively charged. In the latter case, they are called anionic. It is these two types of phospholipids that are found in the blood more often than others.
Since phospholipids can be different, antibodies to them are produced differently. They are able to react with both neutral and anionic phospholipids.
Antiphospholipid syndrome is determined by immunoglobulins that appear in the blood during the development of the disease.
Among them are distinguished:
Lupus immunoglobulins lgG, lgM. These antibodies were first detected in patients with lupus erythematosus system. At the same time, it was possible to detect an increased tendency to thrombosis in them.
Antibodies to cardiolipin antigen. This component of the test allows you to detect syphilis in a person. At the same time, antibodies of class A, G, M will circulate in his blood.
Antibodies, which are a combination of cardiolipin, phosphatadylcholine and cholesterol. They are able to give a positive result when conducting the Wasserman reaction (diagnosis of syphilis), but this result is false.
Total immunoglobulins of classes A, G, M (beta-2-glycoprotein-1-cofactor-dependent antibodies to phospholipids). Since beta-2-glycoprotein-1 are anticoagulant phospholipids, the appearance of antibodies to the blood aimed at their destruction leads to increased formation of blood clots.
The detection of antibodies to phospholipids makes it possible to diagnose the antiphospholipid syndrome, the detection of which is associated with a number of difficulties.
Features of the diagnosis of APS

Antiphospholipid syndrome gives a number of pathological symptoms that suggest this disorder. However, in order to make a correct diagnosis, laboratory tests will be required. And there will be a lot of them. This includes donating blood for general and biochemical analysis, as well as conducting serological tests that make it possible to detect antibodies to phospholipids.
The use of one research method is not enough. Often, patients are prescribed an analysis for the Wasserman reaction, which can give a positive result not only in antiphospholipid syndrome, but also in other diseases. This leads to misdiagnosis.
To minimize the likelihood of a medical diagnostic error, a patient with symptoms of APS should be given a comprehensive examination, which should include:
The detection of lupus antibodies is the test that is performed first if APS is suspected.
Detection of antibodies to cardiolipin antigen (Wassermann reaction). With APS, the analysis will be positive.
Test for beta-2-glycoprotein-1-cofactor-dependent antibodies to phospholipids. The indicators of these antibodies will exceed the permissible limits of the norm.
If antibodies in the blood appeared earlier than 12 weeks before the onset of the first symptoms of APS, then they cannot be considered reliable. Also, based on them, the diagnosis of APS is not confirmed if the tests became positive only 5 days after the onset of the disease. So, to confirm the diagnosis of “antiphospholipid syndrome”, the presence of symptoms of the disorder and a positive antibody test are required (at least one study must give a positive reaction).
Additional diagnostic methods that a doctor may prescribe:
Analysis of the false positive Wasserman reaction.
Carrying out the Coombas test.
Detection in the blood of rheumatoid factor and antinuclear factor.
Determination of cryoglobulins and antibody titer to DNA.
Sometimes doctors, if APS is suspected, are limited to taking blood to detect lupus anticoagulant, but in 50% of cases this leads to the fact that the violation remains unidentified. Therefore, in the presence of symptoms of pathology, the most complete study should be carried out. This will allow timely detection of APS and initiation of therapy. By the way, modern medical laboratories have tests that make it possible to conduct a comprehensive diagnosis, as they are equipped with all the necessary reagents. By the way, some of these systems use snake venom as an auxiliary component.
Reasons for the development of APS
Antiphospholipid syndrome most often manifests against the background of such pathologies as:
Systemic lupus erythematosus.
Systemic scleroderma, rheumatoid arthritis, Sjögren’s syndrome.
Cancers in the body.
Lymphoproliferative diseases.
Autoimmune thrombocytopenic purpura, which can be triggered by the lupus erythematosus system, scleroderma, or rheumatoid arthritis. The presence of purpura at times increases the risk of developing antiphospholipid syndrome.
HIV infection, mononucleosis, hepatitis C, endocarditis, malaria. APS can develop with viral, bacterial and parasitic infections.
Diseases affecting the CNS.
The period of bearing a child, childbirth.
There may be a hereditary predisposition to APS. In this case, the specificity of DR4, DR7, DRw53 will be present in the human blood phenotype.
Taking certain medications, such as psychotropic, birth control and oral contraceptives.
The longer antiphospholipid antibodies are present in the blood, the faster a person will develop APS. And the reason for their appearance does not matter.
Types of API
There are the following types of APS:
Primary antiphospholipid syndrome, which develops on its own, that is, its onset is not preceded by any disease.
Secondary antiphospholipid syndrome, which develops against the background of an autoimmune pathology, for example, with systemic lupus erythematosus.
Catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome, which is rarely diagnosed, but this form of pathology is extremely dangerous. The disease develops rapidly and leads to the formation of blood clots in all vessels of the body. Often this syndrome leads to death.
AFLA-negative syndrome, which is difficult to detect. With this form of the disease, lupus antibodies and antibodies to cardiolipin are absent in the blood.
Sneddon’s syndrome is a disease that develops against the background of APS. At the same time, episodes of cerebral thrombosis occur in a person. Symptoms of the disorder are cyanotic skin and high blood pressure. Sneddon’s syndrome is referred to as one of the possible variants of the course of the disease.
The danger of antiphospholipid syndrome
Antibodies to phospholipids that appear in APS disrupt the normal functioning of the hemostasis system. This leads to the fact that blood clots begin to form in the vessels, a person develops thrombosis.
With APS, not only capillaries are affected, but also large vessels. In general, blood clots can form in any vein or artery that carries blood to various organs. Therefore, the symptoms of this disorder are very diverse.
Complications of APS
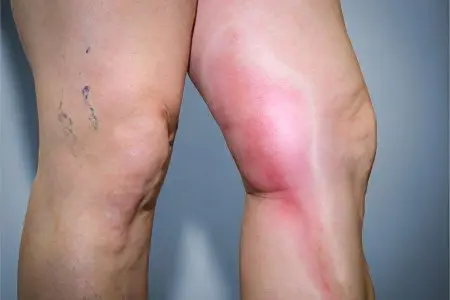
Antiphospholipid syndrome provokes the formation of blood clots in the vessels. Most often, thrombosis affects the veins of the lower extremities. If the thrombus breaks off, then with the blood flow it enters the vessels that feed the lung tissue. This entails the development of a dangerous condition called pulmonary embolism. If a thrombus blocks the main vessel of the lung, then its heart attack occurs, cardiac activity stops. Often PE ends in the death of the patient, and death can occur very quickly.
When a blood clot blocks small vessels, a person has a chance to recover, but at the same time he must be urgently delivered to a medical facility. Even in this case, the likelihood of serious health consequences is extremely high.
Thrombi in APS can form in the renal arteries. Against the background of such thrombosis, severe renal pathologies develop, for example, Budd-Chiari syndrome.
Less commonly, blood clots form in the capillaries of the retina, in the subclavian veins, in the central veins of the adrenal glands, which leads to the development of insufficiency of these organs. Also, against the background of thrombosis, the development of the syndrome of the inferior or superior vena cava is possible.
Thrombosis with blockage of arteries of various localization can lead to heart attack, gangrene, necrosis of the femoral head.
Antiphospholipid syndrome during pregnancy

The development of antiphospholipid syndrome during pregnancy can lead to such serious consequences as:
Abortion.
Miscarriage in early pregnancy. The risk of spontaneous abortion is the higher, the more antibodies to the cardiolipin antigen circulate in the woman’s blood.
The development of fetoplacental insufficiency, which leads to fetal hypoxia with a delay in its development. If medical care is not provided, the risk of intrauterine death of the child remains high.
Development of preeclampsia with eclampsia and preeclampsia.
chorea development.
Thrombus formation.
Increased blood pressure.
The development of the HELLP syndrome with hemolysis, damage to the liver parenchyma and thrombocytopenia.
Premature detachment of the placenta.
Early childbirth.
Against the background of APS, attempts to conceive a child by in vitro fertilization may end unsuccessfully.
How to detect APS during pregnancy
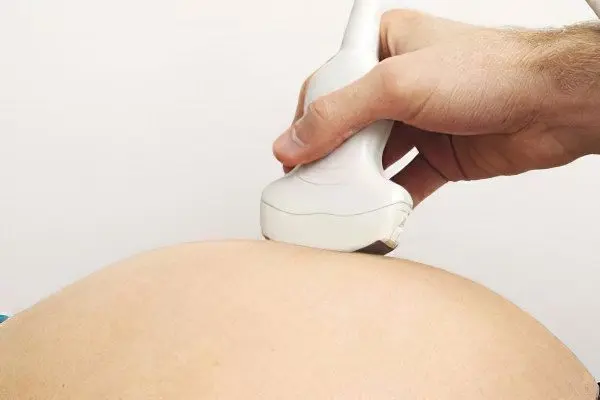
Women who are at risk for developing APS should be under special supervision of a doctor.
According to indications, they can be assigned the following diagnostic procedures:
Regular hemostasiogram.
Unscheduled fetal ultrasound with dopplerography of uteroplacental blood flow.
Ultrasound of the vessels of the legs, head, neck, kidneys, eyes.
Echocardiography to check the functioning of the heart valves.
This will allow timely detection of the development of serious complications of pregnancy, such as DIC, purpura, HUS.
In addition to a gynecologist, a pregnant woman diagnosed with antiphospholipid syndrome may need to consult other narrow specialists, for example, a rheumatologist, cardiologist, neurologist, etc.
Treatment is reduced to taking glucocorticosteroids and antiplatelet drugs. The dose should be selected by the doctor. Heparins and immunoglobulins may also be prescribed. These drugs are administered against the background of the control of the blood picture.
If a woman already suffers from APS, but does not plan pregnancy, then she should not use hormonal drugs for contraception. Otherwise, you can aggravate the course of the disease.
What body systems suffer from APS, symptoms of disorders

Antiphospholipid syndrome is associated with the risk of developing various diseases. Moreover, any organs and systems, even the brain, can suffer. With the defeat of its vessels, the development of a transient ischemic attack or heart attack is possible.
This is accompanied by symptoms such as:
The appearance of seizures.
Dementia, which is constantly progressing.
Psychiatric disorders.
Also, APS can be manifested by the following neurological symptoms:
Severe migraine headaches.
Uncontrollable trembling of the limbs.
Symptoms characteristic of transverse myelitis. They occur because the spinal cord suffers in APS.
The most formidable complication of heart failure is a heart attack. It develops under the condition that blood clots form in the coronary arteries. If their small branches are involved, then a heart attack will be preceded by a violation of the contraction of the heart. Also, APS can lead to the development of heart disease, to the formation of an intracardiac thrombus. Such indirect signs of antiphospholipid syndrome can make it difficult to diagnose the cause of the disease.
Symptoms of APS, depending on which organ was affected by thrombosis, will be as follows:
An increase in blood pressure is observed with thrombosis of the renal arteries.
When a pulmonary artery clot is blocked by a thrombus, pulmonary embolism develops, which leads to a sharp deterioration in a person’s well-being. Sometimes the death of the patient can occur instantly.
Bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract.
Spleen infarction.
The appearance of subcutaneous hemorrhages, skin necrosis, ulcers on the legs – all these symptoms develop with damage to the dermis.
The APS clinic is diverse. It is impossible to describe the exact symptoms, since any organs and systems can be involved in the pathological process.
APS treatment

Treatment of APS should be comprehensive. Its main focus is the prevention of complications of thrombosis.
The patient must follow the following guidelines:
Avoid strenuous physical activity.
You can’t stay motionless for a long time.
Refusal of traumatic sports.
Cancellation of flights.
Drug therapy is reduced to the appointment of the following drugs:
Warfarin is a drug from the group of indirect anticoagulants.
Heparin, Nadroparin calcium, Enoxaparin sodium are drugs related to direct anticoagulants.
Aspirin, Dipyridamole, Pentoxifylline – antiplatelet drugs.
If the patient is in serious condition, then high doses of glucocorticosteroids are administered to him, plasma transfusion is performed.
Taking anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents should be long-term. Sometimes these drugs are prescribed for life.
AFS is not a sentence. If the disease is diagnosed at the initial stage of its development, then the prognosis is favorable. In this case, the patient must follow all the recommendations of the doctor, take the drugs that he prescribes. Women have a high chance of conceiving and having a healthy baby.
The course of the disease is complicated by systemic lupus erythematosus, thrombocytopenia, a persistent increase in blood pressure, a high level of antibodies to the cardiolipin antigen with a tendency to increase.
Without fail, a patient diagnosed with APS should be observed by a rheumatologist. He will need to regularly donate blood for analysis, as well as undergo other diagnostic and therapeutic procedures.
Antiphospholipid antibodies in the blood – normal or pathological?
Sometimes the level of antiphospholipid antibodies can be elevated in a healthy person. In 12% of people, these antibodies are present in the blood, but they do not develop the disease. The older the person, the higher the indicators of pathological immunoglobulins can be. There is also the possibility of a false-positive Wasserman reaction, for which the patient must be prepared. The main thing is not to panic and go through a comprehensive diagnosis.
Video: APS and other thrombophilias in obstetrics:









