Contents
- Indications for testing
- Preparation for analysis
- Types of analyzes and diagnostics
- Deciphering the results of the analysis
- IgG antibodies to Helicobacter pylori
- If Helicobacter pylori is positive, what does it mean?
- The results of the analysis were not analyzed for Helicobacter pylori
- Definition of Helicobacter pylori antigen in feces
- Helicobacter pylori IgM and IgA – what is it?

Helicobacter pylori is a bacterium that normally lives in the gastrointestinal tract of many people. Under favorable conditions, Helicobacter pylori colonies increase, causing pathologies of the stomach and intestines. Before prescribing a course of treatment, the doctor must verify the presence of pathogenic microorganisms in the gastrointestinal tract, clarify the level of their concentration.
An analysis for Helicobacter pylori is prescribed for pain and discomfort in the stomach before eating. Helicobacteriosis provokes the development of serious lesions of the mucous membranes. Timely detection of infection and its elimination can avoid the development of serious cancers and other health problems.
This analysis gives a general idea of the causative agent of the infection, since today it is considered one of the most accurate. The presented spiral-shaped microorganisms often live in the lower part of the stomach, as well as in the duodenum. Such anaerobic microbes instantly die in the air. Often, the disease is transmitted from an infected person to a healthy person through mucus and saliva, as well as by household means. Once in a new organism, the bacteria descend directly into the stomach.
The hydrochloric acid contained in the stomach does not destroy this type of microorganisms. Bacteria burrow into the mucous membranes of the stomach, easily breaking the tissue structure, which leads to defective functioning. Such a potential danger causes serious inflammation, erosion and ulcers. In addition, Helicobacter pylori is able to change the local acidity of the stomach.
These microorganisms easily spread throughout the stomach with a weakened human immunity and long-term existence.
Timely diagnosis can avoid many dangerous consequences. For any symptoms of gastric malaise, the specialist will prescribe an analysis for Helicobacter pylori. Many patients complain of problems in the digestive system. These include recurring acute pain in the stomach, the appearance of heartburn, a feeling of heaviness and rejection of meat fatty foods. As a rule, with helicobacteriosis, severe pain disappears immediately after eating.
Indications for testing

It is difficult to imagine that a person without symptoms of the disease would go for a full-scale examination without any need.
Symptoms that predispose to testing for Helicobacter pylori:
Gastralgia (pain in the stomach and intestines) of varying intensity. They appear during or after eating, are caused by a deficiency of enzymes and a violation of the digestion of food and its stagnation in the stomach.
“Hungry Pains” Appear 2-3 hours after eating, stop during meals. Due to damage to the mucous membrane, its sensitivity is exacerbated, the patient feels how food and water pass through the digestive tract.
Intense heartburn. It occurs due to the reverse reflux of aggressive gastric juice into the esophagus that is not intended for this, with frequent repetitions it is a symptom of pathology.
Feeling of heaviness that occurs even after taking the minimum portions of food. The patient has a feeling of a full stomach.
Frequent nausea, not caused by objective causes (for example, toxemia of pregnancy).
The combination of pain in the stomach with vomiting and the inability to eat and drink.
Slight discomfort in the projection of the stomach, loss of appetite, slight heaviness. Often appear at the initial stage of heliobacteriosis.
The presence of mucus in the stool.
Any of these symptoms is a reason for an immediate visit to the doctor for examination and treatment.
Preparation for analysis

To obtain objective indicators, you need to carefully prepare for testing for Helicobacter pylori.
Necessary preparatory measures:
Complete cessation of smoking a day before the test. Nicotine negatively affects the gastric mucosa, distorting the results of tests.
Complete abstinence from alcohol. The reason is the same.
The ban on the use of tea and coffee, which negatively affect the state of the digestive tract.
Temporary restriction on food intake for 8 hours before analysis.
Since blood for analysis for Helicobacter pylori is taken from a vein on an empty stomach, you can take some food and water with you to the clinic.
Types of analyzes and diagnostics
To study the state of the body, there are several methods. Each of them has its own characteristics.
ELISA for bacteria
An enzyme immunoassay is prescribed to assess the level of concentration of antibodies to Helicobacter pylori in the patient’s blood. If there are antibodies to the bacteria in the blood, it means that the immune system developed them at least 1-2 weeks ago. If the reaction of the body is not yet formed, a false negative result is possible.
Reasons for false positive results:
error of the laboratory assistant who conducted the study;
not enough time has passed since eradication, since antibodies are in the blood some time after a complete cure.
A positive ELISA test indicates the need for a complete examination, studying the results of an extended blood test, which provides more information about the state of the body.
Immunoglobulins in the blood LgG, LgM, LgA

In the human body, when infections or pathogenic microorganisms penetrate into it, immunoglobulins are produced – blood cell proteins that resist foreign viruses. When infected with heliobacteriosis, the human body produces immunoglobulins LgG, LgM, LgA, which actively resist Helicobacter pylori. When they are found in a person’s blood, it should be concluded that he is sick with heliobacteriosis.
The peculiarity of immunoglobulins is that, in pursuit of pathogenic cells, they overtake them anywhere in the human body. These proteins are produced after the development of bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract.
Analysis transcript:
A low or negative level of LgG immunoglobulin indicates one of the following options: the bacterium is absent in the body and the likelihood of developing a peptic ulcer is low, or only 3-4 weeks have passed since the infection. For pain in the gastrointestinal tract, you need to repeat the examination in a week.
An elevated or positive level of LgG immunoglobulin indicates one of two options: the bacterium is present in the body, increasing the risk of developing cancer and stomach ulcers, or the person has recently recovered from heliobacteriosis.
A reduced level of immunoglobulin LgM, usually detected immediately after infection, or its absence, definitely indicates the absence of bacteria, since this protein is detected early after infection.
An increase in the LgM level indicates that the gastrointestinal tract is at an early stage of infection, and it is almost not damaged by the infection.
PCR analysis
The results of a polymerase chain reaction study can fix Helicobacter pylori DNA samples in the blood, which puts the PCR test in first place among all diagnostic methods. A positive test result proves the presence of bacteria in the body, a negative one – its absence. The only thing that is not available when performing a PCR blood test is determining the time of introduction of the bacterium into the body.
If antibacterial therapy or treatment with antiseptics was performed before taking blood for analysis, the results of the study will not be objective. It is better to entrust the interpretation of blood tests to a specialist, although serious laboratories put a table of norms and deviations from it into the results.
Cytological examination
When performing this test during endoscopy, swabs are taken from the mucosa of the antrum of the stomach. The smear area is a place of edema and hyperemia, but not erosion or ulcers. After taking the prints, the laboratory assistant dries and stains the smears.
When examined under a microscope, Helicobacter pylori can be found in the form of a spiral or in the form of wings of a flying gull.
Reference values of cytology:
(+) – low level of contamination (up to 20 microbial bodies);
(++) – medium level (up to 40 microbial bodies);
(+++) – high level (over 40 microbial bodies at 360x magnification).
Additionally, in the presence of inflammation, a cellular infiltrate is detected: (eosinophilia, neutrophilia, lymphocytes, plasma cells). Additionally, dysplasia, proliferation, metaplasia, malignant neoplasms can be detected.
Urease test

The study is performed after taking a biopsy of the mucosa during endoscopy. It is placed in a carrier gel containing urea, a pH indicator, a bacteriostatic agent. Conclusions are made on the basis of a change in the color of the biopsy in the range from yellow to crimson.
Reference values:
Raspberry color appeared in the first hour – severe infection (+++);
In the first 2 hours – a moderate level of infection (++);
By the end of the day – an insignificant level of infection (+);
At a later date – the norm or a negative result.
With a low level of infection, a false negative result can be recorded. To increase the reliability, it is combined with the histological method.
13C urease test, breath
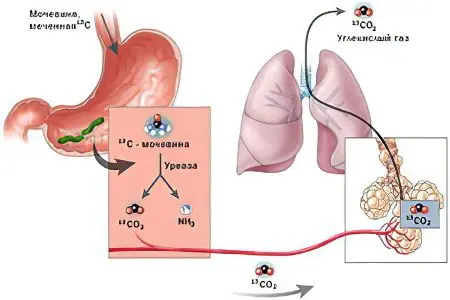
During this test, fasting background samples of exhaled air should be taken. After a light breakfast in the form of juice or milk, the subject drinks an aqueous solution of urea labeled with 13C, the so-called test solution. Then, every 15 minutes, 4 final samples are taken.
Analysis of the test based on the presence of a stabilized isotope using a mass spectrometer:
Mild degree of infection – less than 3,5%;
The average degree is 3,5-6,4%;
Severe degree – 6,5-9,4%;
Very severe degree – over 9,5%.
The norm of Helicobacter pylori with a urease test is 1%.
Hemotest
The analysis is based on determining the titer of antibodies – class G immunoglobulins. Normally, when Helicobacter enters the body, they bind microorganisms, stopping their pathogenic effect. The study is carried out by enzyme immunoassay after taking blood from a vein into a sterile tube. Before the study, you can not eat for 8 hours, drink coffee and alcohol, smoke. To study the dynamics, the analysis is carried out throughout the entire period of treatment.
Deciphering the results of the analysis

Despite the fact that the interpretation of the indicators should be entrusted to the doctor who sent for the examination, all patients want to find out their results on their own.
Interpretation of other values:
0,9-1,1 U / ml – the probability of infection with Helicobacter pylori is doubtful;
Over 1,1 units / ml – bacteria are definitely present in the body. High risk of developing stomach ulcers and stomach cancer.
The norm for the urease test is the absence of a crimson color in the color of the material. The norm for bacterioscopic examination is the absence of pathogens.
IgG antibodies to Helicobacter pylori
Detection of immunoglobulins to Helicobacter pylori is carried out using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, or “sandwich” method. For the study, venous blood is used; before its delivery, you can not smoke for 30 minutes.
The method is based on the fact that after the Helicobacter bacterium enters the body, a local and systemic response develops. It consists in an increase in the titer of immunoglobulin IgM, IgG-, IgA-antibodies in the blood serum. In 100% of cases of infection, IgG-immunoglobulin is detected, in 65-80% of cases – IgA, in 17-20% – IgM, therefore, accurate diagnosis is carried out by determining the concentration of IgG in the blood serum.
The advantages of the method:
Does not require endoscopy, so the method is safe;
Highly sensitive;
Used to prevent primary infection.
The method may not be accurate in determining immunoglobulin titer in the elderly, as they have reduced antibody production, as well as in those patients who take cytostatics. After the treatment of heliobacteriosis, this method is also not effective, because the level of the hormone in the blood after antibiotic treatment for another 6 months remains quite high.
Indications for use:
Complaints of the patient about dyspepsia when it is impossible to carry out endoscopy;
Primary diagnosis of heliobacteriosis;
Monitoring the effectiveness of antibiotic treatment.
Reference values of the examination: the concentration of IgG-immunoglobulin from 0 to 0,9, the result is negative. This may mean the absence of infection or the high effectiveness of therapy.
If Helicobacter pylori is positive, what does it mean?
A positive test result proves the presence of bacteria in the body, a negative one – its absence. Not always positive indicators indicate a disease with heliobacteriosis. Most often, this is a sign of the presence of bacteria in the body. However, immediately after the eradication of Helicobacter pylori, the analysis for its content in the body will still be positive, despite the absence of bacteria – antibodies in the blood do not disappear quickly. It is they who give a false positive result, so the analysis should be taken no earlier than a month after treatment.
This is the only exception to the rule: a positive Helicobacter result means you have the disease or are carriers of the bacterium.
The results of the analysis were not analyzed for Helicobacter pylori
After studying the material provided by the patient, you can absolutely accurately answer the question of whether Helicobacter pylori is present in his body or not, that is, the stool analysis is of high quality.
Definition of Helicobacter pylori antigen in feces

The study is performed by the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Its accuracy is 95%, and it is recommended to determine the presence of bacteria in this way in children, elderly and seriously ill patients.
In order for the result of the analysis to be objective, you need to prepare for the study:
Do not take antibiotics for 4 weeks prior to the study;
3 days before the study, do not eat foods that stain feces: red grape wine, beets, grapes, black currants;
Before the study, exclude foods with coarse fiber from the menu for 2-3 days: bran, radish, cabbage, carrots, beets;
Do not use drugs that increase gastrointestinal peristalsis.
For the study, it is enough to fill a third of the standard container for collecting analyzes. Do not take feces from the toilet, as it may carry traces of detergent. It is advisable to store the container with biomaterial for no longer than 10-12 hours at a temperature of +2 to -8°C.
The result of the analysis can be obtained the next day. Since fecal analysis is a qualitative study, its result is formulated as “positive” or “negative”.
Helicobacter pylori IgM and IgA – what is it?
Class M immunoglobulins are blood proteins that react earlier than other immune fractions to the appearance of Helicobacter bacteria in the body; they can be fixed in the blood at an early stage.
A positive result of the analysis for the presence of IgM immunoglobulin occurs with an increase in antibody titer during infection with heliobacteriosis;
Positive indicators of IgA content are an indicator of the active process of the introduction of bacteria into the gastric mucosa and its inflammation.
In a healthy person, these indicators are absent or present in minimal quantities.









