Contents

What is angina?
Angina – this is an acute inflammation of the palate, lingual and nasopharyngeal tonsils. Most often, the palatine tonsils become inflamed. Angina refers to acute infectious-allergic diseases. In the course of the disease, the palatine tonsils become inflamed.
ICD
ICD-10: J03
ICD-10-KM: J35.01
ICD-9: 034.0
IKB-9-KM: 474.00
Causes of angina
The causative agent of angina is most often hemolytic streptococcus group A, rarely streptococcus aureus. In very rare cases – pneumococcus, Haemophilus influenzae, viruses (enteroviruses, adenoviruses, herpes virus, Epstein-Barr virus, etc.), mycoplasmas, chlamydia, fungi, mixed infection.
The infection can be transmitted by airborne droplets, through food and drink, as well as through direct contact with a sick person. Angina develops most often in the cold, damp season (spring, autumn), it can be a consequence of hypothermia or a manifestation of diseases such as diphtheria, influenza, scarlet fever, whooping cough, and in some cases blood diseases.
Another way of transmission is contact (through dirty dishes). You can also get infected through food, for example, if you drink raw milk from a cow with mastitis. And sometimes a person infects himself. In such cases, angina may be the result of chronic tonsillitis, rhinitis, sinusitis, diseased teeth, and other permanent foci of infections in the body. The situation is complicated by unfavorable conditions: hypothermia, decreased immunity.
Types and symptoms of angina

Symptoms of angina appear after the incubation period ends, which is most often 24-48 hours.
The main symptoms of angina can be called the following:
Angina has an acute onset. In a person, against the background of complete health, health deteriorates sharply.
Body temperature rises, chills occur. The mark on the thermometer can reach 40 ° C.
Headache, aching joints, general weakness.
The throat is very sore, the pains are aggravated during the process of swallowing. On the second day, pain reaches its peak and is present on an ongoing basis.
Lymph nodes increase in size, become painful on palpation. First of all, the submandibular nodes suffer.
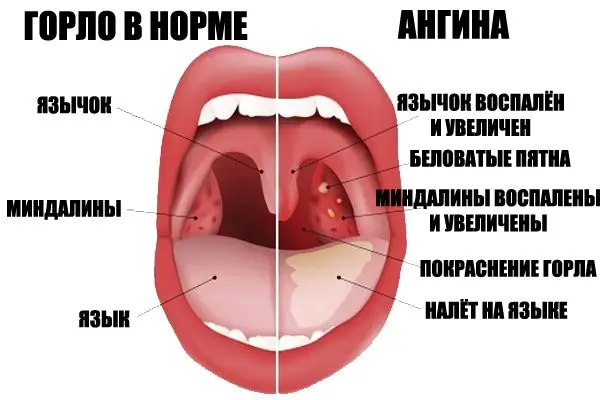
The tonsils swell, increase in size, and dot formations of yellow color can be visualized on them. Their size is 2-3 mm. This picture is characteristic of follicular angina. With lacunar angina, the tonsils are covered with purulent plaque in the form of enclosed areas of irregular shape.
In rare cases, white stones may be present on the tonsils. As a rule, they are small in size, but in practice there were also sizes of 3 centimeters and above.
On average, a sore throat lasts about two weeks, in babies it takes a little longer.
Catarrhal angina
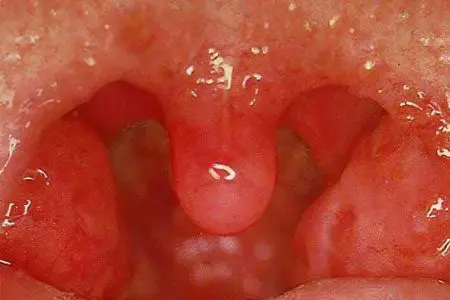
Catarrhal angina usually develops quickly, but the temperature is small 37-38°C. In most cases, a person suffers from dryness and sore throat. After the first unpleasant sensations, the patient feels swelling in the throat and pain when swallowing. The palatine tonsils, when visually examined, appear reddened and swollen, and probing the neck in the region of the submandibular lymphatic gland usually causes quite severe pain. As a rule, the pain increases when swallowing. After a few hours, the human body temperature reaches 39 °C. Angina is accompanied by severe chills and excruciating aches, migraines.
As a rule, catarrhal angina is a precursor of follicular or lacunar angina. Despite the milder degree of angina, it must be treated, any angina poses a threat to human health.
Follicular sore throat
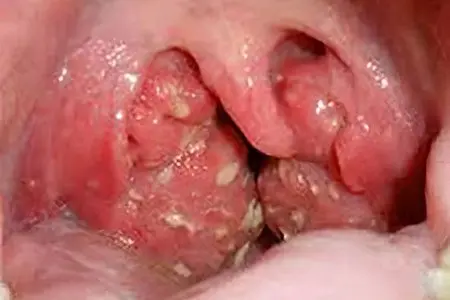
Follicular angina is a longer and more severe disease. It usually causes serious complications.
The main symptoms are also headaches, fever up to 39°C, joint pain and general malaise. All symptoms are much more pronounced than with catarrhal angina. In the oral cavity in many patients, the content of saliva is significantly increased. Follicular angina should be treated only in a hospital with constant medical supervision.
Lacunar angina
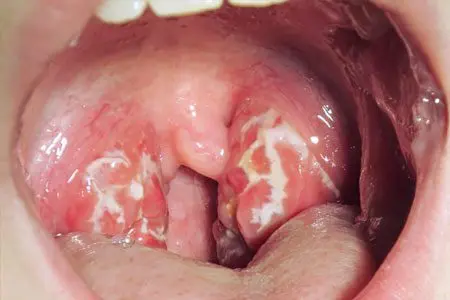
Lacunar tonsillitis is considered no less serious disease. It is accompanied by a noticeable deterioration in the general condition of the body. Temperature rise can reach 40°C.
In addition to headaches, swallowing food and liquids causes discomfort. Quite often pains in a throat are given in ears. The mucous membrane of the tonsils swells and turns red. In patients, white or yellowish plaques typical of angina, the so-called plugs, are formed in the lacunae, consisting mainly of torn cells and bacteria. On examination, swelling and redness of the palatine arches are always noticeable.
How to distinguish angina from acute respiratory infections or pharyngitis?
The main symptoms of a sore throat, and not an acute respiratory disease or a cold, are a rapid increase and retention of body temperature within 39 ° C, the appearance of an acute unpleasant sore throat. It becomes painful to eat, drink and even talk. Later, the patient begins attacks of severe fatigue, malaise, begins to ache in the joints. If you already have these first signs of the disease, you should immediately contact your local doctor.
Also, angina can be confused with acute pharyngitis. But there are differences, sore throats are caused by a specific type of bacteria, streptococci, and the symptoms are often more severe. In addition, streptococci can affect other parts of the throat.
When to see a doctor?
Sometimes a sore throat can cause the throat to swell to the point where breathing becomes difficult. If this happens, medical attention is needed and urgent.
In addition, if a person experiences any of the following symptoms, they should visit a doctor:
Temperature over 39,5 °C
Inflammation of the lymph nodes, the neck becomes stiff to the touch.
Muscle weakness
Sore throat that lasts more than 2 days
Diagnosis of angina
Doctor’s examination:
The doctor will examine your throat, and possibly also your ears and nose, which can also be foci of infection.
The doctor will ask you if there is a rash on your body. The rash may indicate scarlet fever, which is associated with some cases of strep throat.
Gently feeling (palpating) your child’s neck to check for swollen glands (lymph nodes)
Your doctor will listen to your lungs with a stethoscope.
Check for an enlarged spleen (mononucleosis is a dangerous disease that also causes inflammation of the tonsils)
Also, a complete blood count may be ordered.
throat swab
With this simple test, the doctor takes a secret from the throat. The sample will be tested in a laboratory for the presence of streptococcal bacteria.
Some clinics are equipped with a laboratory that can get a test result within a few minutes. However, a second, more reliable test is usually sent to a lab, which can provide results within 24-48 hours.
If the rapid intraclinical test is positive, then you almost certainly have a bacterial infection. If the test result is negative, then you most likely have a viral infection. However, your doctor will wait for a more reliable laboratory test to determine the cause of the infection.
Sore throat treatment
Medicines for the treatment of angina
Fusafunzhin (Bioparox) – 4 inhalations by mouth every 4 hours for 4-5 days. Before use, read the instructions.
Ambazone – keep the tablet in the mouth until it is completely dissolved. After taking the tablet, refrain from eating and drinking for 3 hours.
Gramicidin – a tablet is kept in the mouth (behind the cheek) until it is completely dissolved. Apply 2 tablets (one after another for 20-30 minutes) 4 times a day for 2-3 days.
With severe sore throat: Geksoral, Stopangin, Strepsils, Lugol and other means. Menthol products such as Halls (menthol lozenge) can also reduce pain.
In case of an allergy, take antihistamines: Suprastin, Tavegil, Phenkarol, Loratadin, Claritin
Antibiotics
If the sore throat is caused by a bacterial infection, the doctor will prescribe a course of antibiotics. Amoxicillin is the most powerful antibiotic for angina, you need to take it for 7-10 days.
Amoxicillin is the most effective antibiotic for angina from the group of semi-synthetic broad-spectrum penicillins. The following brands of amoxicillin are represented on the Russian market: Amoxiclav, Flemoxin Solutab.
Of the cheaper ones: Amoxicar, Amoxil, Amosin.
For children: Suprax, Klacid, Azithromycin, Augmentin
Home care
Regardless of whether angina is caused by a viral or bacterial infection, the described tactics will be needed in any case for a speedy recovery.
Remember that if your sore throat is caused by a viral nature, then the doctor will not prescribe antibiotics for you. And this home care will be the only treatment tactic
The home care strategy includes the following:
Get more rest.
Drink more water to prevent dehydration.
Warm liquids — broth, decaffeinated tea, or warm water with honey — and cold treats like ice cream can soothe a sore throat.
Gargle with a salt water solution (you can add a drop of iodine and a teaspoon of apple cider vinegar).
Use a humidifier. Dry air can further aggravate a sore throat.
Lozenges for sore throat (Strepsils, Angi Sept Dr. Theiss, Anti-Angin, Septolete, Faringosept, more details about each remedy here).
In case of high temperature and fever, take paracetamol or ibuprofen (more: Antipyretic drugs – which is more effective?).
[Video] Dr. Berg – What to do if your throat hurts?









